An epistemic community is a network of experts or professionals who share a set of beliefs, values, and knowledge in a particular domain, influencing policy and decision-making processes. This community plays a crucial role in shaping how complex problems are understood and approached by providing authoritative advice based on specialized expertise. Discover how your engagement with epistemic communities can enhance understanding and impact by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
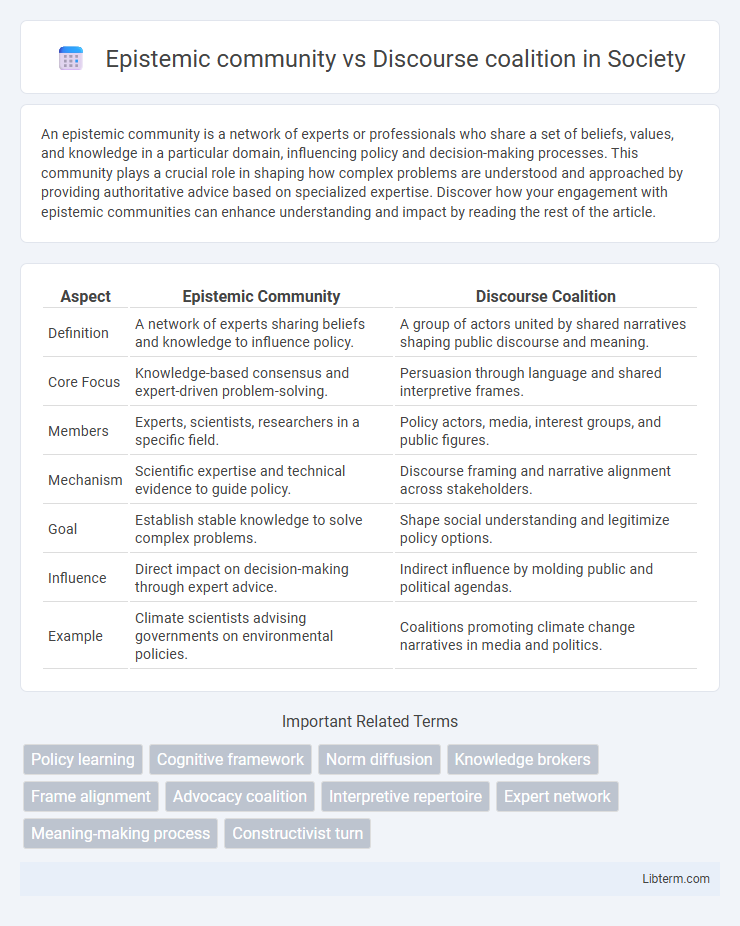
| Aspect | Epistemic Community | Discourse Coalition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A network of experts sharing beliefs and knowledge to influence policy. | A group of actors united by shared narratives shaping public discourse and meaning. |
| Core Focus | Knowledge-based consensus and expert-driven problem-solving. | Persuasion through language and shared interpretive frames. |
| Members | Experts, scientists, researchers in a specific field. | Policy actors, media, interest groups, and public figures. |
| Mechanism | Scientific expertise and technical evidence to guide policy. | Discourse framing and narrative alignment across stakeholders. |
| Goal | Establish stable knowledge to solve complex problems. | Shape social understanding and legitimize policy options. |
| Influence | Direct impact on decision-making through expert advice. | Indirect influence by molding public and political agendas. |
| Example | Climate scientists advising governments on environmental policies. | Coalitions promoting climate change narratives in media and politics. |
Introduction to Epistemic Community and Discourse Coalition
An epistemic community consists of experts who share a set of beliefs, values, and methodologies, influencing policy decisions through authoritative knowledge and consensus. A discourse coalition involves diverse actors who align around shared narratives or storylines, shaping public and political dialogues through language and framing rather than expert consensus. Both concepts explain how knowledge and ideas affect policy-making, but epistemic communities rely on specialized expertise while discourse coalitions emphasize strategic communication across broader networks.
