Divination involves interpreting signs, symbols, or events to gain insight into the future or hidden knowledge. Techniques like tarot reading, astrology, and rune casting are popular methods used across cultures to guide decision-making and self-discovery. Explore this article to learn how divination can enhance Your intuition and awareness.
Table of Comparison
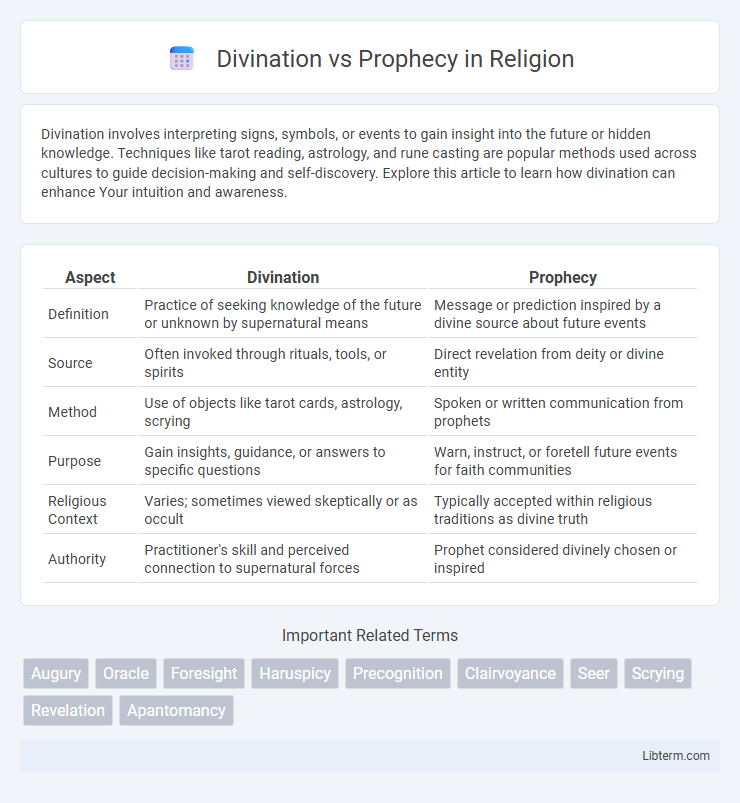
| Aspect | Divination | Prophecy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Practice of seeking knowledge of the future or unknown by supernatural means | Message or prediction inspired by a divine source about future events |
| Source | Often invoked through rituals, tools, or spirits | Direct revelation from deity or divine entity |
| Method | Use of objects like tarot cards, astrology, scrying | Spoken or written communication from prophets |
| Purpose | Gain insights, guidance, or answers to specific questions | Warn, instruct, or foretell future events for faith communities |
| Religious Context | Varies; sometimes viewed skeptically or as occult | Typically accepted within religious traditions as divine truth |
| Authority | Practitioner's skill and perceived connection to supernatural forces | Prophet considered divinely chosen or inspired |
Understanding Divination and Prophecy
Divination involves interpreting signs, symbols, or rituals to gain insight into unknown aspects of the present or future, often relying on tools like tarot cards, runes, or astrology. Prophecy is the declaration of a future event believed to be inspired by a divine source or higher power, often conveyed through visions, dreams, or inspired speech. Understanding divination centers on the methods and symbolic interpretations used to access hidden knowledge, while prophecy emphasizes the authoritative revelation of predetermined future outcomes.
Historical Origins of Divination and Prophecy
Divination and prophecy both stem from ancient practices aimed at understanding the unknown, with divination rooted in ritualistic methods such as casting lots, reading omens, and interpreting signs in Mesopotamian and Ancient Egyptian cultures. Prophecy emerged prominently within religious contexts like those of the Hebrew Bible, where prophets conveyed divine messages and forewarnings believed to be directly inspired by a deity. Historical origins reveal divination as a more technique-based approach while prophecy centers on authoritative revelation, shaping distinct roles in ancient societies' attempts to anticipate future events.
Key Differences Between Divination and Prophecy
Divination involves methods such as tarot reading, astrology, or scrying to gain insight into future events or hidden knowledge, relying on interpretive tools and symbols. Prophecy is typically characterized by direct revelations or messages believed to come from a divine source, often delivered by prophets within religious contexts. The key differences lie in divination's use of practices and rituals for personal or practical guidance, whereas prophecy conveys spiritual or moral truths with authoritative and often communal significance.
Tools and Methods Used in Divination
Divination employs various tools and methods such as tarot cards, rune stones, pendulums, and scrying mirrors to interpret signs and gain insight into future events or hidden knowledge. Practitioners often use astrology charts, palmistry, and tea leaf reading to analyze symbolic patterns that guide decision-making and spiritual understanding. Unlike prophecy, which relies on divine revelation or inspired messages, divination methods emphasize symbolic interpretation and the manipulation of physical objects to access intuitive wisdom.
The Role of Prophets in Ancient Societies
Prophets in ancient societies served as vital intermediaries between the divine and human realms, conveying messages believed to be dictated by gods to guide communities in crucial decisions and moral conduct. Unlike diviners who sought specific information through rituals or omens, prophets provided broader spiritual insights and warnings, often influencing political and social structures. Their role extended beyond prediction, encompassing the interpretation of divine will to maintain social cohesion and reinforce cultural values.
Divinatory Practices Across Cultures
Divinatory practices vary widely across cultures, including tarot reading in the West, I Ching in China, and Ifa divination among the Yoruba people of Nigeria. These methods utilize symbolic tools, such as cards, coins, or casting bones, to interpret hidden knowledge and guide decision-making. Each tradition reflects its culture's spiritual beliefs and cosmology, providing insight into the collective unconscious and future possibilities.
Prophetic Traditions in Major Religions
Prophecy in major religions such as Christianity, Islam, and Judaism involves divine revelation delivered by selected individuals who communicate God's will, guidance, or future events to humanity. Prophetic traditions emphasize ethical teachings, moral accountability, and the unfolding of spiritual destiny, distinguishing them from divination practices that seek to predict the future through occult means. The Hebrew Bible features prophets like Isaiah and Jeremiah, the Quran highlights Muhammad as the final prophet, and Christian texts reference numerous prophetic figures who shape religious doctrine and eschatology.
The Accuracy and Interpretation of Divination
Divination accuracy varies widely depending on the method, practitioner skill, and cultural context, often relying on symbolic interpretation rather than empirical evidence. Interpretation of divination is inherently subjective, with meanings shaped by personal intuition, traditional frameworks, and situational factors influencing the outcome. Unlike prophecy, which claims direct divine revelation, divination invites a more fluid understanding that can adapt based on interpretation and circumstances.
Ethical Considerations in Divination and Prophecy
Ethical considerations in divination and prophecy center on the responsibility of practitioners to avoid manipulation and respect the autonomy of those seeking guidance. Divination often requires transparency about its interpretative nature, ensuring clients understand outcomes are contingent and not guaranteed. Prophecy carries ethical weight in managing the impact of foretold events on individuals' psychological wellbeing and preventing misuse of authoritative claims to influence decisions or behavior.
Modern Perspectives on Divination and Prophecy
Modern perspectives on divination emphasize its role as a psychological tool for introspection and decision-making rather than a literal prediction of the future. Prophecy, in contemporary contexts, is often viewed through a socio-cultural lens, highlighting its impact on shaping beliefs and behaviors rather than as an infallible foretelling. Studies in cognitive science and anthropology explore how both practices influence human perception, emphasizing symbolism and narrative interpretation over deterministic outcomes.
Divination Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com