Energeia embodies the concept of active potential and realization in philosophy, highlighting the transition from possibility to actuality. Understanding its significance can deepen your appreciation of how energy and purpose drive existence and action. Explore the full article to uncover the profound implications of Energeia in both ancient thought and modern contexts.
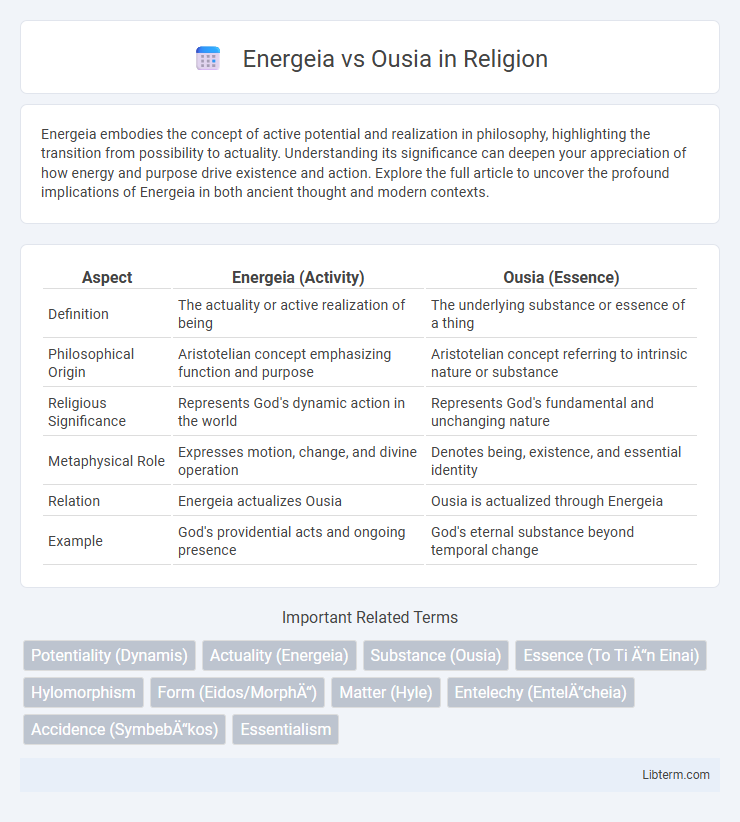
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Energeia (Activity) | Ousia (Essence) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The actuality or active realization of being | The underlying substance or essence of a thing |
| Philosophical Origin | Aristotelian concept emphasizing function and purpose | Aristotelian concept referring to intrinsic nature or substance |
| Religious Significance | Represents God's dynamic action in the world | Represents God's fundamental and unchanging nature |
| Metaphysical Role | Expresses motion, change, and divine operation | Denotes being, existence, and essential identity |
| Relation | Energeia actualizes Ousia | Ousia is actualized through Energeia |
| Example | God's providential acts and ongoing presence | God's eternal substance beyond temporal change |
Introduction to Energeia and Ousia
Energeia and ousia are fundamental concepts in Aristotelian metaphysics, where ousia refers to the essential substance or essence of a thing, representing what it is in its purest form. Energeia, often translated as "actuality," denotes the realization or active fulfillment of a thing's potential, highlighting the dynamic aspect of existence. Understanding the distinction between ousia as the underlying reality and energeia as the manifestation of that reality is crucial for grasping Aristotle's theory of being and change.
Historical Origins of the Terms
Energeia and Ousia stem from ancient Greek philosophy, with origins tracing back to Aristotle's metaphysical works. Energeia signifies "actuality," the realized state of being or activity, whereas Ousia represents "essence" or "substance," the fundamental nature of a thing. These terms became central to scholastic debates about existence and reality, influencing medieval and modern metaphysical thought.
Aristotle’s Distinction: Energeia and Ousia
Aristotle's distinction between Energeia and Ousia is fundamental in his metaphysics, where Energeia refers to actualization or activity, representing the dynamic fulfillment of a thing's potential, while Ousia denotes substance or essence, the underlying reality of an entity. Energeia captures the living expression of a being's nature in motion or function, whereas Ousia is the static substratum that defines what a thing is independently of its states. This differentiation highlights Aristotle's emphasis on the interplay between being (Ousia) and its active realization (Energeia) in understanding existence.
Energeia: The Concept of Actuality
Energeia, a key concept in Aristotelian metaphysics, signifies the state of actuality or being in action, contrasted with potentiality (dunamis) as the capacity for change or development. It represents the fulfillment of purpose and the realization of an essence in a concrete form, essential to understanding the nature of change and existence. In this framework, Ousia refers to substance or essence, while Energeia highlights the active manifestation of that essence in reality.
Ousia: The Nature of Substance or Essence
Ousia, in ancient Greek philosophy, denotes the fundamental nature or essence of a substance, representing what a thing truly is beyond its attributes or actions. Unlike Energeia, which refers to the actuality or activity of an entity, Ousia emphasizes the inherent being or substance that defines existence itself. Understanding Ousia is essential for grasping metaphysical discussions about identity, reality, and the essence underlying phenomena.
Energeia vs Ousia in Metaphysical Debates
Energeia and Ousia represent critical concepts in metaphysical debates, with Energeia referring to actualization or the realized activity of a substance, while Ousia denotes the underlying essence or substance itself. Philosophers, especially Aristotle, emphasize that Energeia captures the dynamic process of being in action, contrasting with Ousia's static nature as the fundamental reality or existence. This distinction informs debates on the nature of being, causality, and change, influencing the interpretation of substance and its properties in classical metaphysics.
Role of Energeia and Ousia in Ontology
Energeia represents the active actuality or dynamic fulfillment of a thing's potential, essential for understanding change and existence in Aristotle's ontology. Ousia, often translated as 'substance' or 'essence,' denotes the underlying being that persists through change, serving as the fundamental entity in metaphysical inquiry. The interplay of Energeia and Ousia is crucial in ontology to explain how entities maintain identity while undergoing processes of actualization and transformation.
Influence on Later Philosophical Thought
Aristotle's distinction between Energeia (actuality) and Ousia (substance) significantly influenced medieval scholasticism, particularly in the works of Thomas Aquinas, who integrated these concepts into Christian metaphysics. This framework shaped early modern philosophy by offering a foundational understanding of existence and change, evident in Spinoza's and Leibniz's ontologies. The interplay between Energeia and Ousia also informed contemporary metaphysical debates on potentiality, essence, and the nature of being, extending its impact on existentialism and process philosophy.
Energeia and Ousia in Contemporary Context
Energeia and Ousia, rooted in Aristotelian philosophy, represent dynamic actuality and essential substance, respectively, influencing contemporary metaphysics and ontology. In modern contexts, Energeia is often aligned with processes, activity, and function, while Ousia corresponds to the underlying essence or being of entities, shaping debates in identity and existence. This distinction informs various fields such as cognitive science, where Energeia relates to mental functions and Ousia to the nature of consciousness.
Conclusion: Comparative Insights and Implications
Energeia, denoting actualization or activity, contrasts with Ousia, which refers to essence or being, highlighting a dynamic interplay between existence and function in Aristotelian philosophy. Understanding these concepts clarifies metaphysical discussions about the nature of reality, where Energeia represents realized potential and Ousia signifies inherent substance. This distinction informs contemporary debates in ontology and philosophy of mind by emphasizing the relationship between what things are and what they do.
Energeia Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com