Mullahs play a significant role in Islamic communities as religious leaders and scholars who interpret Islamic law and guide spiritual practices. Their influence extends to education, social matters, and jurisprudence within many Muslim societies. Explore this article to understand the historical significance and contemporary impact of mullahs on your community.
Table of Comparison
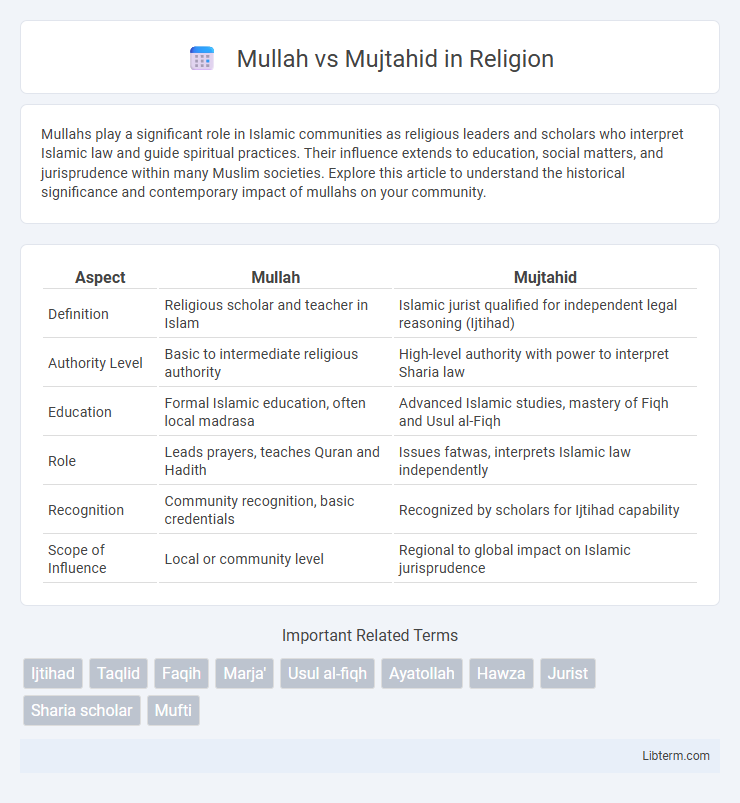
| Aspect | Mullah | Mujtahid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Religious scholar and teacher in Islam | Islamic jurist qualified for independent legal reasoning (Ijtihad) |
| Authority Level | Basic to intermediate religious authority | High-level authority with power to interpret Sharia law |
| Education | Formal Islamic education, often local madrasa | Advanced Islamic studies, mastery of Fiqh and Usul al-Fiqh |
| Role | Leads prayers, teaches Quran and Hadith | Issues fatwas, interprets Islamic law independently |
| Recognition | Community recognition, basic credentials | Recognized by scholars for Ijtihad capability |
| Scope of Influence | Local or community level | Regional to global impact on Islamic jurisprudence |
Understanding the Terms: Mullah and Mujtahid
Mullah refers to an Islamic scholar trained in religious studies, often serving as a teacher or local religious authority, while a Mujtahid possesses the advanced scholarly qualification to perform ijtihad, independently interpreting Islamic law in complex legal matters. The distinction lies in the level of expertise and authority, with Mujtahids holding the capability to derive new legal rulings, whereas Mullahs generally follow established interpretations. Understanding these terms is essential for comprehending Islamic jurisprudence hierarchies and religious leadership roles.
Historical Origins of Mullahs and Mujtahids
Mullahs historically emerged as local religious scholars in Islamic communities, primarily responsible for teaching and interpreting basic religious texts, while Mujtahids developed as higher-ranking scholars with the authority to perform ijtihad, independent legal reasoning in Islamic jurisprudence. The concept of Mujtahid evolved during the early Islamic period, especially within Shia Islam, to address complex legal questions beyond the scope of traditional interpretation. Mullahs generally focus on routine religious education, whereas Mujtahids hold the esteemed role of issuing binding legal opinions based on deep scriptural and jurisprudential expertise.
