Upaveda, the ancient subsidiary knowledge systems rooted in the Vedas, encompass Ayurveda (traditional medicine), Dhanurveda (martial arts), Gandharvaveda (music and arts), and Sthapatyaveda (architecture). These texts serve as specialized manuals enhancing holistic living, health, and cultural practices in Vedic tradition. Discover how Upaveda can enrich your understanding of ancient wisdom by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
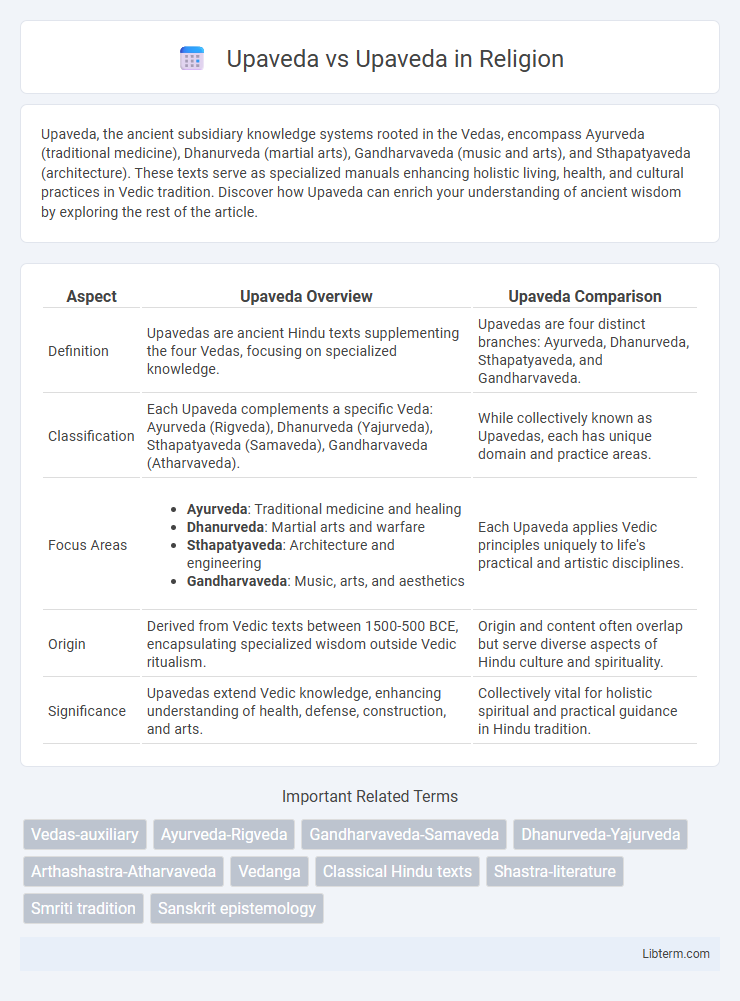
| Aspect | Upaveda Overview | Upaveda Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Upavedas are ancient Hindu texts supplementing the four Vedas, focusing on specialized knowledge. | Upavedas are four distinct branches: Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Sthapatyaveda, and Gandharvaveda. |
| Classification | Each Upaveda complements a specific Veda: Ayurveda (Rigveda), Dhanurveda (Yajurveda), Sthapatyaveda (Samaveda), Gandharvaveda (Atharvaveda). | While collectively known as Upavedas, each has unique domain and practice areas. |
| Focus Areas |
|
Each Upaveda applies Vedic principles uniquely to life's practical and artistic disciplines. |
| Origin | Derived from Vedic texts between 1500-500 BCE, encapsulating specialized wisdom outside Vedic ritualism. | Origin and content often overlap but serve diverse aspects of Hindu culture and spirituality. |
| Significance | Upavedas extend Vedic knowledge, enhancing understanding of health, defense, construction, and arts. | Collectively vital for holistic spiritual and practical guidance in Hindu tradition. |
Introduction to Upavedas
Upavedas are ancient Indian texts that supplement the Vedas by focusing on specialized branches of knowledge such as Ayurveda (medicine), Dhanurveda (martial arts), Gandharvaveda (music and arts), and Sthapatyaveda (architecture). Each Upaveda serves as a practical guide, providing detailed insights into its respective field while maintaining a spiritual foundation rooted in Vedic principles. The study of Upavedas enhances holistic understanding of traditional Indian sciences and their integration with Vedic wisdom.
