A guru is a revered spiritual teacher or guide who imparts wisdom and knowledge to help individuals achieve personal growth and enlightenment. Rooted in various religious and philosophical traditions, a guru offers guidance that nurtures inner transformation and self-awareness. Discover how embracing a guru's teachings can profoundly impact Your journey by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
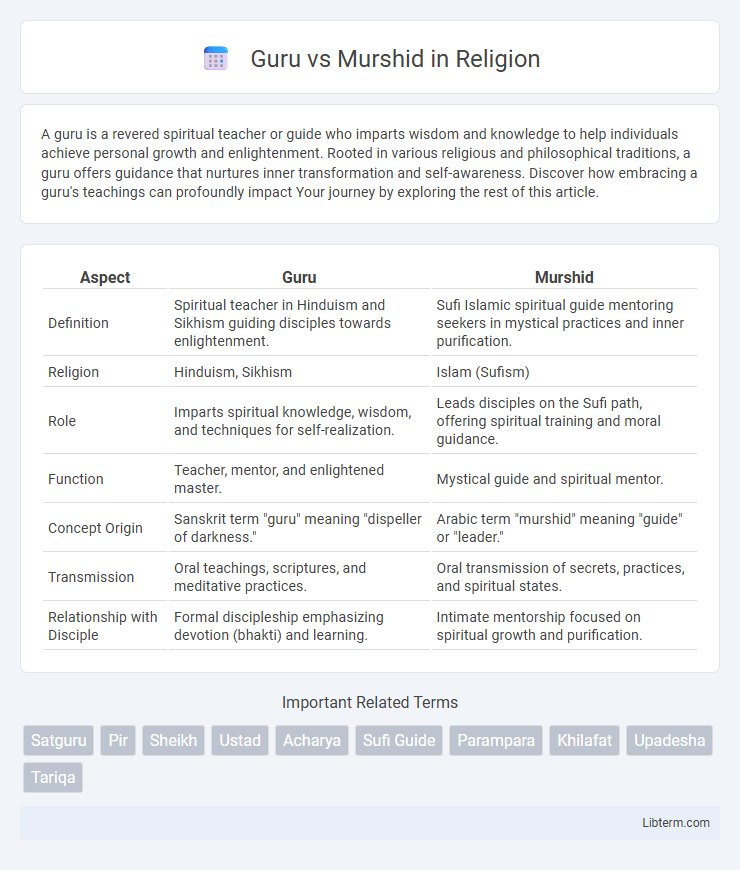
| Aspect | Guru | Murshid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spiritual teacher in Hinduism and Sikhism guiding disciples towards enlightenment. | Sufi Islamic spiritual guide mentoring seekers in mystical practices and inner purification. |
| Religion | Hinduism, Sikhism | Islam (Sufism) |
| Role | Imparts spiritual knowledge, wisdom, and techniques for self-realization. | Leads disciples on the Sufi path, offering spiritual training and moral guidance. |
| Function | Teacher, mentor, and enlightened master. | Mystical guide and spiritual mentor. |
| Concept Origin | Sanskrit term "guru" meaning "dispeller of darkness." | Arabic term "murshid" meaning "guide" or "leader." |
| Transmission | Oral teachings, scriptures, and meditative practices. | Oral transmission of secrets, practices, and spiritual states. |
| Relationship with Disciple | Formal discipleship emphasizing devotion (bhakti) and learning. | Intimate mentorship focused on spiritual growth and purification. |
Understanding the Terms: Guru and Murshid
The term "Guru" primarily originates from Sanskrit, signifying a spiritual teacher or guide who imparts wisdom and knowledge, especially within Hindu and Sikh traditions. "Murshid," an Arabic term widely used in Sufism, refers to a spiritual guide who leads disciples towards inner enlightenment and divine truth through personal mentorship. Understanding the distinct cultural and religious contexts of Guru and Murshid highlights their roles as pivotal figures in guiding spiritual growth and fostering self-realization.
