Parallel computing enables simultaneous processing of multiple tasks, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing computation time for complex problems. This approach is essential in fields like data analysis, scientific simulations, and real-time processing, where large volumes of data require rapid computation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how parallel computing can transform your processing capabilities.
Table of Comparison
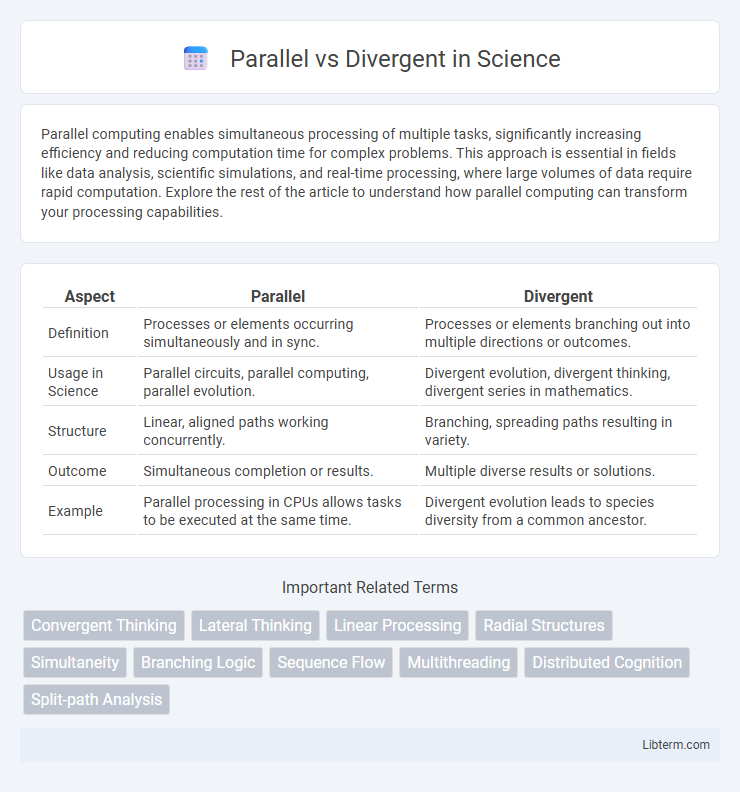
| Aspect | Parallel | Divergent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes or elements occurring simultaneously and in sync. | Processes or elements branching out into multiple directions or outcomes. |
| Usage in Science | Parallel circuits, parallel computing, parallel evolution. | Divergent evolution, divergent thinking, divergent series in mathematics. |
| Structure | Linear, aligned paths working concurrently. | Branching, spreading paths resulting in variety. |
| Outcome | Simultaneous completion or results. | Multiple diverse results or solutions. |
| Example | Parallel processing in CPUs allows tasks to be executed at the same time. | Divergent evolution leads to species diversity from a common ancestor. |
Understanding Parallel and Divergent Concepts
Parallel concepts refer to ideas or processes that occur simultaneously with similar structure or direction, enhancing efficiency and coherence in systems such as parallel computing or storytelling. Divergent concepts emphasize branching paths or variations that explore multiple possibilities or outcomes, crucial in creative thinking and problem-solving frameworks. Understanding parallel and divergent helps optimize workflows by balancing consistency with innovation across diverse fields including technology, education, and management.
Defining Parallel Thinking
Parallel thinking involves multiple individuals or groups exploring the same problem simultaneously from different perspectives, enhancing creativity and comprehensive understanding. This method encourages open-mindedness, where each person contributes unique insights without immediate criticism, fostering a collaborative environment for idea generation. Parallel thinking contrasts with traditional debate by prioritizing collective exploration over opposing viewpoints, optimizing problem-solving efficiency.
Defining Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking involves generating multiple, unique solutions to open-ended problems, emphasizing creativity and exploration beyond conventional boundaries. Unlike parallel thinking, which follows a structured and step-by-step approach, divergent thinking encourages free-flowing ideas and varied perspectives without immediate judgment. This cognitive process is essential for innovation, brainstorming, and problem-solving in complex or ambiguous situations.
Key Differences Between Parallel and Divergent Approaches
Parallel approaches execute multiple tasks simultaneously, maximizing efficiency and reducing overall project time by leveraging concurrency. Divergent approaches emphasize exploring multiple ideas or solutions independently, promoting creativity and innovation without immediate convergence. Key differences include parallel's focus on speed and multitasking versus divergent's emphasis on generating diverse options and creative thinking.
Advantages of Parallel Thinking
Parallel thinking enhances creativity by enabling individuals or teams to explore multiple perspectives simultaneously without conflict. It encourages open-mindedness and reduces biases by allowing ideas to develop independently before comparison or synthesis. Organizations benefit from faster problem-solving and more comprehensive solutions due to the structured yet diverse approach of parallel thinking.
Benefits of Divergent Thinking
Divergent thinking fosters creativity by generating multiple unique solutions and encouraging open-ended exploration, which enhances problem-solving in complex scenarios. This cognitive approach boosts innovation by allowing the mind to break free from conventional patterns and synthesize diverse ideas. Organizations benefit from divergent thinking through increased adaptability and the development of novel products and strategies that meet evolving market demands.
Applications in Problem Solving
Parallel problem solving enhances efficiency by simultaneously exploring multiple solution paths, making it ideal for large-scale computational tasks like data analysis and complex simulations. Divergent problem solving encourages creative thinking by generating a wide range of ideas, often applied in brainstorming sessions and innovation-driven projects. Employing both methods strategically optimizes outcomes in areas such as engineering design, software development, and strategic planning.
Parallel vs Divergent in Creativity
Parallel thinking enhances creativity by encouraging multiple perspectives to explore a problem simultaneously, fostering a comprehensive understanding and innovative solutions. Divergent thinking drives creativity through generating numerous unique ideas and alternatives, promoting originality and creative expansion. Integrating parallel and divergent thinking techniques amplifies the creative process, balancing structured exploration with free-flowing idea generation.
Choosing the Right Approach
Choosing the right approach between parallel and divergent thinking depends on the specific problem-solving needs and desired outcomes. Parallel thinking emphasizes structured, logical steps to analyze information systematically, making it ideal for decision-making and critical evaluation. Divergent thinking fosters creativity and idea generation by encouraging multiple possibilities and open-ended exploration, which suits brainstorming and innovation challenges.
Integrating Parallel and Divergent Thinking
Integrating parallel and divergent thinking enhances problem-solving by combining simultaneous idea generation with broad, creative exploration. Parallel thinking encourages evaluating multiple perspectives at once, while divergent thinking promotes expansive, innovative solutions. Using both approaches fosters comprehensive analysis and increases the likelihood of breakthrough insights in complex decision-making processes.
Parallel Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com