A commandment serves as a fundamental rule or directive designed to guide behavior and decision-making. Rooted in religious or moral frameworks, commandments establish clear boundaries that help maintain order and ethical standards. Explore the rest of this article to understand how commandments influence your daily life and societal norms.
Table of Comparison
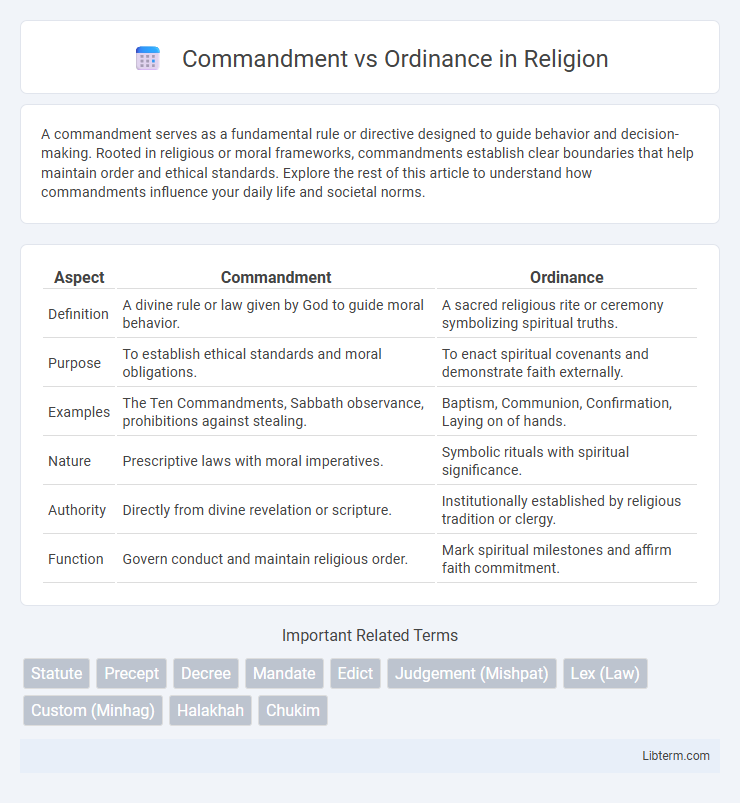
| Aspect | Commandment | Ordinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A divine rule or law given by God to guide moral behavior. | A sacred religious rite or ceremony symbolizing spiritual truths. |
| Purpose | To establish ethical standards and moral obligations. | To enact spiritual covenants and demonstrate faith externally. |
| Examples | The Ten Commandments, Sabbath observance, prohibitions against stealing. | Baptism, Communion, Confirmation, Laying on of hands. |
| Nature | Prescriptive laws with moral imperatives. | Symbolic rituals with spiritual significance. |
| Authority | Directly from divine revelation or scripture. | Institutionally established by religious tradition or clergy. |
| Function | Govern conduct and maintain religious order. | Mark spiritual milestones and affirm faith commitment. |
Definition of Commandment
A commandment is a divine rule or law given by a higher authority, typically found in religious contexts, that mandates specific behaviors or prohibitions. It serves as a fundamental moral guideline intended to govern the conduct of believers, often considered absolute and non-negotiable. Unlike ordinances, which may be rituals or symbolic acts, commandments emphasize ethical obligations and direct commands from scripture or religious doctrine.
Definition of Ordinance
An ordinance is a formal directive or regulation enacted by a governing authority to maintain order and ensure compliance within a specific jurisdiction. It serves as a localized rule, often addressing community standards, public safety, and administrative procedures. Unlike commandments, which are typically moral imperatives from religious texts, ordinances are legal mandates enforced by civil authorities.
Historical Origins of Commandments
Commandments trace their origins to ancient religious texts, notably the Torah, where they are established as divine laws given to guide moral and ethical behavior. These foundational rules, such as the Ten Commandments, emerged from the covenant between God and the Israelites, reflecting a direct divine mandate. In contrast, ordinances typically evolved as community-based regulations, often instituted by religious or civil authorities to govern ritual practices and social order.
Historical Roots of Ordinances
Ordinances find their historical roots in ancient legal and religious systems, where they served as specific rules or regulations enacted by governing authorities to maintain order and ritual practice. Unlike commandments, which often emerge from divine mandates with moral imperatives, ordinances historically functioned as structured protocols established by civil or ecclesiastical leaders to address communal governance. These early ordinances were documented in various codes such as Hammurabi's Code and Mosaic Law, reflecting their dual role in societal law and religious tradition.
Commandments in Major Religions
Commandments in major religions such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam serve as divine laws guiding moral conduct and spiritual practice. The Ten Commandments in Judaism and Christianity emphasize fundamental ethical principles like honoring parents, prohibiting theft, and bearing false witness, which form the foundation of their legal and moral systems. In Islam, commandments are embedded within the Sharia and the Quranic injunctions, including the Five Pillars that structure faith, prayer, charity, fasting, and pilgrimage, reflecting comprehensive directives from God.
Ordinances in Religious Practice
Ordinances in religious practice are formal rites or ceremonies instituted by a religious tradition, often serving as tangible expressions of faith and obedience. Unlike commandments, which are direct divine instructions or moral laws, ordinances typically involve ritual observances such as baptism, communion, or marriage, symbolizing spiritual truths and covenant relationships. These sacred practices reinforce community identity and provide a structured means for believers to experience and affirm their religious commitments.
Key Differences Between Commandments and Ordinances
Commandments are divine laws requiring moral obedience, often relating to ethical behavior and spiritual duties, whereas ordinances are formal rituals or ceremonies prescribed by religious institutions to symbolize faith and commitment. Commandments emphasize obligations or prohibitions intended to guide personal conduct, while ordinances typically involve specific actions like baptism, communion, or sacrifice that publicly express religious beliefs. The key difference lies in commands as mandates governing moral life versus ordinances as symbolic acts reinforcing community identity and religious teachings.
Theological Significance of Each
Commandments hold foundational theological significance as divine laws given by God to guide moral and spiritual behavior, reflecting eternal principles of righteousness and covenantal relationship with the divine. Ordinances carry symbolic and ritualistic importance, serving as outward expressions of faith and acts of obedience designed to commemorate, initiate, or sanctify believers within a faith community. Together, commandments shape ethical living and doctrinal adherence, while ordinances reinforce identity and spiritual connection through tangible practices.
Examples of Commandments and Ordinances
Commandments include moral directives such as "Thou shalt not kill" and "Honor thy father and thy mother," which govern ethical behavior and personal conduct. Ordinances often refer to ritual practices like baptism and the Lord's Supper in Christianity, serving as symbolic acts of faith and obedience. Both commandments and ordinances play essential roles in guiding spiritual life, but commandments primarily address moral imperatives while ordinances focus on ceremonial observances.
Impact on Faith and Daily Life
Commandments shape core beliefs and ethical frameworks that define a believer's relationship with the divine, influencing moral decision-making and spiritual growth. Ordinances are ritual acts that reinforce faith through tangible expressions, providing structure and community cohesion in daily worship and practice. Together, they integrate belief and action, deeply embedding religious principles into everyday life and personal integrity.
Commandment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com