Origin and Historical Background of Upavedas
The Upavedas are auxiliary texts linked to the four Vedas, each specializing in a different domain: Ayurveda (medicine) connected to the Atharvaveda, Dhanurveda (martial arts) tied to the Yajurveda, Gandharvaveda (music and arts) related to the Samaveda, and Arthaveda or Arthasastra (economics and politics) associated with the Rigveda. Originating during the Vedic period, these texts expanded Vedic knowledge by applying philosophical concepts to practical disciplines, reflecting the ancient Indian emphasis on a holistic approach to life. Historically, the Upavedas evolved through oral traditions, eventually being codified in classical Sanskrit literature between 1000 BCE and 500 CE, serving as foundational treatises in their respective fields.
Classification of Upavedas in Vedic Literature
The Upavedas, considered auxiliary texts to the Vedas, are traditionally classified into four distinct branches: Ayurveda for medicine, Dhanurveda for martial arts, Gandharvaveda for music and arts, and Sthapathyaveda for architecture and engineering. Each Upaveda complements the Rigveda, Yajurveda, Samaveda, and Atharvaveda, respectively, serving specialized practical knowledge aligned with Vedic principles. This classification highlights the integrative approach of Vedic literature, combining spiritual teachings with applied sciences to support holistic human development.
Different Types of Upavedas: An Overview
The four principal Upavedas include Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Arthaveda, each focusing on specialized knowledge areas. Ayurveda emphasizes traditional medicine and healing practices, while Dhanurveda deals with warfare, archery, and martial arts techniques. Gandharvaveda centers on music, arts, and aesthetics, and Arthaveda explores economics, politics, and statecraft, highlighting diverse applications of Upavedic wisdom.
Upaveda vs Upaveda: Exploring the Terminological Confusion
Upaveda refers to the traditional ancillary branches of the Vedas, typically including Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Sthapatyaveda, each representing specialized knowledge in medicine, warfare, music, and architecture respectively. The terminological confusion arises when "Upaveda" is interchangeably used to denote both the collective specialties and individual disciplines, leading to ambiguity in scholarly and practical contexts. Clarifying the distinction between the plural form (collective Upavedas) and singular references (specific Upaveda) is essential for accurate understanding of Vedic literature and associated knowledge systems.
Major Upavedas and Their Associations with Each Veda
The four Major Upavedas are Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Shilpayoga, each intricately linked to one of the four Vedas, serving as specialized branches of Vedic knowledge. Ayurveda is associated with the Rigveda, focusing on medical science and holistic health, while Dhanurveda corresponds to the Yajurveda, emphasizing warfare and martial arts. Gandharvaveda relates to the Samaveda, encompassing music and aesthetics, and Shilpayoga is connected to the Atharvaveda, highlighting sculpture, architecture, and craftsmanship.
Core Subjects Covered by Each Upaveda
The classical Upavedas consist of four distinct branches, each linked to a primary Veda and focusing on specialized knowledge: Ayurveda (associated with the Rigveda) emphasizes medical sciences and holistic health practices; Dhanurveda (linked to the Yajurveda) centers on martial arts, weapons training, and military strategy; Gandharvaveda (connected to the Samaveda) concentrates on music, dance, and performing arts; and Arthaveda or Arthashastra (related to the Atharvaveda) deals with economics, politics, governance, and statecraft. Each Upaveda integrates its core subjects with the spiritual and philosophical teachings of its respective primary Veda, reflecting a comprehensive ancient knowledge system. The distinctions in subject matter illustrate the complementary roles these disciplines played in sustaining societal, physical, cultural, and administrative well-being.
Comparative Analysis: Functions and Scope of Each Upaveda
The four Upavedas--Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Shilpa Shastra--each serve distinct functions: Ayurveda focuses on health and medicine, Dhanurveda on warfare and martial skills, Gandharvaveda on music and performing arts, while Shilpa Shastra covers architecture and craftsmanship. Their scope varies from internal wellbeing and physical combat techniques to cultural expressions and structural design, reflecting a comprehensive approach to knowledge in ancient Indian traditions. This comparative analysis highlights how each Upaveda complements the others, collectively enriching Vedic literature and practical applications.
Influence of Upavedas on Ancient Indian Knowledge Systems
Upavedas, comprising Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Arthaveda, significantly shaped ancient Indian knowledge systems by integrating practical disciplines with the Vedic corpus, enhancing medicine, warfare, music, and economics respectively. These specialized texts supplemented the primary Vedas, promoting holistic understanding and application of metaphysical concepts in daily life and societal governance. Their influence extended beyond ritualistic practices to form foundational frameworks for health sciences, martial arts, performing arts, and statecraft in ancient India.
Conclusion: Significance of Understanding Upaveda Distinctions
Understanding the distinctions among the Upavedas--Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Arthaveda--reveals their unique contributions to holistic knowledge in health, warfare, music, and economics. Each Upaveda complements the Vedas by specializing in practical applications that shape ancient Indian culture and philosophy. Recognizing these differences enhances appreciation for their integrated role in sustaining societal well-being and spiritual growth.
Upaveda Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com