Veda is an ancient collection of sacred texts forming the foundation of Hindu philosophy and spirituality. These scriptures encompass hymns, rituals, and guidelines that have guided human life and cosmic understanding for millennia. Discover how the wisdom of the Vedas can enrich your knowledge and spiritual journey by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
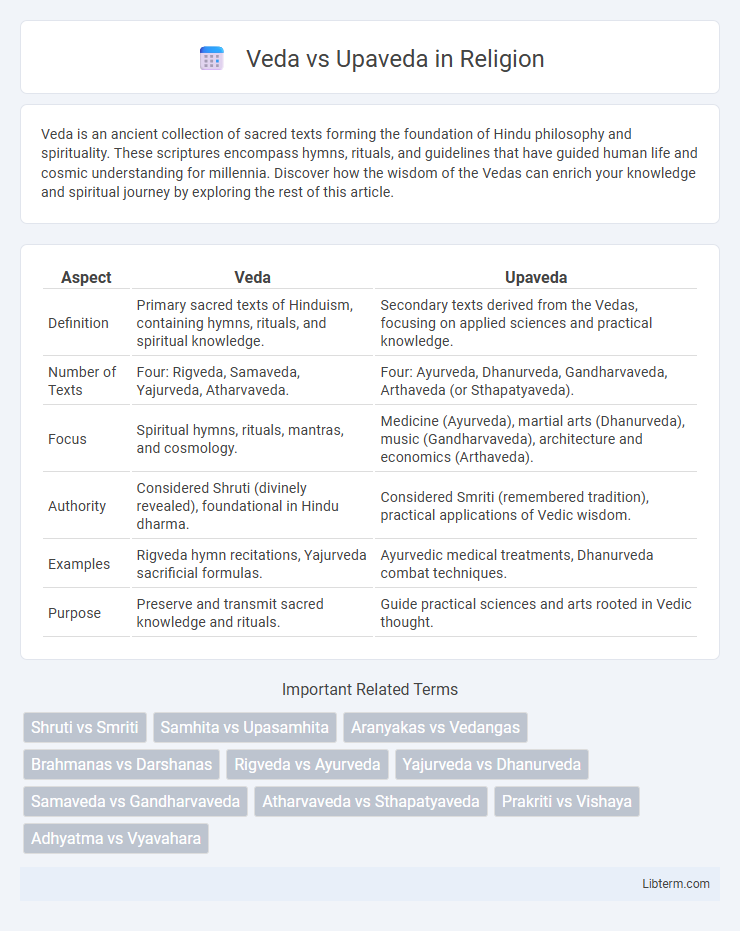
| Aspect | Veda | Upaveda |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Primary sacred texts of Hinduism, containing hymns, rituals, and spiritual knowledge. | Secondary texts derived from the Vedas, focusing on applied sciences and practical knowledge. |
| Number of Texts | Four: Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda, Atharvaveda. | Four: Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, Arthaveda (or Sthapatyaveda). |
| Focus | Spiritual hymns, rituals, mantras, and cosmology. | Medicine (Ayurveda), martial arts (Dhanurveda), music (Gandharvaveda), architecture and economics (Arthaveda). |
| Authority | Considered Shruti (divinely revealed), foundational in Hindu dharma. | Considered Smriti (remembered tradition), practical applications of Vedic wisdom. |
| Examples | Rigveda hymn recitations, Yajurveda sacrificial formulas. | Ayurvedic medical treatments, Dhanurveda combat techniques. |
| Purpose | Preserve and transmit sacred knowledge and rituals. | Guide practical sciences and arts rooted in Vedic thought. |
Introduction to Veda and Upaveda
The Vedas are ancient Indian scriptures consisting of four primary texts--Rigveda, Yajurveda, Samaveda, and Atharvaveda--forming the foundation of Hindu philosophy, rituals, and spiritual knowledge. Upavedas, considered auxiliary texts, are specialized branches linked to each Veda, focusing on practical disciplines like Ayurveda (medicine), Dhanurveda (archery), Gandharvaveda (music), and Arthaveda (economics and politics). While the Vedas emphasize hymns, prayers, and spiritual wisdom, Upavedas apply this knowledge to various aspects of human life and society.
Historical Background of Veda
The Vedas are a corpus of ancient Indian texts composed between 1500 and 500 BCE, foundational to Hindu spiritual knowledge and ritual practice, whereas Upavedas are subsidiary texts that elaborate on specialized disciplines like Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, and Gandharvaveda. The Vedas include four primary collections--Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda, and Atharvaveda--forming the core canonical scriptures transmitted orally through generations. Rooted in early Indo-Aryan culture, the Vedic hymns and mantras encapsulate cosmology, ritual mandates, and philosophical concepts that became central to Indian religious thought.
