Halakha, the collective body of Jewish religious laws derived from the Written and Oral Torah, governs daily life, rituals, and ethical conduct. It provides detailed guidance on prayer, dietary rules, Sabbath observance, and interpersonal relationships, shaping the spiritual and communal life of observant Jews. Explore this article to deepen your understanding of Halakha's impact on faith and practice.
Table of Comparison
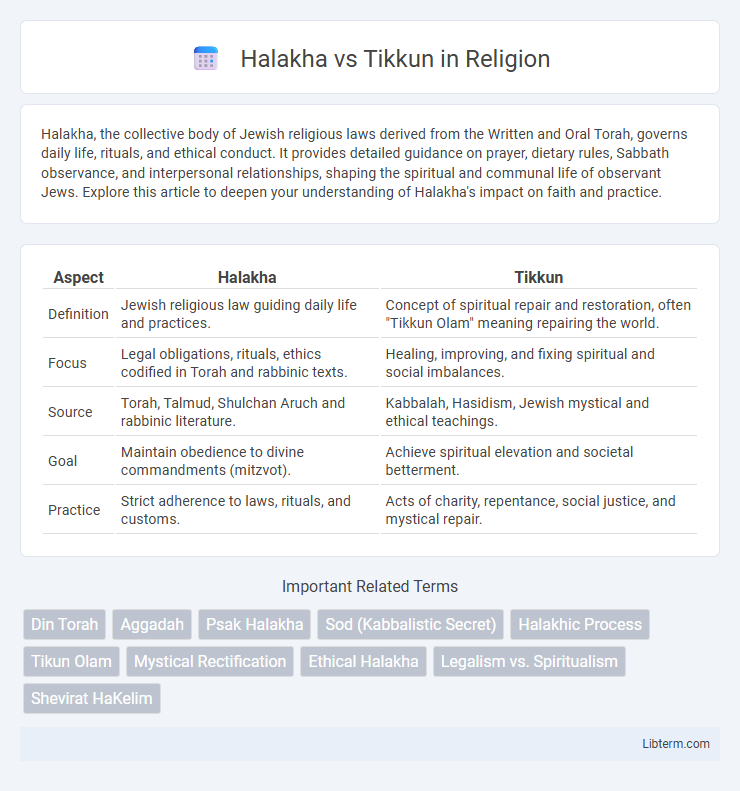
| Aspect | Halakha | Tikkun |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Jewish religious law guiding daily life and practices. | Concept of spiritual repair and restoration, often "Tikkun Olam" meaning repairing the world. |
| Focus | Legal obligations, rituals, ethics codified in Torah and rabbinic texts. | Healing, improving, and fixing spiritual and social imbalances. |
| Source | Torah, Talmud, Shulchan Aruch and rabbinic literature. | Kabbalah, Hasidism, Jewish mystical and ethical teachings. |
| Goal | Maintain obedience to divine commandments (mitzvot). | Achieve spiritual elevation and societal betterment. |
| Practice | Strict adherence to laws, rituals, and customs. | Acts of charity, repentance, social justice, and mystical repair. |
Introduction to Halakha and Tikkun
Halakha refers to the collective body of Jewish religious laws derived from the Written and Oral Torah, guiding daily conduct, rituals, and ethical behavior. Tikkun, often associated with Tikkun Olam, emphasizes spiritual repair and social justice, aiming to improve the world through righteous actions and communal responsibility. While Halakha provides a structured legal framework, Tikkun focuses on transformative healing and moral rectification within and beyond the Jewish tradition.
Defining Halakha: Jewish Law and Practice
Halakha, the comprehensive body of Jewish law, encompasses religious commandments, ethical guidelines, and ritual practices derived from the Torah, Talmud, and rabbinic interpretations. It governs daily life, including dietary regulations, Sabbath observance, and civil law, ensuring continuity and communal identity within Judaism. The interpretative nature of Halakha allows for adaptation while maintaining fidelity to traditional Jewish legal principles.
Understanding Tikkun: The Concept of Repair
Tikkun, rooted in Jewish mysticism, emphasizes the spiritual and ethical repair of the world, contrasting with Halakha's focus on legal compliance and ritual observance. It involves rectifying moral flaws and restoring harmony within oneself and the community, promoting holistic healing beyond mere law adherence. Understanding Tikkun reveals its role in fostering transformation through introspection and social responsibility.
Historical Origins of Halakha and Tikkun
Halakha, rooted in the Torah and Talmudic law, emerged during the Second Temple period as a comprehensive legal framework guiding Jewish religious practice and ethics. Tikkun, derived from the Kabbalistic tradition, particularly the teachings of Rabbi Isaac Luria in the 16th century, emphasizes spiritual repair and cosmic restoration. The historical divergence highlights Halakha's legalistic foundations contrasted with Tikkun's mystical focus on rectifying both individual soul and universal order.
Philosophical Differences: Law vs Transformation
Halakha emphasizes adherence to established Jewish law as a framework for ethical behavior and communal order, focusing on obedience to commandments and legal precision. Tikkun centers on spiritual and personal transformation, promoting repair and improvement of both the self and the world through ethical action and mystical insight. The philosophical divergence lies in Halakha's foundation on legal obligation versus Tikkun's emphasis on ongoing spiritual growth and societal healing.
Halakha’s Role in Daily Jewish Life
Halakha serves as the comprehensive legal framework guiding everyday behavior, religious rituals, and ethical decisions within Jewish life. It encompasses commandments derived from the Torah, Talmud, and rabbinic interpretations, shaping aspects such as dietary laws, prayer routines, and social justice. This structured system ensures continuity and community cohesion, balancing individual actions with collective spiritual obligations.
Tikkun Olam: Repairing the World in Judaism
Tikkun Olam, a central concept in Judaism, emphasizes social justice and the ethical responsibility to repair the world through acts of kindness and justice. Unlike Halakha, which governs religious law and ritual observance, Tikkun Olam focuses on practical efforts to improve society and promote peace. This principle inspires initiatives in charity, environmental stewardship, and community service as vital expressions of Jewish values.
Points of Tension: Legalism and Activism
Halakha emphasizes strict adherence to Jewish law, prioritizing legalism and ritual accuracy, often resisting changes not rooted in traditional texts. Tikkun, rooted in the concept of "repair," focuses on activism and social justice, advocating for transformative action to address contemporary ethical issues. The tension arises as Halakha upholds preserved legal frameworks, while Tikkun pushes for evolving interpretations to meet modern societal needs.
Contemporary Debates: Halakha and Tikkun Today
Contemporary debates on Halakha and Tikkun center on balancing traditional Jewish law with evolving social and ethical imperatives. Halakha, as the codified system of Jewish jurisprudence, often faces scrutiny for its adaptability to modern contexts, while Tikkun, emphasizing repair of the world, drives progressive interpretations that advocate social justice and inclusivity. This dynamic tension influences discourse in religious communities, guiding how Jewish law is practiced and reinterpreted in response to contemporary moral challenges.
Harmonizing Halakha and Tikkun: A Path Forward
Harmonizing Halakha and Tikkun represents a dynamic approach within Jewish thought, emphasizing the integration of traditional legal frameworks with the ethical imperative of repair (Tikkun). This synthesis encourages applying Halakha not only as a static legal code but as a living guide to enact social justice, spiritual growth, and communal healing. The path forward lies in interpreting Halakha through the lens of Tikkun, fostering a Judaism that balances rigorous observance with transformative action.
Halakha Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com