Historical Origins of Guru and Murshid
The terms Guru and Murshid have distinct historical origins rooted in different cultural and religious traditions. Guru originates from Sanskrit, meaning "teacher" or "master," and plays a central role in Hinduism, Sikhism, and Buddhism as a spiritual guide who imparts wisdom and enlightenment. Murshid, deriving from Arabic, means "guide" or "spiritual mentor" in Islamic Sufism, serving as a key figure in guiding disciples on the mystical path toward divine knowledge.
Core Philosophies: Hinduism vs Sufism
Guru in Hinduism embodies the core philosophy of imparting spiritual wisdom through guiding disciples toward self-realization and liberation (moksha), often emphasizing the transmission of sacred knowledge and meditation practices. Murshid in Sufism serves as a spiritual master who leads seekers on the path of divine love and inner purification, focusing on the experiential connection with God and the cultivation of the heart through practices like dhikr (remembrance). Both roles emphasize a transformative teacher-disciple relationship but differ in their ultimate spiritual goals and methodologies, reflecting the distinct metaphysical and devotional frameworks of Hinduism and Sufism.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Guru
A Guru serves as a spiritual guide and teacher who imparts wisdom, knowledge, and discipline to disciples, facilitating their personal and spiritual growth. Their responsibilities include interpreting sacred texts, providing ethical and moral guidance, and nurturing the disciple's progress through personalized instruction and mentorship. The Guru's role extends beyond mere teaching, embodying a living example of spiritual principles and fostering a deep, transformative relationship with the seeker.
Roles and Responsibilities of a Murshid
The Murshid serves as a spiritual guide responsible for mentoring disciples on the path of inner purification and enlightenment, emphasizing direct transmission of esoteric knowledge. Their role includes providing personalized guidance, ensuring adherence to spiritual disciplines, and facilitating the disciple's connection with the divine. Unlike a Guru who may offer broader religious teachings, the Murshid focuses intimately on the disciple's spiritual development and experiential understanding.
Paths to Enlightenment: Guru’s Approach
The Guru's approach to enlightenment emphasizes personalized guidance and transmission of sacred knowledge, often through one-on-one mentorship and direct experiential learning. This path prioritizes the guru's spiritual authority and the disciple's devotion, fostering transformation through disciplined practices, mantras, and meditation. The guru acts as a living embodiment of wisdom, guiding seekers to self-realization by unveiling inner truths and cosmic consciousness.
Paths to Enlightenment: Murshid’s Guidance
A Murshid provides personalized spiritual guidance crucial for navigating complex paths to enlightenment, emphasizing practical wisdom and direct experience. Unlike a Guru, whose role can be broader and more authoritative, a Murshid tailors teachings to the individual's unique spiritual journey, fostering deep inner transformation. This method enhances the seeker's ability to overcome obstacles through customized practices and continuous support.
Teacher-Disciple Relationship: Key Differences
The Teacher-Disciple relationship in the context of Guru and Murshid differs significantly in spiritual and cultural nuances. A Guru, often rooted in Hindu and Sikh traditions, is seen as an enlightened guide who imparts knowledge to the disciple (shishya) through direct, often transformational teaching. Conversely, a Murshid in Sufism embodies a spiritual mentor who leads the disciple (murid) on a mystical path through personal example and esoteric wisdom.
Spiritual Practices: Eastern and Mystical Traditions
Guru and Murshid serve as spiritual guides in Eastern and mystical traditions, each embodying unique approaches to spiritual practices. The Guru, prominent in Hinduism and Sikhism, emphasizes direct transmission of wisdom through meditation, mantra chanting, and disciplined yoga, fostering self-realization and enlightenment. The Murshid, central to Sufism, guides disciples through dhikr (remembrance of God), spiritual exercises, and personalized mentorship, facilitating the inner purification and mystical union with the Divine.
Choosing Your Guide: Guru or Murshid?
Choosing your guide involves understanding the distinct roles of a Guru and a Murshid in spiritual growth. A Guru imparts knowledge and initiates disciples into specific teachings, often emphasizing personal transformation and enlightenment. A Murshid, rooted in Sufi tradition, leads through ongoing mentorship and spiritual companionship, fostering deep inner development and experiential wisdom.
Guru Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com