Harnessing solar power transforms sunlight into clean, renewable energy that reduces electricity bills and carbon footprints. Efficient solar panels maximize energy output, making solar an increasingly affordable and sustainable choice for homes and businesses. Discover how solar power can benefit your energy needs by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
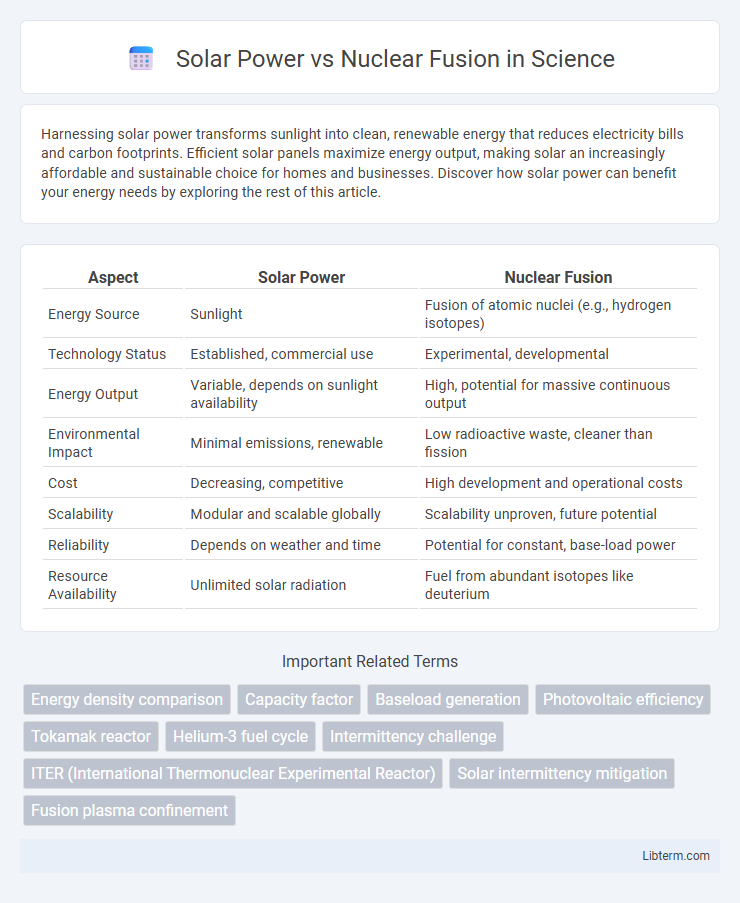
| Aspect | Solar Power | Nuclear Fusion |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Sunlight | Fusion of atomic nuclei (e.g., hydrogen isotopes) |
| Technology Status | Established, commercial use | Experimental, developmental |
| Energy Output | Variable, depends on sunlight availability | High, potential for massive continuous output |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal emissions, renewable | Low radioactive waste, cleaner than fission |
| Cost | Decreasing, competitive | High development and operational costs |
| Scalability | Modular and scalable globally | Scalability unproven, future potential |
| Reliability | Depends on weather and time | Potential for constant, base-load power |
| Resource Availability | Unlimited solar radiation | Fuel from abundant isotopes like deuterium |
Introduction to Solar Power and Nuclear Fusion
Solar power harnesses energy from sunlight using photovoltaic cells, converting solar radiation directly into electricity with increasing global adoption due to its renewable nature and decreasing costs. Nuclear fusion replicates the sun's core process, combining atomic nuclei to release massive amounts of clean energy with ongoing research focused on achieving stable, sustainable fusion reactions. Both energy sources aim to provide environmentally friendly alternatives to fossil fuels, with solar power widely implemented and nuclear fusion promising transformative breakthroughs pending technological advancements.
How Solar Power Works
Solar power harnesses energy from the sun using photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight directly into electricity. These PV cells are composed of semiconductor materials, typically silicon, which generate an electric current when exposed to sunlight through the photoelectric effect. Solar power systems also include inverters to transform the generated direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) for home and industrial use.
