Shekhinah represents the divine presence in Jewish mysticism, symbolizing God's immanence and closeness to humanity. This concept plays a crucial role in spiritual practices and religious understanding, enriching your connection to faith and tradition. Explore the rest of the article to discover deeper insights into Shekhinah's significance and impact.
Table of Comparison
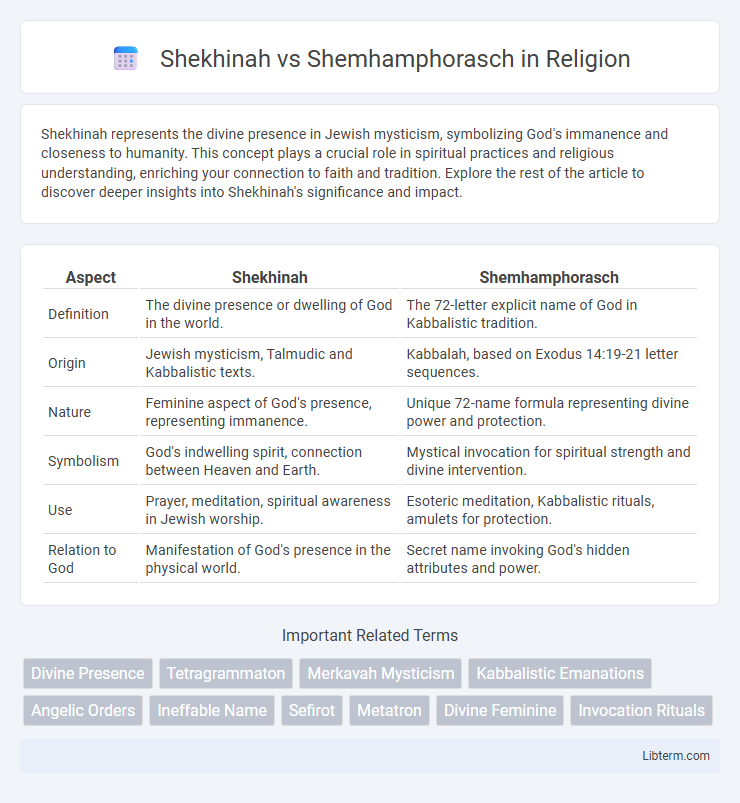
| Aspect | Shekhinah | Shemhamphorasch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The divine presence or dwelling of God in the world. | The 72-letter explicit name of God in Kabbalistic tradition. |
| Origin | Jewish mysticism, Talmudic and Kabbalistic texts. | Kabbalah, based on Exodus 14:19-21 letter sequences. |
| Nature | Feminine aspect of God's presence, representing immanence. | Unique 72-name formula representing divine power and protection. |
| Symbolism | God's indwelling spirit, connection between Heaven and Earth. | Mystical invocation for spiritual strength and divine intervention. |
| Use | Prayer, meditation, spiritual awareness in Jewish worship. | Esoteric meditation, Kabbalistic rituals, amulets for protection. |
| Relation to God | Manifestation of God's presence in the physical world. | Secret name invoking God's hidden attributes and power. |
Introduction: Unveiling Shekhinah and Shemhamphorasch
Shekhinah represents the divine feminine presence and dwelling of God in Jewish mysticism, symbolizing God's immanence within the world. Shemhamphorasch refers to the explicit 72-letter name of God derived from three sequential verses in Exodus, believed to hold immense mystical power in Kabbalistic traditions. Exploring Shekhinah alongside Shemhamphorasch reveals profound aspects of divine manifestation and spiritual connection in Jewish esotericism.
Etymology and Linguistic Origins
Shekhinah derives from the Hebrew root "SHKHn" (sh-kh-n), meaning "to dwell" or "to abide," signifying the divine presence dwelling among people in Jewish mysticism. Shemhamphorasch, stemming from the Hebrew phrase "SHam hamapraSH" (shem ha-mefursal), means "the explicit name," referring to the 72-letter ineffable name of God found in Kabbalistic texts. Both terms hold profound significance in Judaic tradition but differ linguistically: Shekhinah emphasizes divine indwelling and the feminine aspect of God, while Shemhamphorasch highlights the mystical and esoteric aspect of God's hidden or explicit name.
