Fundamentalism is characterized by a strict adherence to specific religious or ideological doctrines, often resisting modern interpretations and changes. This movement typically emphasizes a literal understanding of sacred texts and promotes a return to what it considers original beliefs. Discover how fundamentalism impacts societies and influences global affairs in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
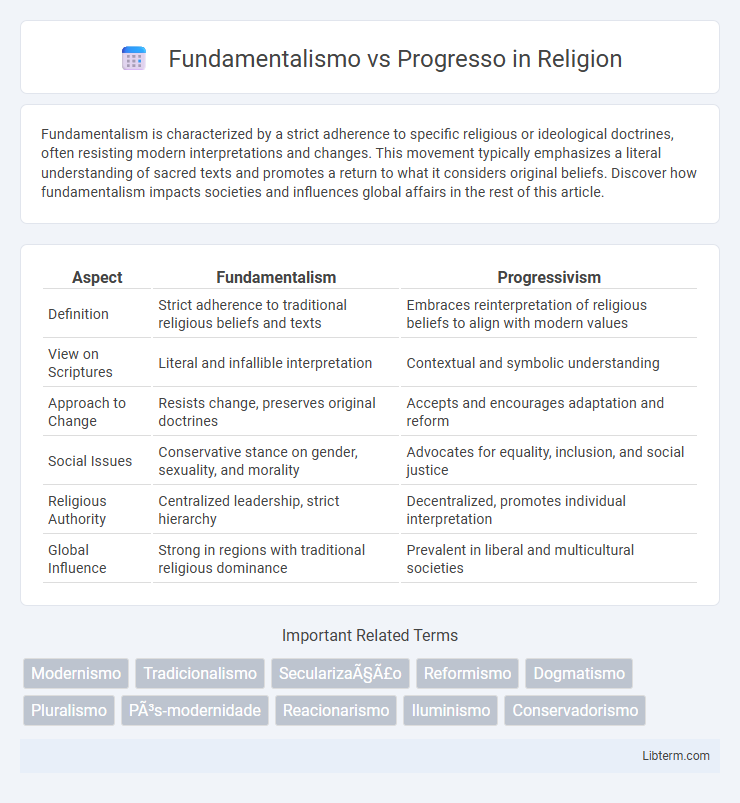
| Aspect | Fundamentalism | Progressivism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strict adherence to traditional religious beliefs and texts | Embraces reinterpretation of religious beliefs to align with modern values |
| View on Scriptures | Literal and infallible interpretation | Contextual and symbolic understanding |
| Approach to Change | Resists change, preserves original doctrines | Accepts and encourages adaptation and reform |
| Social Issues | Conservative stance on gender, sexuality, and morality | Advocates for equality, inclusion, and social justice |
| Religious Authority | Centralized leadership, strict hierarchy | Decentralized, promotes individual interpretation |
| Global Influence | Strong in regions with traditional religious dominance | Prevalent in liberal and multicultural societies |
Definição de Fundamentalismo
Fundamentalismo is defined as a strict adherence to specific theological doctrines typically in reaction against modernist theology and secularism, emphasizing literal interpretations of sacred texts. This ideology often rejects scientific advancements and social changes that contradict traditional religious beliefs, fostering resistance to progressive values such as gender equality and pluralism. The conflict between fundamentalism and progresso highlights the tension between preserving established dogmas and embracing evolutionary social and intellectual developments.
O Conceito de Progresso
The concept of progress embodies the belief in continuous improvement through science, technology, and social reforms, driving societies toward enhanced well-being and innovation. Unlike fundamentalism, which emphasizes adherence to traditional doctrines or absolute truths, progress advocates for adaptability and critical thinking to address contemporary challenges. This dynamic vision of progress champions human rights, education, and sustainable development as essential pillars for collective advancement.
Origens Históricas dos Dois Movimentos
The historical origins of fundamentalism trace back to early 20th-century American Protestant reactions against modernist theology and secular cultural changes. Progressivism emerged in the late 19th and early 20th centuries as a response to social inequalities and industrialization, emphasizing reform, science, and democracy. Both movements reflect divergent responses to modernity, with fundamentalism aiming to preserve traditional beliefs and progressivism advocating societal change.
Principais Crenças do Fundamentalismo
Fundamentalismo is characterized by a strict adherence to literal interpretations of sacred texts, emphasizing unwavering obedience to traditional doctrines and the rejection of modernist or secular influences. Core beliefs include the infallibility of religious scriptures, the necessity of moral absolutism, and the preservation of established religious laws as the ultimate guide for personal and societal conduct. This worldview often contrasts sharply with progressive perspectives that advocate for reinterpretation, social reform, and adaptation to contemporary values.
Valores e Práticas Progressistas
Progressive values emphasize social justice, equality, and environmental sustainability, advocating for policies that protect marginalized communities and promote inclusive growth. Practices such as embracing diversity, supporting renewable energy, and encouraging education reform reflect the core principles of progressivism. This approach contrasts with fundamentalism by prioritizing adaptability and evidence-based solutions to societal challenges.
Contraposição de Perspectivas Sociais
Fundamentalismo emphasizes rigid adherence to traditional values and literal interpretations of religious or ideological doctrines, often resisting social change and diversity. In contrast, progresso advocates for social transformation through innovation, inclusivity, and the embrace of modern values such as equality and human rights. This contraposicao de perspectivas sociais highlights the ongoing tension between preserving cultural identity and pursuing societal evolution.
Impactos Políticos e Culturais
Fundamentalismo and progresso shape political landscapes by driving rigid adherence to traditional ideologies versus embracing reform and innovation, influencing policy-making and governance structures. Cultural impacts manifest in societal norms and values, where fundamentalist movements promote preservation of established beliefs, while progressive forces encourage diversity and inclusion. These opposing dynamics often create tensions that affect social cohesion and political stability.
Conflitos e Pontos de Convergência
Fundamentalismo often emphasizes strict adherence to traditional beliefs, leading to conflicts with progressive movements that advocate for social change and modernization. Despite tensions, both perspectives can converge on shared values such as justice, community well-being, and ethical governance. Understanding these common goals is crucial for fostering dialogue and reducing ideological polarization in socio-political contexts.
Desafios Atuais no Debate Fundamentalismo vs Progresso
Current challenges in the Fundamentalism vs. Progress debate revolve around balancing traditional values with rapid technological and social changes. Conflicts arise as fundamentalist perspectives often resist scientific advancements and cultural shifts, while progressive views push for innovation and reform. Addressing misinformation, ideological polarization, and cultural clashes remains crucial for fostering constructive dialogue and societal cohesion.
Caminhos para o Diálogo e a Convivência
Fundamentalism and progress often clash in societal values, yet pathways to dialogue and coexistence emphasize mutual respect and open communication. Embracing cultural pluralism and fostering educational initiatives can bridge ideological divides, promoting understanding between conservative and progressive groups. Structured forums and community engagement activities serve as effective platforms for exchanging perspectives and cultivating peaceful coexistence.
Fundamentalismo Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com