Christianity is a monotheistic religion centered on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, emphasizing salvation, love, and forgiveness. Its rich traditions and diverse denominations shape cultures and moral values worldwide. Discover how Christianity influences your life and society by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
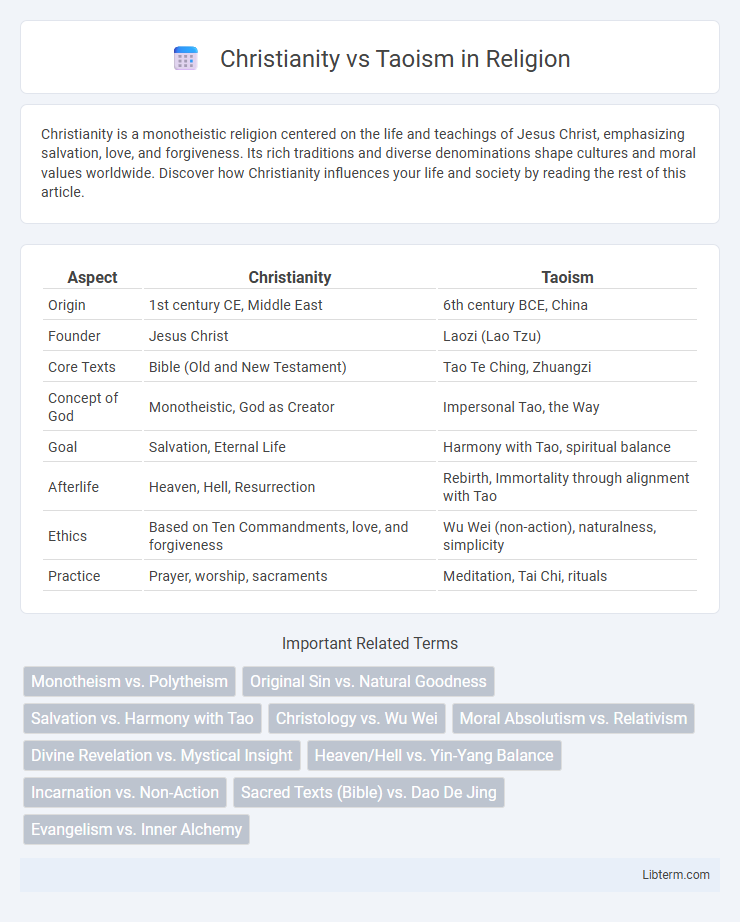
| Aspect | Christianity | Taoism |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | 1st century CE, Middle East | 6th century BCE, China |
| Founder | Jesus Christ | Laozi (Lao Tzu) |
| Core Texts | Bible (Old and New Testament) | Tao Te Ching, Zhuangzi |
| Concept of God | Monotheistic, God as Creator | Impersonal Tao, the Way |
| Goal | Salvation, Eternal Life | Harmony with Tao, spiritual balance |
| Afterlife | Heaven, Hell, Resurrection | Rebirth, Immortality through alignment with Tao |
| Ethics | Based on Ten Commandments, love, and forgiveness | Wu Wei (non-action), naturalness, simplicity |
| Practice | Prayer, worship, sacraments | Meditation, Tai Chi, rituals |
Introduction to Christianity and Taoism
Christianity centers on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ, emphasizing salvation through faith, the Bible as sacred scripture, and the belief in one God. Taoism, originating in ancient China with foundational texts like the Tao Te Ching by Laozi, focuses on living harmoniously with the Tao, or the fundamental nature of the universe, highlighting principles such as simplicity, spontaneity, and balance. Both religions offer distinct worldviews: Christianity prioritizes a personal relationship with God and moral commandments, while Taoism emphasizes natural order and effortless action (wu wei).
Historical Backgrounds of Both Religions
Christianity originated in the 1st century CE in the Roman province of Judea, rooted in the teachings of Jesus of Nazareth and shaped by Jewish traditions and Greco-Roman culture. Taoism, emerging in the 4th century BCE in ancient China, is based on the philosophical ideas attributed to Laozi and the foundational text Tao Te Ching, emphasizing harmony with the Tao, or the natural way. Both religions significantly influenced their respective cultures: Christianity shaped Western civilization through its doctrines and institutions, while Taoism profoundly impacted Chinese philosophy, religion, medicine, and art.
