A saint is often recognized as a person of exceptional holiness and virtue, revered in various religious traditions for their exemplary life and spiritual significance. Their stories inspire faith, moral guidance, and devotion among followers across cultures. Explore the rest of the article to discover the profound impact saints have on your spiritual journey and cultural heritage.
Table of Comparison
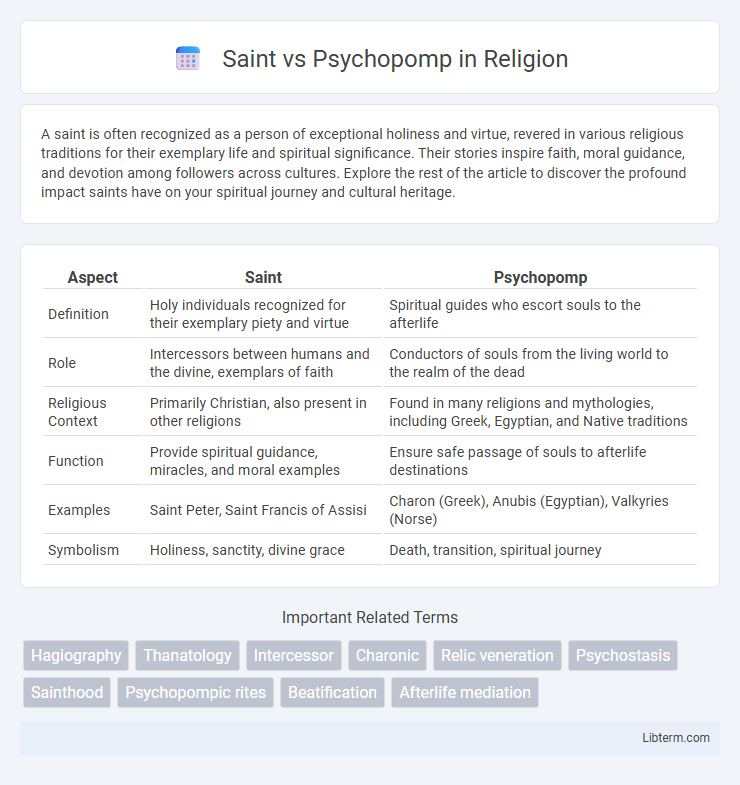
| Aspect | Saint | Psychopomp |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Holy individuals recognized for their exemplary piety and virtue | Spiritual guides who escort souls to the afterlife |
| Role | Intercessors between humans and the divine, exemplars of faith | Conductors of souls from the living world to the realm of the dead |
| Religious Context | Primarily Christian, also present in other religions | Found in many religions and mythologies, including Greek, Egyptian, and Native traditions |
| Function | Provide spiritual guidance, miracles, and moral examples | Ensure safe passage of souls to afterlife destinations |
| Examples | Saint Peter, Saint Francis of Assisi | Charon (Greek), Anubis (Egyptian), Valkyries (Norse) |
| Symbolism | Holiness, sanctity, divine grace | Death, transition, spiritual journey |
Defining Saints and Psychopomps
Saints are individuals recognized for their holiness, virtuous lives, and often canonized by religious authorities for their exemplary faith and moral integrity. Psychopomps are spiritual guides or entities responsible for escorting souls to the afterlife in various religious and mythological traditions. The key distinction lies in saints being venerated humans for their piety, while psychopomps function as supernatural intermediaries between the living and the dead.
Historical Origins of Saints
Saints originated from early Christian traditions honoring holy individuals believed to have led exemplary lives and often performed miracles, serving as intercessors between humanity and the divine. Psychopomps, traced back to ancient mythologies like Greek and Egyptian, are spiritual guides tasked with escorting souls to the afterlife rather than being venerated as holy persons. The historical development of saints centers on sanctification through church recognition, contrasting with psychopomps whose roles are rooted in ritualistic beliefs about death and the soul's journey.
Mythological Roots of Psychopomps
Psychopomps originate from ancient mythologies as supernatural beings guiding souls to the afterlife, prominently featured in Greek, Egyptian, and Norse cultures with figures like Hermes, Anubis, and Valkyries. Unlike saints, who are venerated for their piety and miracles within religious traditions, psychopomps serve a distinct role in the metaphysical transition between life and death. Their mythological roots highlight their function as mediators between worlds, embodying cultural beliefs about death and the soul's journey beyond mortality.
Roles and Functions in the Spiritual Realm
Saints serve as intercessors and exemplars of divine virtues, guiding believers through prayer and moral teachings to attain spiritual growth and salvation. Psychopomps function as spiritual guides who escort souls from the physical world to the afterlife, facilitating the transition between life and death across various cultural mythologies. While saints emphasize ongoing spiritual support and inspiration within earthly life, psychopomps focus primarily on the passage of souls and the mechanics of the afterlife journey.
Symbolism and Iconography
Saints often symbolize holiness and divine intercession, represented by halos, crosses, and specific attributes related to their martyrdom or miracles. Psychopomps are depicted through iconography such as winged figures, dogs, or serpents, embodying the role of guiding souls to the afterlife. The contrasting symbolism emphasizes sanctity and spiritual mediation in saints, against transition and guidance in psychopomps within religious and mythological contexts.
Cross-Cultural Comparisons
Saints are revered figures in many religious traditions known for their holiness, miracles, and moral guidance, often serving as intercessors between the divine and humanity. Psychopomps, present in diverse cultures such as Ancient Egyptian (Anubis), Greek (Hermes), and Shamanistic traditions, function primarily to guide souls safely to the afterlife rather than act as spiritual exemplars. Cross-cultural comparisons reveal that while saints emphasize sanctity and moral virtue within a faith community, psychopomps embody the universal role of spiritual escorts facilitating the transition between life and death.
Saints and Psychopomps in Modern Belief Systems
Saints serve as revered spiritual intermediaries embodying virtues and divine guidance in modern belief systems, often invoked for protection and moral inspiration. Psychopomps, present in diverse contemporary cultures, function primarily as guides for souls transitioning between life and the afterlife, highlighting their critical role in death rituals and afterlife beliefs. Both concepts maintain significant cultural influence, reflecting enduring human concerns with morality, the supernatural, and the journey beyond death.
Influence on Art and Literature
Saints have profoundly influenced art and literature through depictions of their virtues, miracles, and martyrdom, inspiring countless hagiographies, iconography, and devotional works that emphasize moral and spiritual ideals. Psychopomps, as supernatural guides of souls in mythology and folklore, appear in various artistic and literary traditions, symbolizing the transition between life and death and exploring themes of mortality and the afterlife. The contrasting roles of saints and psychopomps underscore the cultural fascination with salvation, redemption, and the human condition in Western and global artistic narratives.
Rituals and Practices Associated with Each
Saints are often honored through rituals such as feast day celebrations, prayers for intercession, and the veneration of relics, aiming to seek blessings and spiritual guidance. Psychopomps are associated with death rites and transitional ceremonies that facilitate the soul's journey to the afterlife, involving rituals like funerary rites, offerings, and rituals to ensure safe passage. The practices around saints emphasize devotion and community worship, whereas psychopomp rituals focus on protection and the metaphysical transition from life to death.
Contemporary Relevance and Interpretations
Saints, revered for their holiness and moral guidance, continue to inspire contemporary spiritual practices and social justice movements, symbolizing hope and ethical integrity in modern society. Psychopomps, entities guiding souls to the afterlife across cultures, remain significant in psychological and spiritual interpretations of death, embodying the transition between life and the beyond. Both figures hold enduring relevance as metaphors for transformation and transcendence in contemporary discussions on mortality and spirituality.
Saint Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com