Educational Requirements: Mullah vs Mujtahid
Mullahs typically complete basic religious education centered on Quranic recitation, Hadith study, and Islamic jurisprudence, often through local madrasas. Mujtahids undergo extensive advanced theological training that includes mastering Usul al-Fiqh (principles of Islamic jurisprudence), Arabic language proficiency, and independent ijtihad (jurisprudential reasoning). This rigorous scholarly education allows Mujtahids to issue binding religious rulings, setting them apart from Mullahs, whose educational scope is more foundational.
Role in Islamic Jurisprudence
Mullahs typically serve as local religious teachers and community leaders, providing basic Islamic education and leading prayers, while Mujtahids hold a higher scholarly status with the authority to perform ijtihad, the independent interpretation of Sharia law. The Mujtahid's role is crucial in shaping Islamic jurisprudence by issuing fatwas and adapting legal rulings to new contexts, a task that requires profound knowledge of Quranic texts, Hadith, and principles of fiqh. Mullahs support the dissemination of Islamic teachings but generally do not engage in the complex legal reasoning necessary for jurisprudential innovation.
Authority in Religious Interpretation
Mullah and Mujtahid differ significantly in their authority over religious interpretation; a Mullah typically serves as a local religious teacher or leader with limited scope in issuing legal rulings. In contrast, a Mujtahid holds the scholarly rank to perform ijtihad, offering independent and authoritative judgments on Islamic law based on deep expertise in jurisprudence. The Mujtahid's interpretations are considered binding within their school of thought, whereas the Mullah primarily transmits established doctrines without exercising independent legal reasoning.
Community Influence and Responsibilities
Mullahs, typically recognized as local religious teachers, play a crucial role in guiding community members through day-to-day religious practices and resolving local disputes, fostering social cohesion at the grassroots level. Mujtahids hold higher scholarly authority, empowered to interpret Sharia law and issue fatwas, significantly influencing broader community norms and legal frameworks. Their responsibilities extend beyond spiritual guidance to shaping socio-political issues, often impacting policy decisions and religious education within the Muslim community.
Differences in Legal Reasoning (Ijtihad vs. Taqlid)
Mullahs primarily engage in taqlid, relying on established legal rulings and interpretations handed down by earlier scholars, thus following precedent without independent analysis. Mujtahids exercise ijtihad, applying rigorous scholarly reasoning to derive new legal judgments directly from foundational Islamic texts such as the Quran and Sunnah. The fundamental difference lies in the role of ijtihad as a process of independent interpretation versus taqlid as adherence to established authority within Islamic jurisprudence.
Recognition and Qualification Processes
Mullahs typically gain recognition through traditional madrasa education, focusing on foundational Islamic jurisprudence and Quranic studies, with their authority often locally acknowledged. Mujtahids undergo extensive certification processes, including mastering advanced principles of ijtihad and Usul al-fiqh, enabling them to issue independent legal opinions (fatwas) recognized by broader Shia scholarly communities. The qualification of Mujtahids requires rigorous scholarly assessment, often validated through endorsements by prominent religious authorities, distinguishing them from Mullahs who function primarily as learned teachers rather than independent jurists.
Contemporary Significance of Both Titles
Mullah and Mujtahid represent distinct levels of Islamic scholarship, with Mujtahid holding the authority to interpret Sharia law independently, a role pivotal in shaping contemporary Islamic jurisprudence. The contemporary significance of Mujtahid lies in their influence on modern legal rulings and adaptability of Islamic law to current issues, whereas Mullahs primarily serve as local religious leaders focusing on teaching and community guidance. Understanding the differentiation between these titles highlights the evolving dynamics of religious authority and legal interpretation in contemporary Muslim societies.
Mullah vs Mujtahid: Key Distinctions Summarized
Mullah and Mujtahid differ primarily in religious authority and scholarly attainment within Islamic jurisprudence; a Mullah typically serves as a local mosque leader or teacher, while a Mujtahid possesses advanced qualifications to independently interpret Sharia law. The Mujtahid engages in ijtihad, applying deep knowledge of Quran, Hadith, and legal principles to issue new religious rulings, whereas the Mullah generally follows established interpretations. This distinction underlines the Mujtahid's higher role in Islamic legal scholarship compared to the more community-focused responsibilities of a Mullah.
Mullah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com