Nirvana represents the ultimate state of liberation and peace in Buddhist philosophy, where one transcends suffering and the cycle of rebirth. Achieving nirvana involves deep meditation, ethical living, and profound wisdom that dissolves attachment and desire. Explore the rest of this article to understand how you can embark on the path toward this transformative spiritual goal.
Table of Comparison
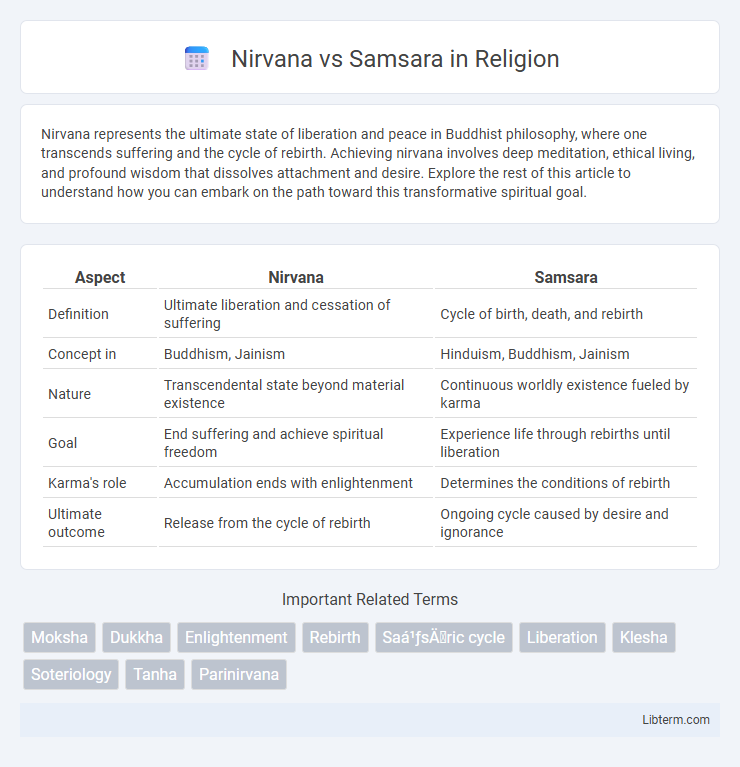
| Aspect | Nirvana | Samsara |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ultimate liberation and cessation of suffering | Cycle of birth, death, and rebirth |
| Concept in | Buddhism, Jainism | Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism |
| Nature | Transcendental state beyond material existence | Continuous worldly existence fueled by karma |
| Goal | End suffering and achieve spiritual freedom | Experience life through rebirths until liberation |
| Karma's role | Accumulation ends with enlightenment | Determines the conditions of rebirth |
| Ultimate outcome | Release from the cycle of rebirth | Ongoing cycle caused by desire and ignorance |
Understanding Nirvana: The Ultimate Liberation
Nirvana represents the ultimate liberation in Buddhist philosophy, characterized by the cessation of suffering and the extinguishment of desires and attachments. It transcends Samsara, the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma and craving. Achieving Nirvana entails awakening to the true nature of reality, resulting in profound peace and freedom from the endless cycle of suffering inherent in Samsara.
Defining Samsara: The Cycle of Birth and Rebirth
Samsara is defined as the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth governed by karma and desire within Hinduism and Buddhism. This cycle perpetuates suffering and attachment, trapping souls in an endless loop of existence across different lifetimes. Liberation from Samsara, achieving Nirvana, signifies the cessation of this cycle and the attainment of spiritual freedom and enlightenment.
Origins and Philosophical Foundations
Nirvana and Samsara originate from ancient Indian spiritual traditions, primarily found within Buddhism and Hinduism. Samsara represents the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, driven by karma and desire, symbolizing worldly suffering and impermanence. Nirvana signifies the ultimate liberation from Samsara's cycle, embodying spiritual awakening, cessation of suffering, and attainment of eternal peace and enlightenment.
Key Differences Between Nirvana and Samsara
Nirvana represents the state of ultimate liberation and freedom from the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth that defines Samsara. Samsara encompasses the continual cycle of suffering and desire driven by karma, perpetuating existence in the physical world. Key differences include Nirvana's transcendence of suffering and attachment, whereas Samsara is characterized by impermanence, ignorance, and the persistence of worldly suffering.
The Role of Suffering in Both Concepts
Suffering plays a central role in both Nirvana and Samsara, serving as the fundamental catalyst for spiritual awakening and liberation. In Samsara, suffering manifests through the cycle of birth, death, and rebirth, driven by desire, attachment, and ignorance. Nirvana represents the cessation of this suffering, achieved by extinguishing cravings and delusions, thus breaking free from Samsara's perpetual cycle.
Paths to Escaping Samsara
Nirvana represents the ultimate liberation from Samsara, the cyclic existence of birth, death, and rebirth characterized by suffering. Paths to escaping Samsara include the Noble Eightfold Path, which emphasizes right understanding, ethical conduct, and mental discipline through meditation and mindfulness. Following these practices leads to enlightenment, ending the cycle of suffering and achieving Nirvana.
Achieving Nirvana: Practices and Disciplines
Achieving Nirvana involves disciplined practices such as mindfulness meditation, ethical conduct, and insight into the nature of suffering and impermanence. Following the Noble Eightfold Path, including right view, right intention, and right concentration, is essential to transcend Samsara's cycle of birth, death, and rebirth. Continuous cultivation of wisdom (prajna) and detachment from desires leads to liberation from suffering and attainment of ultimate peace.
Nirvana and Samsara in Buddhist Thought
Nirvana in Buddhist thought represents the ultimate cessation of suffering and the cycle of rebirth, characterized by the extinguishing of desire, ignorance, and attachment. Samsara is the continuous cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma and craving, perpetuating suffering and dissatisfaction. Achieving Nirvana means liberation from Samsara, resulting in spiritual freedom and profound peace.
Nirvana vs Samsara in Hinduism
Nirvana in Hinduism represents the ultimate liberation (moksha) from the cycle of Samsara, which is the endless cycle of birth, death, and rebirth driven by karma. Samsara is associated with worldly suffering and attachment, while Nirvana signifies the realization of the self's unity with Brahman, transcending material existence. Achieving Nirvana entails overcoming ignorance (avidya) and desires, leading to eternal peace and freedom from karmic bondage.
The Spiritual Significance of Transcendence
Nirvana represents the ultimate spiritual transcendence, signifying liberation from the cycle of Samsara, which encompasses continuous birth, death, and rebirth marked by suffering. Achieving Nirvana involves detachment from worldly desires and the cessation of karmic accumulation, allowing the soul to attain a state of eternal peace and bliss beyond material existence. Samsara embodies spiritual entrapment, while Nirvana symbolizes the profound awakening and freedom intrinsic to many Eastern philosophical traditions.
Nirvana Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com