Ethnicity encompasses shared cultural practices, language, and heritage that shape group identity and social belonging. It influences traditions, customs, and perspectives that profoundly impact individual and collective experiences. Explore the rest of the article to understand how ethnicity shapes society and personal identity.
Table of Comparison
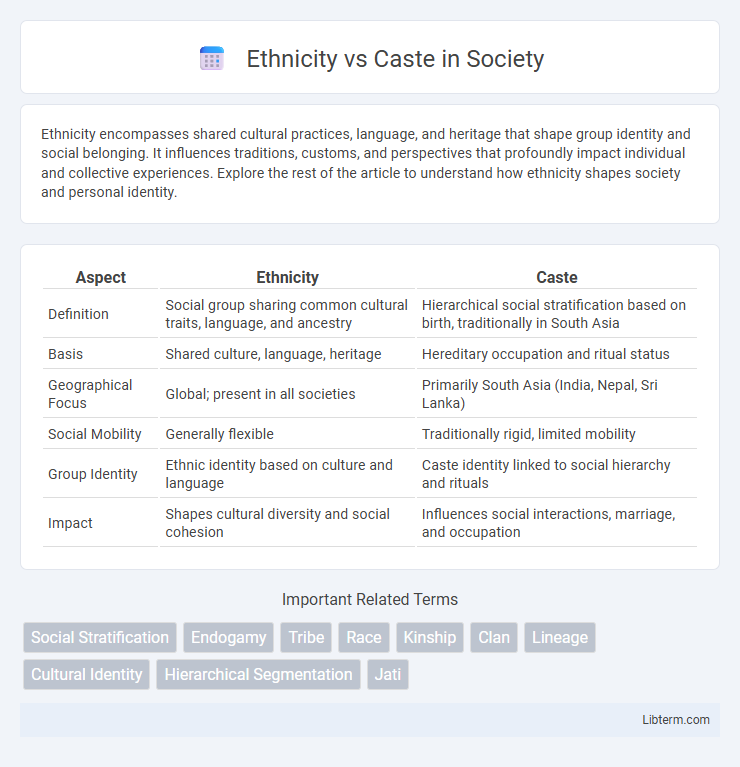
| Aspect | Ethnicity | Caste |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Social group sharing common cultural traits, language, and ancestry | Hierarchical social stratification based on birth, traditionally in South Asia |
| Basis | Shared culture, language, heritage | Hereditary occupation and ritual status |
| Geographical Focus | Global; present in all societies | Primarily South Asia (India, Nepal, Sri Lanka) |
| Social Mobility | Generally flexible | Traditionally rigid, limited mobility |
| Group Identity | Ethnic identity based on culture and language | Caste identity linked to social hierarchy and rituals |
| Impact | Shapes cultural diversity and social cohesion | Influences social interactions, marriage, and occupation |
Defining Ethnicity and Caste
Ethnicity refers to a group of people who share common cultural traits, language, ancestry, and often a shared history that shapes their collective identity. Caste, primarily observed in South Asian societies, is a rigid social stratification system determined by birth, categorizing individuals into hereditary groups with specific social roles and restrictions. While ethnicity is fluid and based on cultural affiliation, caste is a hierarchical structure deeply embedded in social and religious traditions.
Historical Origins of Ethnicity and Caste
Ethnicity originates from shared cultural traits, language, and ancestry that create a collective identity rooted in common historical experiences and migration patterns. Caste, particularly prominent in South Asia, developed as a rigid social stratification system based on hereditary occupational roles and ritual purity, deeply embedded in ancient religious texts like the Manusmriti. While ethnicity emphasizes cultural and genealogical bonds, caste historically institutionalized social hierarchy and division within specific ethnic groups, influencing societal structures for millennia.
Key Differences Between Ethnicity and Caste
Ethnicity refers to a group of people who share common cultural traits, language, ancestral heritage, and social practices, often linked to geographic origins. Caste is a rigid social stratification system primarily found in South Asia, characterized by hereditary status, occupation-based roles, and social hierarchy. Unlike ethnicity, which is fluid and broad, caste defines fixed social positions and enforces endogamy within defined groups.
Social Structures and Hierarchies
Ethnicity and caste both shape social structures and hierarchies by defining group identities and influencing social interactions. Ethnicity is based on shared cultural traits, language, and ancestry, promoting group solidarity but allowing mobility across social strata. Caste, primarily found in South Asian contexts, enforces rigid hereditary status distinctions that determine social roles, occupation, and marriage prospects, creating a stratified and often immobile social hierarchy.
Ethnicity Across Global Societies
Ethnicity across global societies encompasses shared cultural traits, language, ancestry, and social experiences that define group identity beyond mere classification. Unlike caste systems, which are rigid social hierarchies rooted in birthright primarily in South Asia, ethnicity is dynamic and fluid, influenced by migration, intermarriage, and evolving cultural practices worldwide. Recognizing ethnicity's role in shaping social cohesion and conflict helps explain diverse patterns of inclusion and exclusion in multicultural settings globally.
Caste System in South Asia
The caste system in South Asia is a hierarchical social structure deeply rooted in Hindu tradition, dividing people into rigid groups based on birth and occupation. This system enforces social stratification, dictating access to resources, social status, and marriage prospects, often leading to discrimination and social exclusion for lower castes, known as Dalits or "untouchables." Despite legal measures to abolish caste discrimination, the caste system remains influential in India's social, economic, and political life, impacting millions across the region.
Cultural Identity and Group Affiliation
Ethnicity and caste both shape cultural identity and group affiliation through shared heritage, language, and traditions, yet ethnicity is primarily based on common ancestry and cultural traits, while caste is a hereditary social stratification system often linked to occupation and social hierarchy. Ethnic groups foster a sense of belonging rooted in historical background and collective cultural expression, whereas caste affiliation determines social roles and status within a rigid societal framework. These distinctions influence personal identity and community interactions differently across various regions and societies.
Impact on Social Mobility
Ethnicity and caste significantly influence social mobility, with ethnicity often shaping access to resources through cultural identity and community networks, while caste imposes rigid hierarchical barriers that restrict movement across social strata. Ethnic groups may experience varying degrees of integration and discrimination affecting economic opportunities, whereas caste systems enforce hereditary occupation and social status, limiting upward mobility. Empirical studies reveal that caste-based discrimination results in persistent inequality, whereas ethnic diversity sometimes fosters social mobility through affirmative policies and intercultural cooperation.
Discrimination and Social Inequality
Ethnicity and caste both contribute significantly to discrimination and social inequality, with ethnicity often linked to cultural and racial identities, while caste is a rigid social hierarchy primarily rooted in South Asian societies. Discrimination based on ethnicity typically results in marginalization and unequal access to resources, jobs, and political power, whereas caste-based discrimination institutionalizes social stratification and restricts upward mobility through hereditary status. Both systems perpetuate deep-rooted social inequalities by reinforcing exclusion and limiting opportunities for affected groups.
Contemporary Debates: Ethnicity vs Caste
Contemporary debates on ethnicity versus caste highlight the complex interplay between social identity and structural hierarchy, with ethnicity often linked to shared cultural traits and language, while caste emphasizes hereditary social stratification primarily in South Asia. Scholars argue ethnicity can foster group solidarity and political mobilization beyond rigid caste boundaries, yet caste remains a persistent factor influencing social discrimination and access to resources. The debate continues over whether modern societies can transcend caste divisions through ethnic identity or if hybrid identities will shape future social dynamics.
Ethnicity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com