Doctrine shapes the foundational principles and beliefs that guide organizations, legal systems, or religious frameworks in their decision-making processes. Understanding the key elements of doctrine can enhance your ability to analyze how rules and values influence behavior across different contexts. Explore the rest of the article to discover how doctrine impacts various fields and your everyday choices.
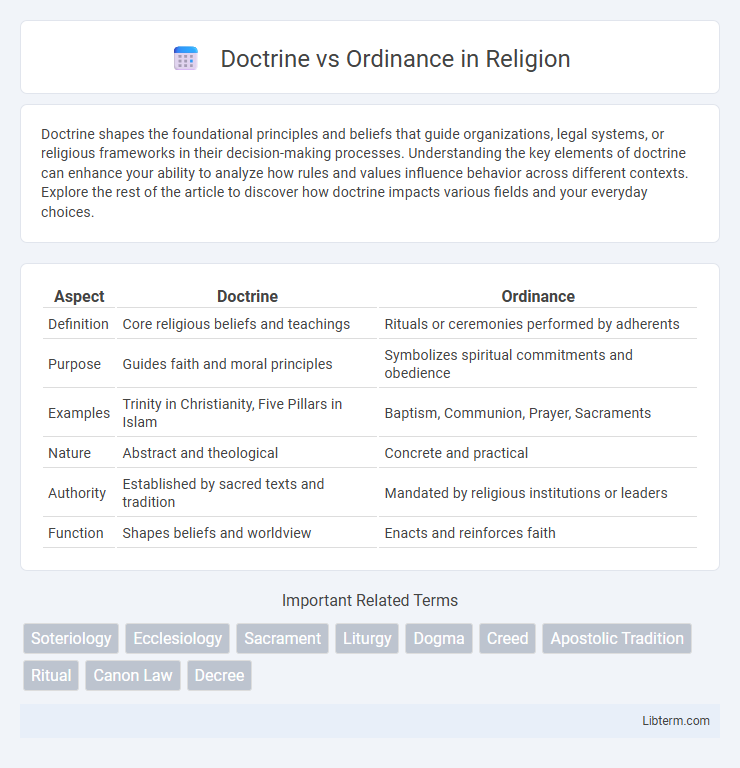
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Doctrine | Ordinance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Core religious beliefs and teachings | Rituals or ceremonies performed by adherents |
| Purpose | Guides faith and moral principles | Symbolizes spiritual commitments and obedience |
| Examples | Trinity in Christianity, Five Pillars in Islam | Baptism, Communion, Prayer, Sacraments |
| Nature | Abstract and theological | Concrete and practical |
| Authority | Established by sacred texts and tradition | Mandated by religious institutions or leaders |
| Function | Shapes beliefs and worldview | Enacts and reinforces faith |
Understanding Doctrine: Definition and Scope
Doctrine refers to a set of beliefs or teachings formally established by a religious, political, or organizational authority, serving as a guiding framework for practice and decision-making. It encompasses core principles intended to shape behavior, justify policies, and unify adherents within a system of thought. The scope of doctrine extends beyond mere rules to include underlying philosophies and interpretations that influence institutional identity and long-term strategy.
Defining Ordinance: Meaning and Function
Ordinance refers to a specific, authoritative decree or regulation enacted by a governing body or religious authority to direct behavior and ensure order within a community or organization. In religious contexts, ordinances are formal rites or ceremonies, such as baptism or communion, that symbolize and enact spiritual truths and commitments. These prescribed actions function as tangible expressions of faith, reinforcing doctrinal teachings through practice and observance.
Key Differences Between Doctrine and Ordinance
Doctrine refers to a set of core beliefs or teachings held and promoted by a religious group, serving as guiding principles for faith and practice. Ordinance denotes specific rituals or practices, such as baptism or communion, that are formally instituted and observed within a religious community. The key difference lies in doctrine encompassing theoretical beliefs, while ordinances involve concrete, prescribed ceremonial acts.
Historical Development of Doctrines and Ordinances
The historical development of doctrines and ordinances reflects their distinct roles in religious traditions, where doctrines are formalized beliefs shaped by theological debates and ecumenical councils, such as the Nicene Creed in Christianity. Ordinances evolved as prescribed religious practices or rites, like baptism and communion, often codified through church authority to guide communal worship and individual piety. Over time, doctrines provided the foundational theological framework, while ordinances served as tangible expressions of faith within various religious communities.
Theological Significance of Doctrines
Doctrines hold foundational theological significance as they represent officially established beliefs that shape faith and practice within religious traditions. Unlike ordinances, which are symbolic rites or ceremonies performed in obedience to divine commands, doctrines provide the essential framework for understanding God's nature, salvation, and moral law. Their role is critical in unifying believers under a coherent set of teachings that guide spiritual growth and ethical conduct.
The Role of Ordinances in Religious Practice
Ordinances serve as formal, prescribed religious rites that symbolize core theological beliefs and foster communal identity among believers. Distinct from doctrine, which encompasses the fundamental teachings and dogmas of a faith, ordinances function as tangible expressions of those beliefs through rituals such as baptism and communion. Their consistent observance reinforces spiritual discipline and communal unity within religious practice.
Scriptural Foundations: Doctrine vs Ordinance
Doctrine refers to the set of core beliefs derived from biblical teachings, serving as foundational truths in Christianity, such as the Trinity, salvation, and resurrection, grounded in scriptures like John 3:16 and Romans 10:9. Ordinances, including Baptism and the Lord's Supper, are scripturally mandated practices symbolizing these doctrines, established by Christ in passages like Matthew 28:19 and 1 Corinthians 11:23-26. The distinction emphasizes doctrine as theological truths for belief, while ordinances are outward, scriptural acts of obedience reflecting those beliefs.
Examples of Doctrines in Major Religions
Christianity emphasizes the doctrine of the Trinity, which defines God as three persons in one essence: Father, Son, and Holy Spirit. In Islam, the doctrine of Tawhid asserts the absolute oneness and uniqueness of Allah, rejecting any form of polytheism. Hinduism presents the doctrine of Dharma, referring to the moral order and duties that govern individuals in society and the cosmos.
Common Ordinances Across Faith Traditions
Common ordinances across faith traditions, such as baptism, communion, and marriage, serve as symbolic acts embodying core doctrinal beliefs and spiritual commitments. These ordinances function as outward expressions of inner faith, often instituted by religious authority to unify community practice and reinforce theological principles. While doctrine comprises the comprehensive set of beliefs and teachings, ordinances provide tangible rituals that manifest and affirm those doctrines within communal worship.
Impact on Believers: Doctrine and Ordinance Compared
Doctrine shapes the foundational beliefs and worldview of believers, guiding their faith, moral decisions, and spiritual identity over time. Ordinances, such as baptism or communion, serve as tangible acts of obedience and public expressions of faith that reinforce doctrinal truths through ritual participation. The impact on believers arises from doctrine providing cognitive and ethical frameworks, while ordinances foster communal belonging and experiential connection to those beliefs.
Doctrine Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com