Bhakti represents a deep devotion and love towards a personal deity, forming the core of many spiritual traditions. This path emphasizes surrender, prayer, and loving service as means to attain spiritual fulfillment and inner peace. Discover how Bhakti can transform your spiritual journey by exploring the rich practices and teachings detailed in this article.
Table of Comparison
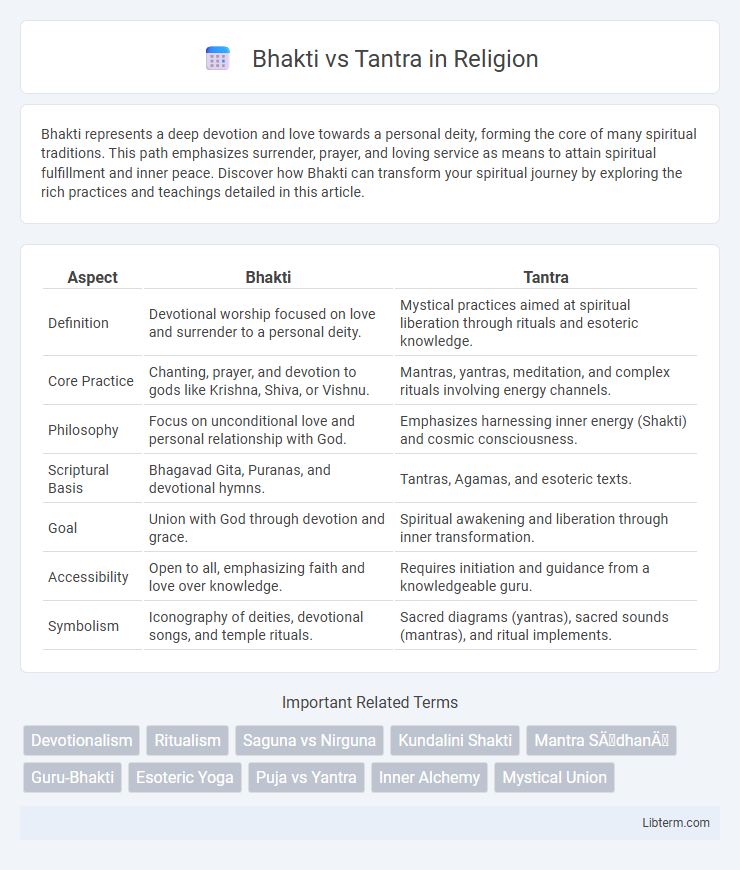
| Aspect | Bhakti | Tantra |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Devotional worship focused on love and surrender to a personal deity. | Mystical practices aimed at spiritual liberation through rituals and esoteric knowledge. |
| Core Practice | Chanting, prayer, and devotion to gods like Krishna, Shiva, or Vishnu. | Mantras, yantras, meditation, and complex rituals involving energy channels. |
| Philosophy | Focus on unconditional love and personal relationship with God. | Emphasizes harnessing inner energy (Shakti) and cosmic consciousness. |
| Scriptural Basis | Bhagavad Gita, Puranas, and devotional hymns. | Tantras, Agamas, and esoteric texts. |
| Goal | Union with God through devotion and grace. | Spiritual awakening and liberation through inner transformation. |
| Accessibility | Open to all, emphasizing faith and love over knowledge. | Requires initiation and guidance from a knowledgeable guru. |
| Symbolism | Iconography of deities, devotional songs, and temple rituals. | Sacred diagrams (yantras), sacred sounds (mantras), and ritual implements. |
Understanding Bhakti: The Path of Devotion
Bhakti, the path of devotion, centers on a deeply emotional and personal relationship between the devotee and the divine, emphasizing love, surrender, and constant remembrance of God. It promotes practices such as prayer, chanting, and ritual worship to cultivate spiritual connection and inner transformation. Unlike Tantra, which involves esoteric rituals and energy manipulations, Bhakti focuses on simplicity and heartfelt devotion as a means to attain liberation and divine grace.
Exploring Tantra: The Science of Ritual and Energy
Tantra is an ancient spiritual science emphasizing ritual practices and the harnessing of subtle energies within the body to achieve higher states of consciousness. Rooted in esoteric traditions, Tantra utilizes mantras, mudras, yantras, and meditation techniques to awaken kundalini energy and balance the chakras for holistic transformation. Unlike Bhakti, which centers on devotional love and surrender, Tantra systematically explores the energetic anatomy and ritual precision to transcend ordinary perception.
