Catholicism is a major branch of Christianity centered on the teachings of Jesus Christ and guided by the authority of the Pope and the Roman Catholic Church. It emphasizes the sacraments, including the Eucharist, baptism, and confession, as essential to spiritual life and salvation. Discover more about Catholicism's rich traditions, beliefs, and practices in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
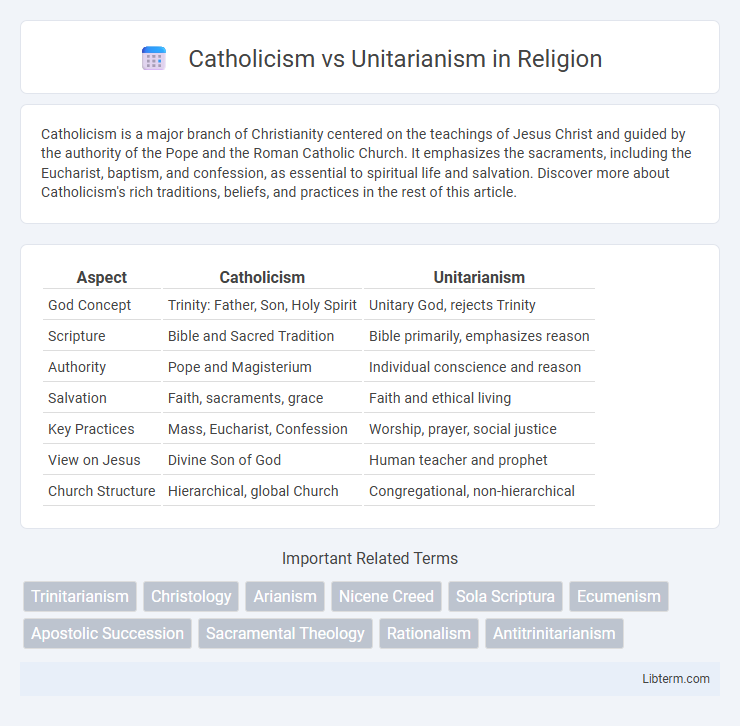
| Aspect | Catholicism | Unitarianism |
|---|---|---|
| God Concept | Trinity: Father, Son, Holy Spirit | Unitary God, rejects Trinity |
| Scripture | Bible and Sacred Tradition | Bible primarily, emphasizes reason |
| Authority | Pope and Magisterium | Individual conscience and reason |
| Salvation | Faith, sacraments, grace | Faith and ethical living |
| Key Practices | Mass, Eucharist, Confession | Worship, prayer, social justice |
| View on Jesus | Divine Son of God | Human teacher and prophet |
| Church Structure | Hierarchical, global Church | Congregational, non-hierarchical |
Origins and Historical Development
Catholicism originated in the 1st century AD, rooted in the teachings of Jesus Christ and the apostolic tradition, becoming the largest Christian denomination through its establishment of the Roman Catholic Church and the papacy. Unitarianism emerged in the 16th century during the Protestant Reformation, emphasizing the oneness of God and rejecting the Trinity, gaining prominence through figures like Michael Servetus and its development in Transylvania and later in England and America. The historical development of Catholicism centers on doctrinal consolidation, ecumenical councils, and missionary expansion, whereas Unitarianism evolved as a liberal theological movement focusing on rationalism and individual conscience.
Core Doctrinal Differences
Catholicism upholds the doctrine of the Trinity, affirming one God in three persons: Father, Son, and Holy Spirit, while Unitarianism rejects the Trinity, emphasizing the unity of God as a single person. Catholics believe in the divinity of Jesus Christ, His sacrificial atonement, and the authority of Church tradition alongside Scripture, whereas Unitarians view Jesus primarily as a moral teacher and often rely solely on the Bible for doctrine. The Catholic Church practices sacraments such as the Eucharist and Baptism as means of grace, which Unitarians typically interpret symbolically rather than sacramentally.
Concepts of God and the Trinity
Catholicism affirms the doctrine of the Trinity, teaching that God exists as three coequal and coeternal persons: the Father, the Son (Jesus Christ), and the Holy Spirit, united in one divine essence. Unitarianism, in contrast, rejects the Trinity, emphasizing the oneness of God as a single person and typically views Jesus as a distinct, subordinate being or moral teacher rather than divine. This fundamental difference in understanding God's nature shapes the theological frameworks and worship practices within each tradition.
Authority: Scripture and Tradition
Catholicism upholds both Scripture and Tradition as authoritative, with the Magisterium interpreting their combined truth, while Unitarianism prioritizes Scripture alone as the sole authority for faith and practice. The Catholic Church teaches that Sacred Tradition, alongside Sacred Scripture, is divinely inspired and essential for understanding God's revelation, whereas Unitarianism rejects such Tradition as secondary or non-binding. This fundamental difference shapes how each approaches doctrine, worship, and theological interpretation within their respective communities.
Worship Practices and Rituals
Catholicism emphasizes the Eucharist as the central act of worship, with rituals including the Mass, confession, and the veneration of saints and sacraments such as baptism and confirmation. Unitarianism practices are generally simpler, focusing on congregational worship, prayer, and scripture reading without traditional sacraments or rituals. Catholic rituals are highly structured and sacramental, while Unitarian worship centers on personal spiritual growth and reason-based faith.
Salvation and the Role of Grace
Catholicism teaches that salvation is attained through faith, good works, and the sacraments, emphasizing the essential role of divine grace bestowed by the Church. Unitarianism emphasizes salvation through individual reason, moral living, and personal spiritual growth, often rejecting original sin and the need for sacramental grace. Grace in Catholicism is seen as a supernatural gift from God, while Unitarians typically view grace more metaphorically as inspiration or inner guidance.
The Role of Church Leadership
Catholicism emphasizes a hierarchical church leadership with the Pope as the supreme spiritual authority, followed by cardinals, bishops, and priests who oversee doctrinal unity and sacramental administration. Unitarianism adopts a more decentralized leadership structure, often congregational, with ministers and lay members sharing authority and decision-making responsibilities. This fundamental difference shapes their approaches to religious authority, governance, and community engagement within each tradition.
Moral Teachings and Ethical Perspectives
Catholicism emphasizes moral teachings rooted in natural law, divine revelation, and Church tradition, advocating for the sanctity of life, social justice, and adherence to the Ten Commandments. Unitarianism promotes ethical perspectives centered on individual conscience, reason, and universal human dignity, often encouraging social reform, tolerance, and personal responsibility. Both frameworks seek moral integrity but differ in authoritative sources and doctrinal rigidity.
Interfaith Relations and Ecumenism
Catholicism emphasizes ecumenism through the Vatican II Council, promoting dialogue and unity among Christian denominations, including efforts to reconcile doctrinal differences with Protestant and Orthodox churches. Unitarianism, known for its liberal theology and inclusivist approach, actively engages in interfaith relations by fostering mutual respect and cooperation across diverse religious traditions. Both traditions contribute uniquely to interfaith harmony, with Catholicism focusing on doctrinal unity and Unitarianism prioritizing religious pluralism.
Contemporary Influence and Global Reach
Catholicism, with over 1.3 billion adherents worldwide, maintains a significant contemporary influence through the Vatican's diplomatic presence and extensive social services, shaping global culture, education, and politics. Unitarianism, representing a smaller yet impactful community, emphasizes individual spiritual freedom and social justice, particularly resonating in North America and parts of Europe. The global reach of Catholicism is marked by its historical institutions and missionary work, whereas Unitarianism's influence is more localized, thriving in progressive religious circles and interfaith dialogues.
Catholicism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com