Syncretism blends different religious, cultural, or philosophical beliefs into a cohesive system, promoting understanding and harmony among diverse traditions. This process shapes societies by integrating elements from various origins, influencing art, rituals, and social values. Explore the rest of the article to discover how syncretism impacts your worldview and cultural experiences.
Table of Comparison
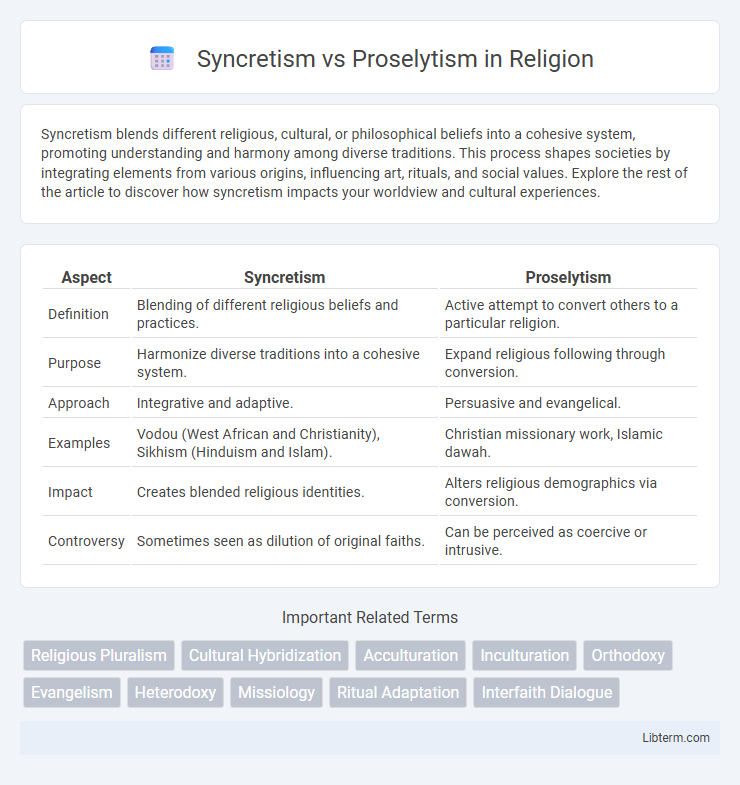
| Aspect | Syncretism | Proselytism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blending of different religious beliefs and practices. | Active attempt to convert others to a particular religion. |
| Purpose | Harmonize diverse traditions into a cohesive system. | Expand religious following through conversion. |
| Approach | Integrative and adaptive. | Persuasive and evangelical. |
| Examples | Vodou (West African and Christianity), Sikhism (Hinduism and Islam). | Christian missionary work, Islamic dawah. |
| Impact | Creates blended religious identities. | Alters religious demographics via conversion. |
| Controversy | Sometimes seen as dilution of original faiths. | Can be perceived as coercive or intrusive. |
Introduction to Syncretism and Proselytism
Syncretism refers to the blending of different religious beliefs and practices into a cohesive system, often occurring naturally within multicultural societies. Proselytism involves actively seeking to convert individuals from one religion to another, usually driven by missionary efforts or organized campaigns. Both terms highlight distinct approaches to religious interaction: syncretism emphasizes integration and adaptation, while proselytism centers on persuasion and conversion.
Defining Syncretism: Blending Beliefs
Syncretism refers to the blending of diverse religious beliefs and practices into a cohesive system, often resulting from cultural interaction and exchange. It emphasizes the harmonization of different traditions, creating new rituals and doctrines that incorporate elements from multiple faiths without demanding exclusive adherence. This contrasts sharply with proselytism, which seeks to convert individuals to a singular belief system, often rejecting syncretic approaches as compromising doctrinal purity.
Proselytism Explained: Spreading Faith
Proselytism involves actively seeking to convert individuals to a particular faith through direct engagement, evangelism, and persuasive communication. It emphasizes the promotion of exclusive religious beliefs, aiming to expand a religious community by influencing personal convictions and practices. Unlike syncretism, which blends different traditions, proselytism maintains doctrinal purity while encouraging new adherents to adopt specific religious tenets.
Historical Origins of Syncretism
Syncretism has deep historical origins rooted in the blending of religious, cultural, and philosophical traditions during periods of cultural contact, such as the Hellenistic era where Greco-Roman beliefs merged with Eastern religions. It often arose organically as communities adapted foreign deities and rituals into their own systems, evident in examples like the fusion of Egyptian and Greek gods or the integration of indigenous beliefs with Christianity in colonial contexts. This contrasts with proselytism, which is characterized by active efforts to convert individuals to a particular faith, rather than the passive, gradual blending seen in syncretism.
The Evolution of Proselytism Across Cultures
Proselytism has evolved across cultures from aggressive conversion tactics to more nuanced forms of religious dialogue and exchange, reflecting changes in social dynamics and global interconnectedness. Syncretism often emerges as a parallel process, blending elements of different beliefs to create hybrid spiritual practices rather than seeking outright conversion. This shift highlights how proselytism adapts within multicultural societies, balancing persuasion with respect for existing traditions.
Key Differences Between Syncretism and Proselytism
Syncretism involves blending elements from different religious or cultural traditions to create a new, hybrid belief system, emphasizing integration and coexistence. Proselytism seeks to convert individuals from their current faith to another, emphasizing active evangelism and doctrinal purity. The key difference lies in syncretism's focus on fusion and mutual adaptation, whereas proselytism prioritizes conversion and exclusivity.
Syncretism in Contemporary Religious Practices
Syncretism in contemporary religious practices involves the blending of elements from different faith traditions to create new, hybrid forms of spirituality that reflect diverse cultural contexts. This process often facilitates interfaith dialogue and accommodates globalization by allowing believers to incorporate rituals, beliefs, and symbols from multiple religions. Unlike proselytism, which emphasizes conversion and exclusive adherence, syncretism promotes religious pluralism and adaptability in a rapidly changing world.
Proselytism in Modern Society
Proselytism in modern society often involves active efforts by religious or ideological groups to convert individuals through direct communication, media campaigns, and social services. This practice influences cultural dynamics by promoting specific belief systems, sometimes leading to tensions in diverse, pluralistic communities. The rise of digital platforms has amplified proselytism, enabling targeted outreach but also raising ethical debates about consent and religious freedom.
Sociocultural Impacts of Syncretism and Proselytism
Syncretism fosters cultural blending by integrating diverse religious beliefs and practices, leading to greater social cohesion and multicultural identity formation. Proselytism often drives religious conversion efforts that can cause social tensions and cultural disruptions within communities. Both processes significantly influence societal values, norms, and intergroup relations, shaping cultural evolution and conflict dynamics.
Conclusion: The Future of Religious Interactions
The future of religious interactions will likely involve a dynamic balance between syncretism and proselytism, as global interconnectedness fosters both blending and conversion efforts. Syncretism enables cultural and theological integration, promoting coexistence and mutual respect among diverse faiths. Proselytism, however, continues to drive active religious expansion, shaping identity and belief systems in an increasingly pluralistic world.
Syncretism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com