Feminist perspectives emphasize equality, advocating for social, political, and economic rights that dismantle gender-based discrimination. Exploring the history and impact of feminist movements reveals the ongoing struggle for justice and empowerment. Discover how feminism shapes society and influences your worldview by reading the rest of this article.
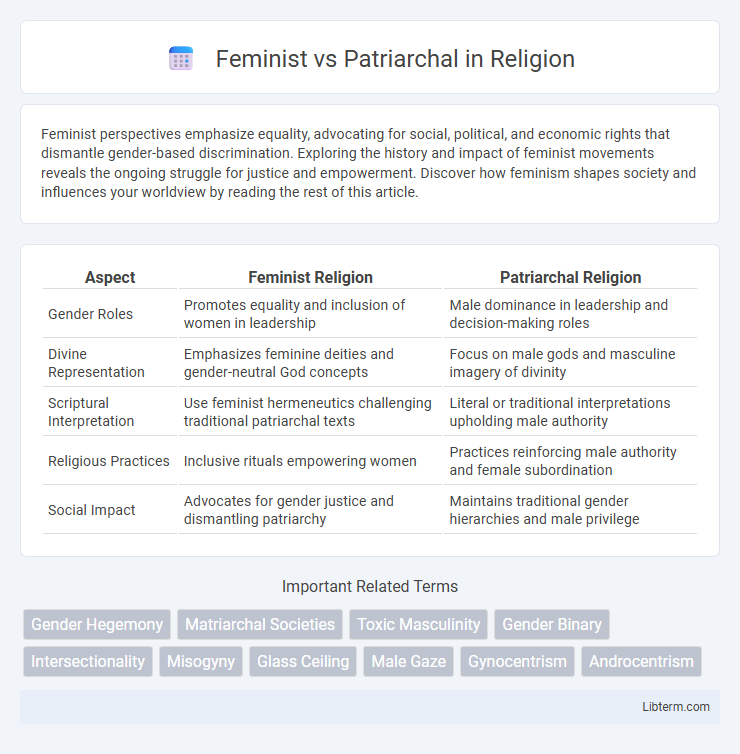
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Feminist Religion | Patriarchal Religion |
|---|---|---|
| Gender Roles | Promotes equality and inclusion of women in leadership | Male dominance in leadership and decision-making roles |
| Divine Representation | Emphasizes feminine deities and gender-neutral God concepts | Focus on male gods and masculine imagery of divinity |
| Scriptural Interpretation | Use feminist hermeneutics challenging traditional patriarchal texts | Literal or traditional interpretations upholding male authority |
| Religious Practices | Inclusive rituals empowering women | Practices reinforcing male authority and female subordination |
| Social Impact | Advocates for gender justice and dismantling patriarchy | Maintains traditional gender hierarchies and male privilege |
Understanding Feminism: Core Principles and Goals
Feminism centers on achieving gender equality by challenging systemic patriarchy that perpetuates male dominance and unequal power structures. Core principles include advocating for women's rights, dismantling gender roles, and promoting social, political, and economic equity. The movement strives to create inclusive societies where all genders have equal opportunities and representation.
The Patriarchal System: Origins and Impact
The patriarchal system, rooted in ancient agrarian societies, established male dominance through inheritance, religious doctrines, and social structures that prioritize men's authority over women. It has perpetuated gender inequality by limiting women's access to education, economic opportunities, and political power, embedding systemic bias in legal and cultural institutions worldwide. The enduring impact is seen in contemporary gender wage gaps, underrepresentation of women in leadership, and persistent societal norms reinforcing male privilege.
Gender Roles: Feminist Perspectives vs. Patriarchal Norms
Feminist perspectives challenge traditional gender roles by advocating for equality and dismantling the binary constraints imposed by patriarchal norms, which often prescribe rigid roles based on biological sex. Patriarchal societies typically enforce male dominance and female submissiveness, limiting personal freedom and perpetuating systemic inequality. Feminism promotes the deconstruction of these roles to enable diverse expressions of identity and equitable participation across all social, economic, and political domains.
Power Dynamics in Society: Feminist and Patriarchal Approaches
Feminist approaches challenge traditional patriarchal power structures by advocating for gender equality, dismantling systemic oppression, and promoting female agency in social, political, and economic spheres. Patriarchal systems maintain hierarchical dominance through male-centered authority, enforcing gender roles that restrict women's access to resources and decision-making positions. Power dynamics in society are thus shaped by competing ideologies, where feminist frameworks aim to redistribute influence equitably, contrasting with patriarchal models that perpetuate male supremacy.
Representation in Media: Challenging Patriarchal Narratives
Feminist representation in media actively challenges patriarchal narratives by promoting diverse, multidimensional characters that defy traditional gender roles. This shift enhances visibility for marginalized voices and encourages critical discussions on power dynamics and inequality. Media portraying feminist themes often confronts stereotypes, fostering a culture of inclusivity and gender equity.
Education and Socialization: Shaping Gender Ideologies
Feminist perspectives in education emphasize dismantling gender stereotypes and promoting equality through inclusive curricula that highlight diverse role models and challenge traditional norms. Patriarchal socialization often reinforces gender hierarchies by inculcating distinct roles for males and females, limiting opportunities and perpetuating bias within academic and social frameworks. Educational systems and socialization processes play crucial roles in shaping gender ideologies, influencing both individual identity formation and broader societal power dynamics.
Legal Rights: Advancements through Feminist Movements
Feminist movements have significantly advanced legal rights by challenging patriarchal systems that historically favored male dominance in family law, property rights, and voting. Landmark achievements include the establishment of equal pay laws, reproductive rights, and protections against gender-based violence, which directly confront legal disparities rooted in patriarchy. These reforms reflect the ongoing struggle to achieve gender equality within legal frameworks dominated by patriarchal traditions.
Workplace Equality: Feminist Gains vs. Patriarchal Barriers
Feminist movements have driven significant workplace equality gains, such as closing gender pay gaps, increasing female leadership representation, and advocating for comprehensive maternity and parental leave policies. Patriarchal barriers persist through systemic biases, unequal opportunities for career advancement, and entrenched cultural norms that discourage women's participation in STEM fields and executive roles. Data from organizations like the World Economic Forum highlight ongoing disparities, with women holding less than 30% of senior management positions globally despite feminist-driven policy reforms.
Intersectionality: Beyond Traditional Feminism and Patriarchy
Intersectionality expands the analysis of feminist and patriarchal structures by addressing overlapping systems of oppression related to race, class, gender, and sexuality, which traditional feminism often overlooks. Kimberle Crenshaw's framework reveals how marginalized groups experience unique forms of discrimination within patriarchal societies that single-axis approaches fail to capture. This multidimensional perspective fosters more inclusive strategies for social justice, challenging both gender-based hierarchies and interconnected inequalities.
Towards Equality: Dialogue and Future Prospects
The feminist movement challenges patriarchal structures by advocating for gender equality through inclusive dialogue and policy reform. Emphasizing shared human rights, ongoing conversations between feminists and traditional patriarchal societies aim to dismantle systemic biases and promote equitable opportunities. Future prospects hinge on collaborative efforts that integrate diverse perspectives, fostering social environments where gender equity becomes a fundamental and sustained norm.
Feminist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com