Origins and Development of Upaveda
The Upavedas originated as complementary texts to the primary Vedas, evolving to address specific practical disciplines such as medicine (Ayurveda), music (Gandharvaveda), martial arts (Dhanurveda), and architecture (Sthapatyaveda). While the Vedas are ancient scriptures foundational to Hindu philosophy and rituals, the Upavedas developed later to systematize applied knowledge in diverse fields closely linked to Vedic traditions. These texts expanded the scope of Vedic wisdom by providing specialized guidance that supported various aspects of cultural and societal practices in ancient India.
Core Concepts of the Vedas
The Vedas are ancient Indian scriptures comprising four primary texts: Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda, and Atharvaveda, which form the foundation of Vedic knowledge emphasizing rituals, hymns, and spiritual wisdom. Upavedas refer to the subsidiary texts linked to the Vedas, focusing on applied knowledge such as Ayurveda (medicine), Dhanurveda (martial arts), Gandharvaveda (music), and Arthaveda (economics and polity). The core concepts of the Vedas include Dharma (cosmic law), Rita (order), and the pursuit of knowledge through yoga, meditation, and sacred rites to achieve spiritual liberation (moksha).
Main Branches and Types of Upaveda
The Vedas consist of four main branches: Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda, and Atharvaveda, each encompassing hymns, rituals, chants, and philosophical teachings central to Hindu tradition. Upavedas are specialized auxiliary texts linked to each Veda, focusing on practical applications such as Ayurveda (medicine related to Atharvaveda), Dhanurveda (martial arts linked to Yajurveda), Gandharvaveda (music and arts associated with Samaveda), and Sthapathya Veda (architecture and construction tied to Rigveda). These Upavedas extend the spiritual knowledge of the core Vedas into disciplines that influence health, warfare, artistic expression, and structural design.
Philosophical Differences: Veda vs Upaveda
The Vedas are ancient Hindu scriptures comprising hymns, rituals, and philosophical teachings central to Dharma and spiritual knowledge. Upavedas, considered subsidiary texts linked to each Veda, delve into specialized practical disciplines such as Ayurveda (medicine), Dhanurveda (martial arts), Gandharvaveda (music), and Arthashastra (economics and politics). Philosophically, Vedas emphasize metaphysical concepts of the self (Atman), cosmic order (Rta), and ultimate reality (Brahman), while Upavedas focus on applying Vedic wisdom to practical human endeavors and sciences.
Literary Structure and Language
The Vedas consist of four primary texts--Rigveda, Samaveda, Yajurveda, and Atharvaveda--characterized by their hymns, mantras, and rituals composed in Vedic Sanskrit featuring a complex metrical structure and archaic linguistic forms. Upavedas, which include Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Arthaveda, serve as auxiliary texts focusing on specific practical disciplines and employ a more accessible and technical language style, often written in classical Sanskrit. The literary structure of the Vedas emphasizes poetic and liturgical expression, while Upavedas prioritize systematic and instructional content aligned with their respective fields.
Influence on Indian Culture and Society
The Vedas, as the oldest and most authoritative scriptures of Hinduism, form the foundational framework for Indian rituals, spirituality, and moral values, profoundly shaping Indian culture and societal norms. Upavedas, considered auxiliary texts linked to Vedas, specialize in practical disciplines like Ayurveda, Dhanurveda (martial arts), Gandharvaveda (music), and Sthapatyaveda (architecture), deeply influencing various aspects of daily life and traditional Indian knowledge systems. Together, Vedas and Upavedas reinforce the synthesis of spiritual wisdom and practical skills that underpin the continuity of Indian civilization and its cultural heritage.
Modern Relevance and Interpretation
The Vedas, ancient Hindu scriptures, form the primary foundation of spiritual knowledge, while the Upavedas, considered auxiliary texts, specialize in applied sciences like Ayurveda (medicine), Dhanurveda (martial arts), Gandharvaveda (music), and Sthapatyaveda (architecture). In modern relevance, the Upavedas offer practical frameworks that integrate seamlessly with contemporary health, wellness, and cultural practices, providing holistic approaches grounded in centuries-old wisdom. Interpretation of both Vedas and Upavedas continues to evolve, blending traditional insights with modern scientific understanding to address today's societal and existential challenges.
Conclusion: Unraveling Veda and Upaveda
Vedas represent the core ancient Indian scriptures forming the foundation of Hindu philosophy, comprising Rigveda, Yajurveda, Samaveda, and Atharvaveda, while Upavedas are specialized texts linked to each Veda, focusing on practical disciplines like Ayurveda, Dhanurveda, Gandharvaveda, and Sthapatyaveda. Both Vedas and Upavedas collectively embody a holistic knowledge system, integrating spiritual wisdom with applied sciences essential for ancient Indian culture and lifestyle. Understanding their distinct yet complementary roles enriches appreciation of Vedic literature's profound legacy and its continuing influence on modern practices.
Veda Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com