Personal faith shapes your values and guides decisions through a deeply held belief system. It influences emotional resilience, moral judgments, and overall well-being, creating a sense of purpose and connection. Explore the rest of this article to understand how personal faith can transform your life and strengthen your inner resolve.
Table of Comparison
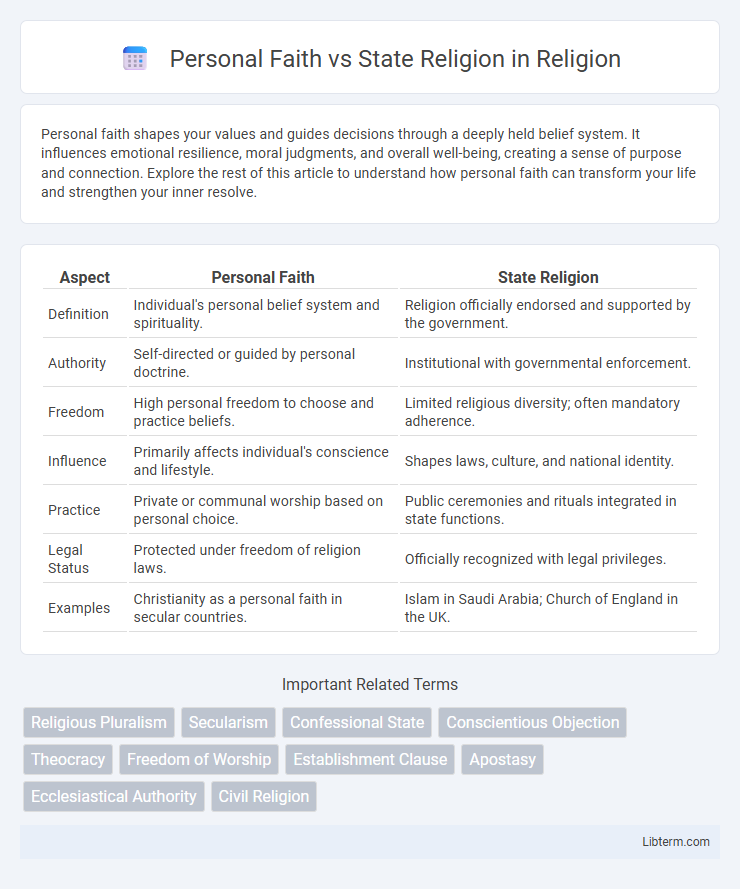
| Aspect | Personal Faith | State Religion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual's personal belief system and spirituality. | Religion officially endorsed and supported by the government. |
| Authority | Self-directed or guided by personal doctrine. | Institutional with governmental enforcement. |
| Freedom | High personal freedom to choose and practice beliefs. | Limited religious diversity; often mandatory adherence. |
| Influence | Primarily affects individual's conscience and lifestyle. | Shapes laws, culture, and national identity. |
| Practice | Private or communal worship based on personal choice. | Public ceremonies and rituals integrated in state functions. |
| Legal Status | Protected under freedom of religion laws. | Officially recognized with legal privileges. |
| Examples | Christianity as a personal faith in secular countries. | Islam in Saudi Arabia; Church of England in the UK. |
Defining Personal Faith and State Religion
Personal faith represents an individual's spiritual beliefs and practices guided by personal convictions and experiences, independent of institutional authority. State religion refers to an officially endorsed or established religion recognized by a government, often influencing public policy and national identity. The distinction lies in personal faith being private and autonomous, while state religion integrates spirituality with political and social frameworks.
Historical Roots of State Religions
State religions often have historical roots deeply intertwined with the consolidation of political power and cultural identity, such as the establishment of Christianity as the state religion in the Roman Empire under Emperor Constantine in the 4th century. These religions historically served to unify diverse populations, legitimize rulers, and integrate religious authority with state governance, influencing legal and social frameworks. In contrast, personal faith emphasizes individual belief and spiritual experience, often resisting institutional control and allowing for religious pluralism beyond state-imposed doctrines.
The Growth of Individual Religious Expression
The growth of individual religious expression challenges the dominance of state religion by fostering personal faith practices beyond official doctrines. Digital platforms and global communication empower believers to explore diverse spiritual paths, creating vibrant, decentralized faith communities. This shift enhances religious pluralism and encourages freedom of conscience within societies traditionally dominated by uniform religious authority.
Legal Frameworks: Freedom of Religion
Legal frameworks surrounding freedom of religion vary significantly, balancing personal faith and state religion influences based on constitutional protections and international human rights standards. Countries with secular constitutions often enshrine the right to worship freely without state interference, while nations with designated state religions may impose restrictions or preferences affecting minority religious groups. Judicial interpretations and legislation continually shape how freedom of religion is upheld, ensuring personal faith practices are protected against discrimination and coercion.
Tensions Between Personal Belief and Institutional Doctrine
Tensions between personal faith and state religion often arise from conflicts between individual beliefs and official doctrines imposed by religious institutions intertwined with government power. These conflicts can lead to social marginalization, legal restrictions, or persecution of minorities who diverge from sanctioned religious norms, highlighting challenges in maintaining religious freedom. The dynamic interplay between personal conscience and institutional authority remains a critical issue in pluralistic societies striving for both unity and diversity.
Social Impacts of State-Endorsed Religion
State-endorsed religion often shapes societal norms and can marginalize minority faiths, affecting social cohesion and individual freedoms. Institutional favoritism impacts education, legal systems, and political representation, leading to potential social divisions and reduced pluralism. The intersection of religion and state power influences citizens' identity and community dynamics, often provoking debates over inclusivity and secular governance.
The Role of Conscience in Faith Decisions
Conscience serves as the fundamental guide in personal faith decisions, allowing individuals to interpret religious beliefs independently from state-imposed doctrines. Historical and contemporary cases demonstrate how protecting conscience rights fosters religious freedom and prevents the coercion of personal beliefs by government authorities. Legal frameworks, such as constitutional guarantees and international human rights laws, emphasize the importance of conscience in maintaining a clear distinction between personal faith and official state religion.
Case Studies: Personal Faith Challenging the State
In numerous case studies, individuals have demonstrated how personal faith can directly challenge the authority of state-imposed religions, often leading to legal and social conflicts. Notable examples include the refusal of conscientious objection in countries with mandatory religious practices and the rise of underground religious movements in authoritarian regimes enforcing state religion. These instances highlight the tension between personal spiritual autonomy and governmental control, emphasizing the ongoing struggle for religious freedom in diverse political contexts.
Balancing Diversity in Pluralistic Societies
Balancing personal faith with state religion in pluralistic societies requires policies that protect individual religious freedoms while maintaining social cohesion. Legal frameworks should ensure equal rights for all faiths, preventing dominance by any single religion and fostering mutual respect among diverse communities. Effective dialogue and inclusive governance promote harmony, preventing religious conflicts and supporting multicultural integration.
The Future of Personal Faith Amid State Influence
Personal faith faces evolving challenges as state religions increasingly seek to consolidate influence through legal frameworks and public policies, potentially restricting individual spiritual expression. Demographic shifts and digital platforms empower diverse religious identities to flourish, complicating monolithic state narratives. Emerging trends suggest a nuanced coexistence where personal faith adapts through hybrid practices, resilience in private spheres, and advocacy for religious freedom amid state-imposed uniformity.
Personal Faith Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com