Defining Epistemic Communities
Epistemic communities are networks of professionals with recognized expertise and authoritative knowledge in a specific domain, who share a set of beliefs, causal understandings, and normative values. These communities influence policy outcomes by providing policymakers with information and framing problems based on their specialized knowledge. In contrast, discourse coalitions consist of diverse groups united by common narratives and language, emphasizing the social construction of meaning rather than shared expertise.
Understanding Discourse Coalitions
Discourse coalitions consist of diverse actors who share a set of storylines and common beliefs, shaping policy debates through discursive practices rather than formal authority. Unlike epistemic communities founded on expert consensus and scientific knowledge, discourse coalitions influence understanding and decision-making by framing issues within particular narratives. This collective framing drives political agendas by constructing shared meanings and promoting specific interpretations among stakeholders.
Key Characteristics: Epistemic Communities
Epistemic communities consist of networks of professionals with recognized expertise and authoritative knowledge in a specific domain, sharing normative beliefs, causal understandings, and a common policy enterprise. These communities influence policy by providing decision-makers with pertinent information and technical expertise, thereby shaping problem definitions and solutions. Their key characteristics include shared normative beliefs, causal beliefs, common policy objectives, and a shared notion of validity that guides their knowledge claims.
Core Features: Discourse Coalitions
Discourse coalitions consist of diverse actors united by shared storylines that shape policy debates and public understanding, emphasizing the power of language and narratives in governance. These coalitions do not require specialized knowledge but rely on rhetorical alignment and common interpretations across varied participants. Their core feature lies in constructing and stabilizing discourses that influence agendas and legitimize certain policy solutions over others.
Theoretical Foundations and Origins
Epistemic communities originate from social constructivist and international relations theories, emphasizing shared expertise, normative beliefs, and causal understandings that influence policy decisions through consensus among experts. Discourse coalitions stem from discourse theory and social constructivism, highlighting how groups form around shared narratives and language, shaping policy debates by framing issues and mobilizing support. Both concepts address the role of knowledge in policymaking but differ in their focus on expert consensus versus broader communicative practices.
Differences in Knowledge Production and Policy Influence
Epistemic communities consist of experts sharing specialized knowledge and methods, producing scientific consensus that directly informs policymaking through evidence-based recommendations. Discourse coalitions are broader networks including diverse actors aligned by shared narratives, shaping policy by framing issues and influencing public and political debates rather than relying on technical expertise. The key difference lies in epistemic communities' focus on objective knowledge production, while discourse coalitions emphasize discursive strategies to mobilize support and reconfigure policy agendas.
Case Studies: Comparative Applications
Epistemic communities consist of expert networks that share a set of beliefs and causal understandings to influence policy, often examined through case studies like climate change negotiations. Discourse coalitions, on the other hand, involve broader groups including various actors united by shared narratives, exemplified in cases such as the framing of European Union integration debates. Comparative applications reveal how epistemic communities drive technocratic consensus, while discourse coalitions shape public perceptions and political discourse across diverse policy realms.
Criticisms and Limitations of Each Concept
Epistemic communities face criticism for their potential elitism and lack of engagement with diverse stakeholder perspectives, often limiting policy impact to expert consensus without accounting for broader societal values. Discourse coalitions are limited by their fluidity and often ambiguous boundaries, making it difficult to determine influence or representativeness within policy debates. Both concepts struggle to address power dynamics adequately, with epistemic communities overly emphasizing knowledge authority and discourse coalitions underestimating the role of institutional structures.
Conclusion: Integrating Insights for Policy Analysis
Epistemic communities provide specialized knowledge and consensus crucial for shaping effective policies, while discourse coalitions influence the framing and legitimacy of policy debates through shared narratives and language. Integrating these insights enhances policy analysis by combining expert-driven evidence with the dynamic social construction of policy meanings. This holistic approach leads to more informed, adaptable, and context-sensitive policy decisions.
Epistemic community Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com