Core Concepts: Divine Presence vs. Sacred Name
Shekhinah represents the divine presence, embodying God's immanence and dwelling within the world and the human soul. Shemhamphorasch refers to the 72-letter sacred name of God derived from biblical verses, symbolizing divine power and mystical attributes. The core distinction lies in Shekhinah emphasizing God's intimate presence, while Shemhamphorasch centers on the esoteric and potent divine name used in Kabbalistic traditions.
Historical Development in Jewish Mysticism
Shekhinah, representing the divine presence, evolved in Jewish mysticism from early biblical interpretations to Kabbalistic teachings emphasizing God's immanence and dwelling among people. The Shemhamphorasch, a 72-letter name of God derived from Exodus 14:19-21, gained prominence in medieval Kabbalah as a powerful mystical formula for invoking divine attributes and spiritual protection. Both concepts reflect the historical development of Jewish mystical thought, intertwining the experiential aspect of God's presence (Shekhinah) with esoteric knowledge embodied in the divine name (Shemhamphorasch).
Symbolic Representations and Iconography
Shekhinah symbolizes the divine feminine presence in Jewish mysticism, often represented by light, clouds, or a radiant throne, embodying purity and spiritual closeness to God. Shemhamphorasch, referring to the 72-letter Divine Name, is depicted through intricate Hebrew letter permutations and mystical seals, symbolizing divine power and mystical knowledge. Iconography of Shekhinah emphasizes nurturing and immanence, while Shemhamphorasch emphasizes esoteric authority and spiritual mastery.
Roles in Kabbalistic Texts
Shekhinah represents the divine feminine presence and immanence within Kabbalistic texts, embodying God's nurturing and indwelling aspect. Shemhamphorasch refers to the explicit 72-letter name of God, associated with divine power, cosmic order, and mystical invocations used by practitioners to access higher spiritual realms. While Shekhinah symbolizes closeness and manifestation of the divine in the world, Shemhamphorasch functions as a transcendental tool for spiritual elevation and mystical control over divine energies.
Ritual Usage and Spiritual Practices
Shekhinah represents the divine presence in Jewish mysticism, commonly invoked in Kabbalistic rituals to foster spiritual connection and divine illumination. In contrast, Shemhamphorasch pertains to the 72-fold name of God, utilized in ceremonial magic and meditation practices aimed at invoking specific angelic forces for protection and guidance. Both are integral to esoteric traditions, with Shekhinah emphasizing divine immanence and Shemhamphorasch focusing on structured invocation within ritual frameworks.
Interpretations by Major Scholars
Shekhinah, often interpreted as the divine presence in Jewish mysticism, is extensively analyzed by scholars such as Gershom Scholem, who emphasizes its role in Kabbalistic tradition as the feminine aspect of God. In contrast, Shemhamphorasch, identified with the 72-letter name of God in Kabbalah, is discussed by figures like Aryeh Kaplan, who explores its uses in angelology and mystical practices. Both concepts are central in esoteric Judaism, with Shekhinah representing the immanent divine presence and Shemhamphorasch symbolizing mystical power through divine names.
Impact on Modern Esoteric Traditions
Shekhinah symbolizes the divine feminine presence and is pivotal in Kabbalistic mysticism, influencing modern esoteric traditions through its emphasis on spiritual feminine energy and divine immanence. The Shemhamphorasch, representing the 72-fold name of God, plays a crucial role in ritual magic and angelology, providing practitioners with tools for divine invocation and spiritual empowerment. Together, these concepts shape contemporary esoteric practices by integrating mystical theology with practical magical applications, enriching the spiritual landscape with layers of symbolic and ritual significance.
Conclusion: Comparing Theological Significance
Shekhinah represents the divine presence and immanence of God dwelling among humanity in Jewish mysticism, emphasizing closeness and spiritual enlightenment. In contrast, Shemhamphorasch refers to the 72-letter explicit name of God, symbolizing divine power and authority in Kabbalistic traditions. The theological significance lies in Shekhinah's focus on relational experience of God's presence, while Shemhamphorasch highlights the mystical, transcendent aspects of God's hidden name and esoteric knowledge.
Shekhinah Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com