Understanding Nuclear Fusion Technology
Nuclear fusion technology replicates the sun's energy production by merging atomic nuclei, releasing vast amounts of clean energy without greenhouse gas emissions. Fusion reactors, such as tokamaks and inertial confinement systems, aim to achieve sustained plasma conditions at extremely high temperatures exceeding 100 million degrees Celsius. Despite technical challenges in maintaining stability and energy output, nuclear fusion promises a virtually limitless energy source with significantly higher efficiency compared to solar power.
Energy Output Comparison
Solar power harnesses energy from sunlight, with typical commercial photovoltaic panels producing around 150-200 watts per square meter under optimal conditions. Nuclear fusion promises vastly higher energy output, with experimental reactors like ITER aiming to generate over 500 megawatts of thermal power from a compact facility, translating to millions of watts per square meter. Fusion's superior energy density and continuous baseline power present a significant advantage over solar's reliance on weather and daylight variability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Solar power generates clean energy by harnessing sunlight, producing zero greenhouse gas emissions and minimal environmental disruption during operation. Nuclear fusion promises vast energy output with virtually no radioactive waste or carbon footprint, offering long-term sustainability if technical challenges are overcome. Both technologies aim to reduce dependence on fossil fuels, but solar power currently provides widely accessible renewable energy with proven environmental benefits.
Safety Concerns: Solar vs Nuclear Fusion
Solar power presents minimal safety concerns, primarily involving equipment installation and maintenance risks, without radiation or catastrophic accident potential. Nuclear fusion promises a safer alternative to fission, with no long-lived radioactive waste and minimal risk of meltdown, but challenges remain in controlling plasma and managing neutron radiation effects on reactor materials. Both energy sources offer significant safety improvements over traditional fossil fuels, though nuclear fusion technology is still under development and requires robust containment strategies to ensure operational safety.
Cost Analysis and Economic Feasibility
Solar power installation costs have decreased by approximately 85% over the past decade, with utility-scale projects averaging $0.03 to $0.06 per kilowatt-hour, making it one of the most affordable renewable energy sources. Nuclear fusion, while promising nearly limitless clean energy, remains economically unfeasible due to high research, development, and operational expenses, with current experimental reactors costing billions without commercial-scale energy output. Economic feasibility favors solar power for immediate deployment and cost-effective energy production, whereas nuclear fusion's viability depends on future technological breakthroughs and substantial capital investment.
Scalability and Infrastructure Requirements
Solar power scalability depends heavily on available land and sunlight exposure, requiring extensive photovoltaic panel installations and grid upgrades to handle variable energy input. Nuclear fusion demands massive, highly specialized infrastructure, including experimental reactors like tokamaks, and faces significant challenges in achieving continuous, commercially viable energy output. While solar energy benefits from modular expansion and relatively quick deployment, fusion requires decades of technological advancement and substantial capital investment before large-scale energy production becomes feasible.
Future Prospects of Solar and Nuclear Fusion
Solar power advancements focus on increasing photovoltaic efficiency and large-scale energy storage, promising a sustainable and cost-effective future energy source. Nuclear fusion, while technologically complex, offers the potential for nearly limitless clean energy with ongoing research in magnetic confinement and inertial confinement methods. Both technologies aim to reduce carbon emissions significantly, with solar power currently leading deployment and fusion expected to revolutionize energy by mid-century.
Conclusion: Choosing the Optimal Energy Source
Solar power offers a renewable, widely available energy source with minimal environmental impact and rapidly declining costs, making it ideal for decentralized energy systems. Nuclear fusion promises a nearly limitless, clean energy supply with high output and low greenhouse gas emissions but remains in experimental stages with significant technological and economic challenges. Selecting the optimal energy source depends on balancing immediate accessibility and scalability of solar power against the long-term potential and innovation required for nuclear fusion development.
Solar Power Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com