Reverence inspires deep respect and admiration for people, beliefs, or nature, creating a profound emotional connection. It cultivates humility and fosters ethical behavior by recognizing the intrinsic value of what is revered. Discover how embracing reverence can transform your perspective and enrich your life in the rest of this article.
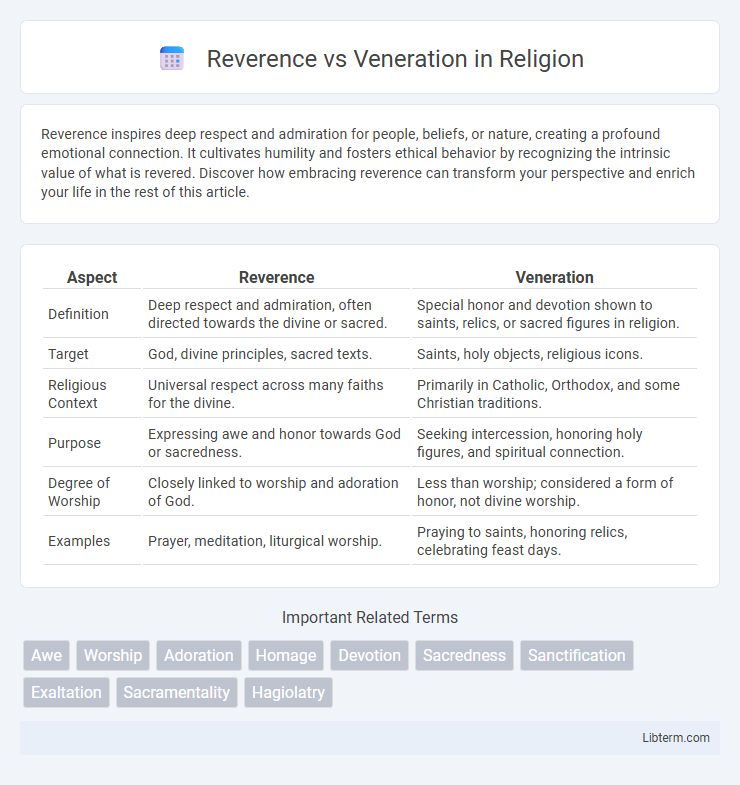
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reverence | Veneration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deep respect and admiration, often directed towards the divine or sacred. | Special honor and devotion shown to saints, relics, or sacred figures in religion. |
| Target | God, divine principles, sacred texts. | Saints, holy objects, religious icons. |
| Religious Context | Universal respect across many faiths for the divine. | Primarily in Catholic, Orthodox, and some Christian traditions. |
| Purpose | Expressing awe and honor towards God or sacredness. | Seeking intercession, honoring holy figures, and spiritual connection. |
| Degree of Worship | Closely linked to worship and adoration of God. | Less than worship; considered a form of honor, not divine worship. |
| Examples | Prayer, meditation, liturgical worship. | Praying to saints, honoring relics, celebrating feast days. |
Understanding Reverence: A Deep-Rooted Respect
Reverence denotes a profound, deeply rooted respect that transcends mere admiration, often encompassing awe and solemnity toward a person, deity, or principle. It involves a heartfelt recognition of worth and an inner attitude of honor that influences behavior and thought. Unlike veneration, which emphasizes outward expressions and ritualistic homage, reverence is primarily an internal, enduring sense of esteem grounded in ethical or spiritual recognition.
Defining Veneration: Honoring the Worthy
Veneration involves honoring individuals or objects deemed worthy due to their exemplary qualities, spiritual significance, or moral virtue, highlighting deep respect and admiration without implying worship. It is a practice commonly observed in various religious and cultural traditions where saints, ancestors, or sacred relics receive special recognition. This form of honor acknowledges inherent value and inspires emulation while maintaining a clear distinction from the reverence reserved for the divine.
Reverence vs Veneration: Key Differences
Reverence and veneration both express deep respect, but reverence emphasizes profound admiration and awe often directed toward people, ideas, or nature, while veneration specifically relates to honoring saints, religious figures, or sacred objects. Reverence is more general and inward-focused, highlighting personal humility and recognition of greatness, whereas veneration is outward and ritualistic, involving specific acts like prayer or rituals. Understanding these distinctions is crucial in religious studies, anthropology, and contexts where respect and honor carry different cultural or spiritual meanings.
Historical Origins of Reverence and Veneration
Reverence and veneration, rooted in ancient religious and cultural traditions, have distinct historical origins that highlight different expressions of respect and devotion. Reverence emerged primarily from philosophical and spiritual teachings in civilizations such as ancient Greece and Confucian China, emphasizing deep respect for moral principles and the sacred. Veneration developed through ritualistic practices in early agrarian societies and religious systems like Hinduism and Christianity, focusing on honoring saints, deities, or ancestors through ceremonies and offerings.
Reverence in Religious and Secular Contexts
Reverence involves deep respect and awe often directed towards sacred figures, deities, or religious symbols, embodying a profound spiritual acknowledgment that transcends ordinary admiration. In secular contexts, reverence extends to influential leaders, historical monuments, or cultural traditions, emphasizing honor and solemn regard without necessarily invoking worship. This dual application highlights reverence as a versatile concept that fosters connection, humility, and recognition of significance across diverse human experiences.
Veneration: Traditions and Practices Worldwide
Veneration involves deep respect shown through rituals, prayers, and offerings that honor saints, ancestors, or sacred figures across cultures. In Catholicism, veneration includes acts like lighting candles and pilgrimages to shrines, while Hinduism expresses it through pujas and prostrations to deities. East Asian traditions, such as ancestor worship in China and Japan, emphasize veneration with ceremonies and altar offerings that sustain familial and spiritual bonds.
The Psychological Impact of Reverence
Reverence, characterized by profound respect and awe, profoundly influences psychological well-being by fostering humility and a sense of connectedness to something greater than oneself. This emotional state enhances mental clarity, reduces stress, and promotes empathy by encouraging self-transcendence and deeper interpersonal bonds. Distinct from veneration, which often implies ritualistic or religious devotion, reverence stimulates a more universal psychological response that supports emotional resilience and personal growth.
Veneration’s Role in Cultural Identity
Veneration plays a crucial role in cultural identity by reinforcing shared values and traditions through the respectful honoring of ancestors, sacred objects, and historical figures. This practice fosters community cohesion and a collective sense of belonging, deeply embedding cultural heritage within social rituals. Unlike general reverence, veneration often involves specific ceremonies and symbols that preserve and transmit cultural narratives across generations.
Reverence and Veneration in Modern Society
Reverence in modern society manifests as deep respect for individuals, traditions, and cultural heritage, often expressed through rituals and formal acknowledgments. Veneration extends beyond respect, embodying admiration or devotion, frequently directed towards historical figures, religious icons, or moral ideals that shape communal identity. Both concepts influence social dynamics by fostering cohesion and continuity through recognition of shared values and esteemed legacies.
Harmonizing Reverence and Veneration for Personal Growth
Harmonizing reverence and veneration fosters personal growth by deepening respect for sacred principles and honoring influential figures who inspire ethical living. Integrating reverence's profound admiration with veneration's active homage cultivates humility, wisdom, and a stronger moral foundation. Embracing both concepts encourages continuous self-improvement and meaningful connections with tradition and spirituality.
Reverence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com