Allegorical interpretation unlocks deeper meanings behind texts by revealing symbolic and metaphorical layers beyond the literal words. This method enriches understanding by connecting narratives to broader spiritual, moral, or philosophical themes. Explore the rest of the article to discover how allegorical reading can transform your perception of literature.
Table of Comparison
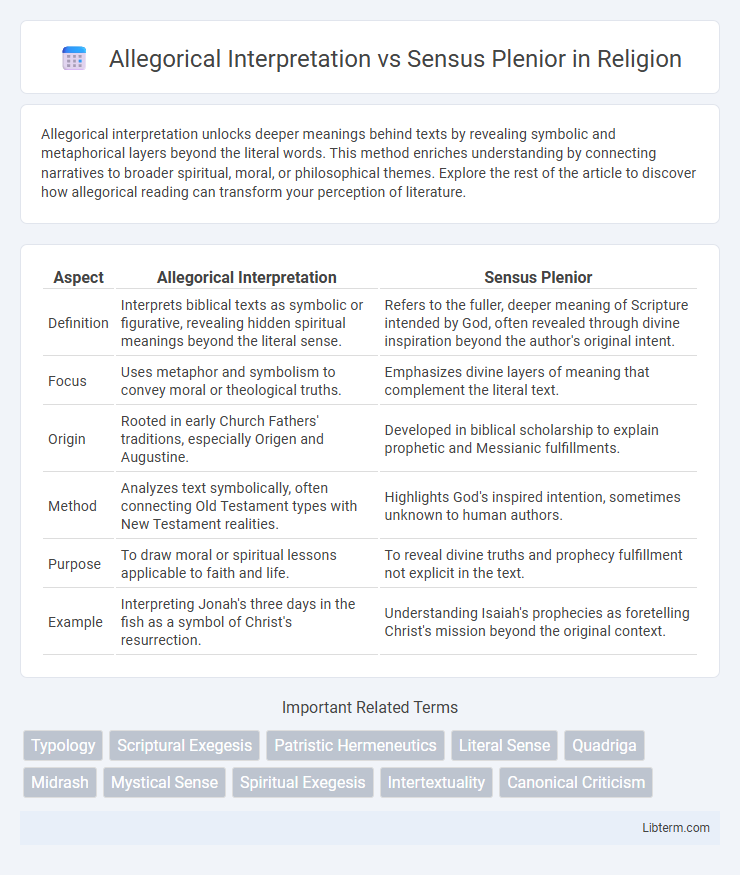
| Aspect | Allegorical Interpretation | Sensus Plenior |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interprets biblical texts as symbolic or figurative, revealing hidden spiritual meanings beyond the literal sense. | Refers to the fuller, deeper meaning of Scripture intended by God, often revealed through divine inspiration beyond the author's original intent. |
| Focus | Uses metaphor and symbolism to convey moral or theological truths. | Emphasizes divine layers of meaning that complement the literal text. |
| Origin | Rooted in early Church Fathers' traditions, especially Origen and Augustine. | Developed in biblical scholarship to explain prophetic and Messianic fulfillments. |
| Method | Analyzes text symbolically, often connecting Old Testament types with New Testament realities. | Highlights God's inspired intention, sometimes unknown to human authors. |
| Purpose | To draw moral or spiritual lessons applicable to faith and life. | To reveal divine truths and prophecy fulfillment not explicit in the text. |
| Example | Interpreting Jonah's three days in the fish as a symbol of Christ's resurrection. | Understanding Isaiah's prophecies as foretelling Christ's mission beyond the original context. |
Understanding Allegorical Interpretation
Allegorical interpretation involves deciphering deeper symbolic meanings within a text beyond its literal sense, often revealing spiritual or moral lessons. This method emphasizes the use of metaphors and imagery to convey truths that extend past the surface narrative. Unlike sensus plenior, which seeks a divinely intended fuller meaning known only to God, allegorical interpretation relies on human insight to extract symbolic significance.
Defining Sensus Plenior
Sensus Plenior, a Latin term meaning "fuller sense," refers to the deeper or more complete meaning intended by God but not fully grasped by the human author of a biblical text. Unlike allegorical interpretation, which often imposes symbolic or moral meanings based on human insight, Sensus Plenior arises from the divine inspiration that reveals additional layers of theological significance beyond the immediate context. This hermeneutical approach underscores the dynamic interaction between Scripture's human and divine authorship, highlighting that biblical passages may possess multifaceted meanings fulfilled in later revelation or Christological fulfillment.