Core Beliefs: God vs The Tao
Christianity centers on the belief in one omnipotent, personal God who creates, governs, and interacts with the universe, emphasizing salvation through Jesus Christ. Taoism centers on the Tao, an impersonal, ineffable force representing the natural order and underlying essence of all existence, guiding harmony and balance without anthropomorphic attributes. The core difference lies in Christianity's focus on a distinct, personal deity versus Taoism's emphasis on an abstract, spontaneous principle governing life.
Foundational Texts: Bible and Tao Te Ching
The Bible, central to Christianity, comprises the Old and New Testaments, offering historical narratives, laws, prophecies, and teachings about salvation through Jesus Christ. Taoism's foundational text, the Tao Te Ching by Laozi, emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao, focusing on simplicity, humility, and naturalness. While the Bible presents a linear divine plan centered on a personal God, the Tao Te Ching explores an impersonal, continuous flow underlying existence without formal doctrines.
Creation, Existence, and Cosmology
Christianity teaches that God created the universe ex nihilo, with a purposeful order reflecting divine intention and moral design. Taoism views creation as an ongoing, spontaneous process arising from the Tao, an infinite and ineffable source that sustains natural harmony and balance. While Christianity posits a linear cosmology culminating in divine judgment, Taoist cosmology emphasizes cyclical patterns and the interdependence of all phenomena within the cosmos.
Concepts of Salvation and Enlightenment
Christianity centers on salvation through faith in Jesus Christ, emphasizing repentance, grace, and eternal life with God. Taoism focuses on enlightenment by aligning with the Tao, the natural way of the universe, seeking harmony, balance, and inner peace. While Christianity promises spiritual redemption and resurrection, Taoism pursues wisdom and transformation through meditation and living in accordance with nature.
Moral Teachings and Ethical Guidance
Christianity emphasizes the Ten Commandments and Jesus' teachings on love, forgiveness, and compassion as core moral principles guiding ethical behavior. Taoism promotes living in harmony with the Tao through virtues such as humility, simplicity, and non-action (wu wei), encouraging natural spontaneity and balance in moral decisions. Both traditions offer profound ethical frameworks, with Christianity focusing on divine commandments and Taoism on alignment with the natural order.
Rituals, Practices, and Worship
Christianity centers its rituals on sacraments such as baptism and communion, with worship typically conducted in churches involving prayers, hymns, and sermons. Taoism emphasizes natural harmony through practices like Tai Chi, meditation, and offerings at temples, focusing on aligning with the Tao through simplicity and spontaneity. Both religions employ rituals to foster spiritual connection, yet Christianity prioritizes communal worship and divine grace, whereas Taoism values individual balance and universal flow.
Afterlife: Heaven, Hell, and Immortality
Christianity teaches that after death, souls face judgment leading to eternal destinations of Heaven or Hell based on faith and moral conduct, with Heaven offering eternal communion with God and Hell serving as eternal separation from Him. Taoism emphasizes harmony with the Tao, viewing the afterlife less as a binary judgment and more as a transformation or continuation in alignment with the natural flow of life and death, often highlighting spiritual immortality through balance and inner cultivation. This contrast reflects Christianity's focus on moral accountability and eternal reward or punishment, while Taoism prioritizes spiritual harmony and unity with the universe beyond physical death.
Christianity and Taoism in the Modern World
Christianity in the modern world emphasizes global missionary work, social justice, and adaptation to contemporary cultural contexts, with over 2.3 billion adherents influencing politics, education, and humanitarian efforts. Taoism, while less widespread with roughly 12 million followers, continues to shape modern spiritual practices through its principles of harmony, balance, and natural living, impacting areas like traditional Chinese medicine and mindfulness. Both religions face challenges of modernization while contributing uniquely to global discussions on ethics, environmentalism, and personal well-being.
Christianity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com