Norm reinforcement strengthens social expectations by consistently encouraging adherence to group standards and behaviors. This process enhances cohesion and predictability within communities, promoting stability and shared values. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical ways to effectively reinforce norms in your environment.
Table of Comparison
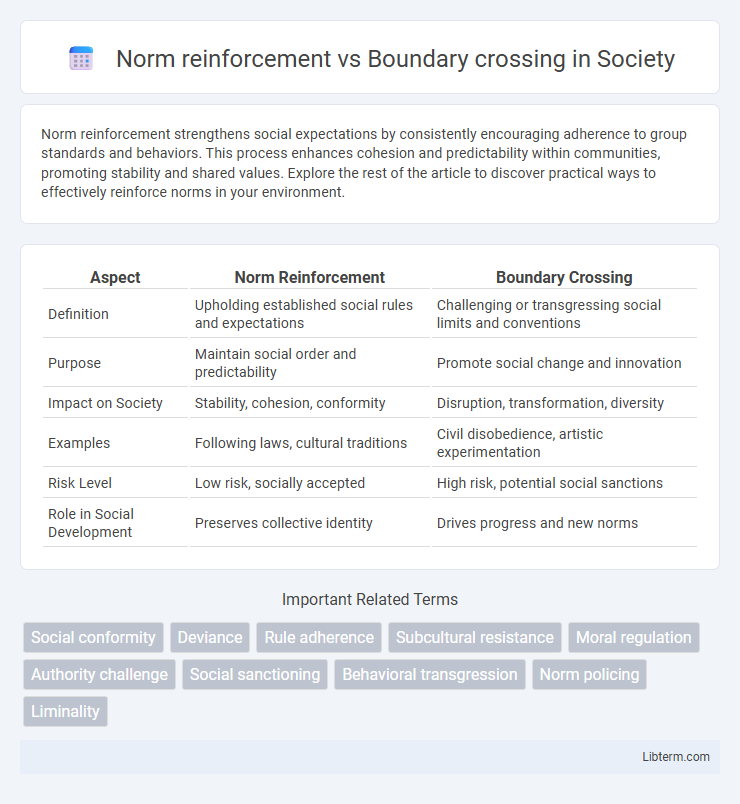
| Aspect | Norm Reinforcement | Boundary Crossing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Upholding established social rules and expectations | Challenging or transgressing social limits and conventions |
| Purpose | Maintain social order and predictability | Promote social change and innovation |
| Impact on Society | Stability, cohesion, conformity | Disruption, transformation, diversity |
| Examples | Following laws, cultural traditions | Civil disobedience, artistic experimentation |
| Risk Level | Low risk, socially accepted | High risk, potential social sanctions |
| Role in Social Development | Preserves collective identity | Drives progress and new norms |
Understanding Norm Reinforcement
Understanding norm reinforcement involves recognizing how consistent adherence to social or organizational rules strengthens behavior patterns and promotes stability within a group. It emphasizes positive reinforcement mechanisms such as rewards and social approval that encourage individuals to conform to expected standards. This process helps maintain order and predictability by embedding norms deeply into daily interactions, contrasting with boundary crossing, which challenges or redefines these established limits.
Defining Boundary Crossing
Boundary crossing involves moving beyond established social, professional, or cultural norms to foster innovation, collaboration, or understanding across different domains. Unlike norm reinforcement, which maintains existing rules and behaviors, boundary crossing challenges the status quo and encourages the integration of diverse perspectives. This process often leads to the creation of new frameworks, solutions, or ways of thinking that transcend traditional limitations.
Psychological Foundations of Social Norms
Norm reinforcement strengthens adherence to social expectations by activating internalized psychological mechanisms such as conformity, reciprocity, and fairness, which promote group cohesion and predictability. Boundary crossing challenges these established norms by introducing behaviors or ideas that deviate from typical social rules, often triggering cognitive dissonance and reevaluation of existing norms. Psychological foundations emphasize the balance between maintaining social order through norm reinforcement and enabling social change through boundary crossing, driven by underlying motivations like identity preservation and social influence.
Societal Benefits of Norm Reinforcement
Norm reinforcement fosters social cohesion by promoting consistent behaviors aligned with shared values, enhancing trust within communities. Strengthening established norms reduces conflict and uncertainty, facilitating cooperation and collective problem-solving. Societal benefits include increased stability, predictability, and the efficient functioning of social institutions.
Risks and Rewards of Boundary Crossing
Boundary crossing involves navigating social or professional norms to foster innovation and collaboration, presenting risks such as misunderstanding, conflict, or reputational damage if boundaries are breached inappropriately. The rewards include enhanced creativity, expanded networks, and access to diverse perspectives that can drive problem-solving and organizational growth. Effective norm reinforcement helps maintain trust and clarity while allowing strategic boundary crossing to capitalize on these benefits without compromising group cohesion.
Norm Reinforcement in Cultural Contexts
Norm reinforcement in cultural contexts strengthens shared values and behaviors, promoting social cohesion and stability within communities. It plays a critical role in preserving traditions and collective identity by encouraging conformity to established social expectations and roles. This reinforcement helps mitigate conflicts and misunderstandings by maintaining clear cultural guidelines and fostering mutual respect.
Boundary Crossing and Social Change
Boundary crossing challenges established social norms by facilitating interactions between diverse groups, thereby fostering innovative perspectives and solutions. This dynamic process plays a crucial role in social change by promoting inclusivity and disrupting entrenched power structures. Empirical studies highlight how boundary crossing enables marginalized communities to influence mainstream discourse, accelerating cultural transformation and policy reform.
Strategies for Balancing Norms and Boundaries
Effective strategies for balancing norm reinforcement and boundary crossing involve establishing clear communication channels that encourage mutual understanding while respecting individual differences. Implementing adaptive frameworks allows organizations to maintain core values while promoting innovation through selective boundary crossing. Regular training and feedback mechanisms help employees navigate the delicate interplay between adhering to established norms and exploring new opportunities for growth.
Real-World Examples: Norm Reinforcement vs Boundary Crossing
Norm reinforcement occurs when individuals or groups adhere to established social conventions, such as workplaces enforcing dress codes to maintain professionalism. Boundary crossing happens when these norms are intentionally challenged or redefined, exemplified by tech startups adopting casual dress to promote innovation and creativity. The dynamic tension between norm reinforcement and boundary crossing shapes organizational culture and drives social evolution.
Future Implications for Society
Norm reinforcement ensures stability by upholding established social rules, fostering predictable interactions that support societal cohesion. Boundary crossing challenges conventional limitations, encouraging innovation and diversity in thought, behavior, and cultural interactions. Future societal implications include balancing these dynamics to promote adaptive growth while maintaining ethical standards and social order.
Norm reinforcement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com