Historical Background of Both Approaches
Allegorical interpretation, rooted in the early Christian and Hellenistic traditions, emerged as a method to uncover deeper spiritual meanings beneath the literal biblical text, often influenced by Platonic philosophy. Sensus plenior, a concept formalized in 20th-century biblical scholarship, emphasizes the "fuller sense" intended by God but not explicitly understood by the human author, highlighting a divine layer of meaning revealed through later revelation and canonical context. Both approaches reflect evolving theological perspectives on scripture's complexity, with allegory focusing on symbolic meaning and sensus plenior on divine intentional depth beyond human authorial intent.
Key Theological Foundations
Allegorical interpretation emphasizes symbolic meanings in biblical texts, aligning closely with early Christian and patristic traditions that seek deeper spiritual truths beyond the literal sense. Sensus plenior, a term coined by modern theologians, acknowledges an author-intended fuller meaning inspired by divine revelation, which may remain hidden to the original human author but revealed to the inspired reader. Both frameworks underscore the multilayered nature of scripture, yet sensus plenior uniquely bridges human and divine authorship, affirming theological foundations of biblical inspiration and hermeneutics.
Methodological Differences
Allegorical interpretation emphasizes extracting symbolic or hidden meanings from biblical texts, often linking Old Testament events as foreshadows of New Testament realities. Sensus plenior refers to the "fuller meaning" intended by God but not necessarily recognized by the human author, requiring a recognition of divine inspiration beyond literal or allegorical reading. Methodologically, allegorical interpretation relies on symbolic connections and thematic parallels, whereas sensus plenior depends on theological insight into the divine author's ultimate intention, transcending traditional exegesis.
Scriptural Examples of Allegory
Allegorical interpretation of Scripture involves uncovering hidden or spiritual meanings beyond the literal text, as seen in Galatians 4:21-31, where Paul's allegory of Hagar and Sarah contrasts the old and new covenants. This method contrasts with sensus plenior, which implies a fuller divine meaning intended by God but not always perceived by the human author. Scriptural examples like the parables of Jesus illustrate allegory by symbolizing deeper theological truths through narrative elements.
Scriptural Examples of Sensus Plenior
Sensus plenior, meaning "fuller sense," reveals a deeper divine meaning in Scripture that surpasses the human author's original intent, often evident in prophetic texts like Isaiah 53, which Christians interpret as foreshadowing Christ's atonement. Unlike allegorical interpretation, which reads symbolic meanings into biblical narratives, sensus plenior acknowledges God's layered communication within the same text, as seen in Psalm 22 where David's suffering anticipates Jesus' crucifixion. This interpretive approach respects the historical context while uncovering divine truths fulfilled in later revelation, highlighting the progressive unfolding of biblical theology.
Advantages and Limitations
Allegorical interpretation reveals deeper spiritual meanings and encourages theological reflection beyond the literal text, promoting rich doctrinal insights and moral application within scriptural study. Its limitation lies in the subjective nature of symbolism, which can lead to varied and sometimes conflicting interpretations without clear textual anchors. In contrast, sensus plenior emphasizes an intended fuller meaning that the human author may not have consciously known, offering a divinely inspired perspective that harmonizes with the canonical context, yet this approach depends heavily on authoritative theological frameworks for validation and can be less accessible for independent exegetical analysis.
Impact on Biblical Exegesis
Allegorical interpretation emphasizes symbolic meanings behind biblical narratives, often revealing spiritual or moral truths beyond the literal text. Sensus plenior refers to a deeper, divinely intended sense recognized in scripture by the Spirit, surpassing the original human author's understanding. Integrating sensus plenior enhances biblical exegesis by uncovering layered theological insights, while allegorical interpretation broadens scriptural application but risks subjective readings.
Contemporary Relevance and Debates
Allegorical interpretation, historically rooted in early Christian exegesis, emphasizes symbolic meanings beyond the literal text, often revealing spiritual truths, while sensus plenior refers to the "fuller sense" intended by divine inspiration but sometimes hidden from the original human author. Contemporary debates revolve around the legitimacy and boundaries of these methods in biblical hermeneutics, questioning the balance between authorial intent and theological insight. Current scholarship highlights the relevance of sensus plenior in bridging ancient texts with modern theological contexts, whereas allegorical interpretation faces critiques for potentially subjective or anachronistic readings.
Allegorical Interpretation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com