Historical Roots: Origins of Bhakti and Tantra
Bhakti originated in ancient India as a devotional movement rooted in the Vedic tradition, emphasizing personal devotion to deities like Vishnu and Shiva through prayer, chanting, and ritual worship. Tantra emerged around the same period, blending indigenous tribal practices with Vedic and Buddhist elements, focusing on esoteric rituals, meditation, and symbolic worship to harness spiritual energy. Both traditions share origins in early Indian religious culture but differ in their approaches; Bhakti centers on loving devotion, while Tantra emphasizes transformative practices and mystical experience.
Fundamental Philosophies: Core Beliefs Compared
Bhakti centers on devotion and love towards a personal deity, emphasizing surrender, emotional connection, and worship as paths to spiritual liberation. Tantra incorporates complex rituals, meditation, and esoteric practices aimed at transcending duality and harnessing universal energies for spiritual awakening. Both philosophies seek moksha but differ fundamentally: Bhakti relies on heartfelt devotion while Tantra engages transformative techniques to unite the practitioner with cosmic consciousness.
Practices and Techniques: Mantras, Meditation, and More
Bhakti emphasizes devotion through singing bhajans, chanting mantras like the Hare Krishna, and engaging in rituals to foster a personal connection with the divine. Tantra incorporates complex mantras, meditation techniques such as visualization and breath control, and ritualistic practices aimed at harnessing spiritual energy and attaining enlightenment. Both traditions use mantras and meditation but differ in purpose: Bhakti seeks emotional devotion, while Tantra focuses on transformational spiritual power.
The Experience of the Divine: Personal vs. Universal
Bhakti emphasizes a personal experience of the divine through devotional love and intimate connection with a specific deity, fostering emotional closeness and heartfelt surrender. Tantra, however, promotes a universal experience of the divine by recognizing the sacred in all aspects of existence, integrating physical, spiritual, and cosmic elements to transcend individual identity. This contrast reflects Bhakti's focus on personal devotion versus Tantra's goal of realizing the divine as an all-encompassing, infinite reality.
God and the Self: Approaches to Spiritual Union
Bhakti emphasizes devotion and surrender to a personal God, fostering a loving relationship that dissolves the ego and unites the self with the divine through heartfelt worship and grace. Tantra explores the union of God and the Self by activating inner energies and chakras, using rituals and meditative practices to transcend duality and realize non-dual awareness. Both paths seek spiritual union but diverge in approach--Bhakti through emotional devotion and Tantra through experiential transformation of consciousness.
Social and Cultural Influence: Impact on Society
Bhakti movement emphasized personal devotion to deities, fostering social inclusivity by breaking caste barriers and promoting vernacular languages, which enhanced cultural unity across diverse communities. Tantra practices, often esoteric and ritualistic, influenced elite spiritual circles and regional art forms, embedding complex symbolism in temple architecture and performance arts. Both Bhakti and Tantra shaped Indian society by offering distinct pathways to spirituality, influencing social norms, cultural expressions, and collective religious identity.
Misconceptions and Modern Interpretations
Bhakti is often misconceived solely as devotional worship limited to rituals, while Tantra is wrongly associated with dark magic or taboo practices, obscuring their true spiritual depth. Modern interpretations emphasize Bhakti's role in expressing unconditional love and surrender to the divine, and Tantra's use of symbolic rituals and meditative techniques aimed at personal transformation and spiritual awakening. Both traditions complement each other by integrating emotional devotion with esoteric practice, challenging outdated stereotypes and enriching contemporary spiritual paths.
Choosing Your Spiritual Path: Bhakti or Tantra?
Choosing your spiritual path involves understanding the core differences between Bhakti and Tantra traditions. Bhakti emphasizes devotion and surrender to a personal deity, fostering a relationship based on love and faith, while Tantra focuses on harnessing spiritual energy through rituals, meditation, and esoteric practices to achieve liberation. Both paths offer unique methods for spiritual growth, and the choice depends on whether one resonates more with emotional devotion or experiential transformation through mystical disciplines.
Bhakti Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com