Personal sin reflects actions and thoughts that violate moral and ethical principles, affecting your spiritual well-being and relationships. Understanding its impact helps you recognize the need for repentance and personal growth. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to confront and overcome personal sin effectively.
Table of Comparison
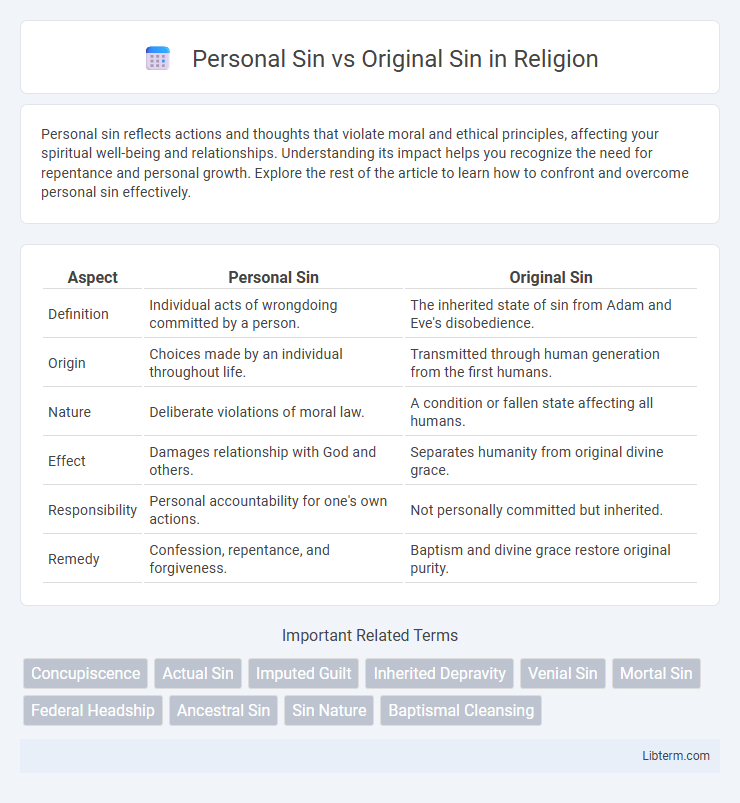
| Aspect | Personal Sin | Original Sin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual acts of wrongdoing committed by a person. | The inherited state of sin from Adam and Eve's disobedience. |
| Origin | Choices made by an individual throughout life. | Transmitted through human generation from the first humans. |
| Nature | Deliberate violations of moral law. | A condition or fallen state affecting all humans. |
| Effect | Damages relationship with God and others. | Separates humanity from original divine grace. |
| Responsibility | Personal accountability for one's own actions. | Not personally committed but inherited. |
| Remedy | Confession, repentance, and forgiveness. | Baptism and divine grace restore original purity. |
Defining Personal Sin: An Overview
Personal sin refers to individual acts or thoughts that intentionally violate God's law, reflecting a conscious choice to do wrong. It contrasts with original sin, which is the inherent fallen state inherited from Adam and Eve, affecting human nature universally. Understanding personal sin emphasizes moral responsibility and the need for repentance and forgiveness in Christian theology.
Understanding Original Sin: Origins and Meaning
Original sin originates from the biblical account of Adam and Eve's disobedience in the Garden of Eden, symbolizing the inherited fallen state of humanity. It represents the collective condition of sinfulness passed down through generations, affecting every human from birth. Understanding original sin highlights the theological foundation for humanity's need for salvation and divine grace.
Biblical Foundations for Both Sins
Biblical foundations establish original sin as the inherited condition from Adam's transgression in Genesis 3 and Romans 5:12, highlighting humanity's fallen state. Personal sin, described throughout Scripture in passages like James 1:14-15 and 1 John 1:8-10, refers to individual acts of disobedience against God's commandments. Both sins underscore humanity's need for salvation through Christ, as emphasized in Romans 3:23-24 and 1 John 3:4.
Key Differences: Personal Sin vs Original Sin
Personal sin refers to individual acts of wrongdoing committed consciously and freely, whereas original sin denotes the inherited fallen state passed from Adam and Eve to all humanity. Key differences include personal sin being actual violations of moral law, while original sin represents the inherent separation from God and the loss of original holiness. Personal sin can be forgiven through repentance and grace, but original sin signifies the condition requiring baptism and divine redemption.
Theological Perspectives on Sin
Theological perspectives distinguish personal sin as individual acts of moral failure, directly attributable to human choice, whereas original sin refers to the inherited fallen state stemming from Adam and Eve's transgression, affecting all humanity. Personal sin involves conscious decisions that violate divine law and disrupt one's relationship with God, while original sin is considered a fundamental condition impacting human nature and necessitating divine grace for redemption. Different Christian traditions emphasize varying interpretations of original sin's effects, with Catholicism highlighting baptism's cleansing power and Protestantism focusing on justification by faith.
Effects of Original Sin on Humanity
Original Sin fundamentally alters human nature by introducing a hereditary state of separation from God, resulting in an innate inclination towards moral wrongdoing and spiritual death. This fallen condition disrupts the original harmony, causing suffering, death, and a weakened will susceptible to sin, which all humans inherit from Adam and Eve. Personal sin builds upon this corrupted nature, manifesting as individual acts that further distance people from divine grace and eternal salvation.
Consequences of Personal Sin
Personal sin leads to a rupture in an individual's relationship with God, resulting in spiritual death, guilt, and a weakened conscience. It impedes sanctification and invites temporal punishments and moral consequences, such as habitual wrongdoing and loss of grace. Unlike original sin, which marks the inherent fallen state of humanity, personal sins reflect deliberate acts that require repentance and divine forgiveness to restore spiritual health.
Redemption and Forgiveness: Overcoming Sin
Personal sin refers to individual acts of wrongdoing that separate a person from God, while original sin denotes the inherited fallen state from Adam and Eve. Redemption through Jesus Christ offers forgiveness and spiritual cleansing for both personal and original sins, restoring the relationship between humanity and God. Divine grace enables believers to overcome sin by faith, transforming lives through repentance and renewal in Christ.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Personal sin refers to individual acts of wrongdoing consciously committed, whereas original sin denotes the inherent sinful state inherited from Adam and Eve's disobedience. A common misconception is that original sin is an actual act one personally commits, but it is instead a condition affecting human nature. Clarifying this distinction helps in understanding moral responsibility and the need for personal repentance distinct from the inherited fallen nature.
Personal Responsibility in the Light of Original Sin
Personal sin refers to the individual acts of transgression against divine law, highlighting human accountability for moral choices, while original sin denotes the inherited fallen state stemming from Adam and Eve's initial disobedience. The concept of original sin emphasizes the innate tendency toward wrongdoing, but personal responsibility remains paramount as each person consciously decides to commit or resist sin. Understanding original sin as a condition reinforces the necessity for repentance and moral vigilance in exercising free will to overcome personal sin.
Personal Sin Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com