Enlightenment represents a profound awakening to knowledge, wisdom, and self-awareness that transforms perspectives and understanding. Cultivating enlightenment encourages deeper insight into your own consciousness and the nature of reality, fostering clarity and purpose. Continue reading to explore how enlightenment can impact your life and guide your personal growth journey.
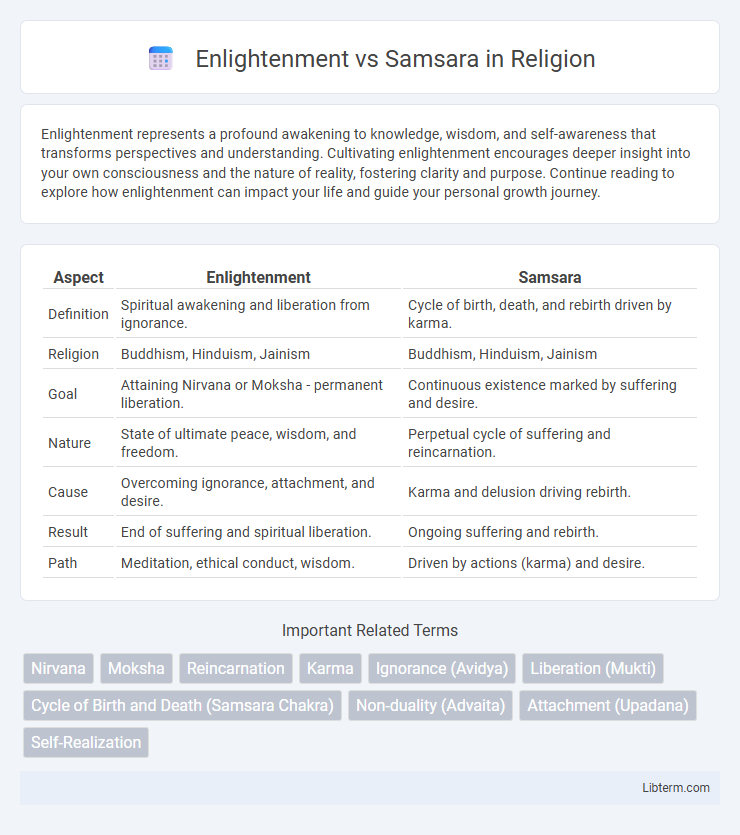
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Enlightenment | Samsara |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Spiritual awakening and liberation from ignorance. | Cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma. |
| Religion | Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism | Buddhism, Hinduism, Jainism |
| Goal | Attaining Nirvana or Moksha - permanent liberation. | Continuous existence marked by suffering and desire. |
| Nature | State of ultimate peace, wisdom, and freedom. | Perpetual cycle of suffering and reincarnation. |
| Cause | Overcoming ignorance, attachment, and desire. | Karma and delusion driving rebirth. |
| Result | End of suffering and spiritual liberation. | Ongoing suffering and rebirth. |
| Path | Meditation, ethical conduct, wisdom. | Driven by actions (karma) and desire. |
Understanding Enlightenment: A Path to Liberation
Enlightenment represents the profound awakening and realization of ultimate truth, leading to liberation from the cycle of Samsara--the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma and desire. Understanding Enlightenment involves recognizing the impermanent nature of existence, transcending ego and attachments, and achieving a state of lasting inner peace and freedom from suffering. This path to liberation emphasizes mindfulness, ethical living, and deep meditation as essential practices to overcome Samsara's limitations and attain spiritual liberation.
Defining Samsara: The Cycle of Birth and Death
Samsara refers to the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth that binds sentient beings through karma and ignorance. This perpetual process is marked by suffering and dissatisfaction, as souls remain trapped in the material world without spiritual liberation. Enlightenment, in contrast, represents the awakening that breaks free from Samsara, achieving Nirvana and eternal peace beyond the cycle of existence.
Core Philosophies Behind Enlightenment and Samsara
Enlightenment in Hinduism and Buddhism represents liberation from the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, characterized by the realization of ultimate truth and the cessation of suffering. Samsara denotes the continuous cycle of existence, marked by karma and the perpetual experience of pain, desire, and ignorance. The core philosophy behind enlightenment emphasizes self-realization and transcendence, whereas samsara underscores the binding nature of worldly attachments and the impermanence of life.
Key Differences Between Enlightenment and Samsara
Enlightenment represents the cessation of suffering and the realization of ultimate truth, characterized by liberation from the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, known as samsara. Samsara denotes the continuous cycle of existence driven by karma and ignorance, marked by perpetual attachment, desire, and suffering. Key differences include enlightenment's attainment of spiritual awakening and freedom, whereas samsara embodies ongoing samsaric bondage and existential suffering.
The Human Experience: Trapped in Samsara
The human experience is often described as being trapped in Samsara, the endless cycle of birth, death, and rebirth characterized by suffering, attachment, and ignorance. Enlightenment represents liberation from Samsara through awakening, self-realization, and the cessation of desire and ego-driven illusions. This state transcends worldly existence, offering profound peace, clarity, and spiritual freedom beyond the human condition's inherent dissatisfaction.
The Journey Toward Enlightenment
The journey toward enlightenment involves transcending Samsara, the cyclical realm of birth, death, and rebirth characterized by suffering and attachment. Practitioners engage in meditation, ethical living, and wisdom cultivation to break free from Samsara's cycle and attain Nirvana, a state of ultimate liberation and peace. This transformative path requires deep self-awareness and detachment from desires, enabling realization of the true nature of existence beyond worldly illusions.
Practices Leading from Samsara to Enlightenment
Meditation techniques such as Vipassana and mindfulness cultivate awareness that disrupts the cycle of Samsara by fostering detachment from material desires and mental afflictions. Ethical disciplines like the Noble Eightfold Path guide practitioners through right speech, right action, and right livelihood, which purify karma and reduce suffering. Consistent engagement in compassion and wisdom development accelerates the transformation from ignorance to Enlightenment, enabling liberation from samsaric existence.
Major Religious Perspectives on Enlightenment vs. Samsara
Major religious perspectives on enlightenment versus samsara emphasize the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth as a fundamental problem in Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, where samsara represents the continuous suffering and ignorance binding sentient beings. Hinduism describes enlightenment (moksha) as liberation from samsara through self-realization and union with Brahman, while Buddhism defines enlightenment (nirvana) as the cessation of cravings and the extinguishing of the cycle of suffering. Jainism views enlightenment as achieving kevala jnana, a pure knowledge state that breaks free from samsara, highlighting the importance of strict ethical conduct and asceticism.
Overcoming Attachments: Breaking the Cycle of Samsara
Overcoming attachments is essential to breaking the cycle of samsara, a cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by desire and ignorance. Enlightenment, as taught in Buddhism, represents liberation from samsara by realizing the impermanent nature of all phenomena and cultivating non-attachment. Through mindfulness and insight meditation, practitioners weaken craving and aversion, ultimately achieving Nirvana and freedom from suffering.
Achieving Inner Freedom: Embracing Enlightenment
Achieving inner freedom involves transcending samsara, the endless cycle of birth, death, and suffering, by embracing enlightenment, a state of profound spiritual awakening and liberation. Enlightenment dissolves attachment and ignorance, allowing the mind to experience pure awareness and unconditioned peace. This transformative realization breaks the bonds of karmic entanglement and ego-driven desires, leading to true freedom beyond worldly illusions.
Enlightenment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com