Cultural pluralism celebrates the coexistence of diverse cultural groups within a society, encouraging mutual respect and understanding among different traditions and practices. It enriches communities by fostering cultural exchange, social cohesion, and a broader perspective on identity. Discover how embracing cultural pluralism can transform your community and enhance social harmony in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
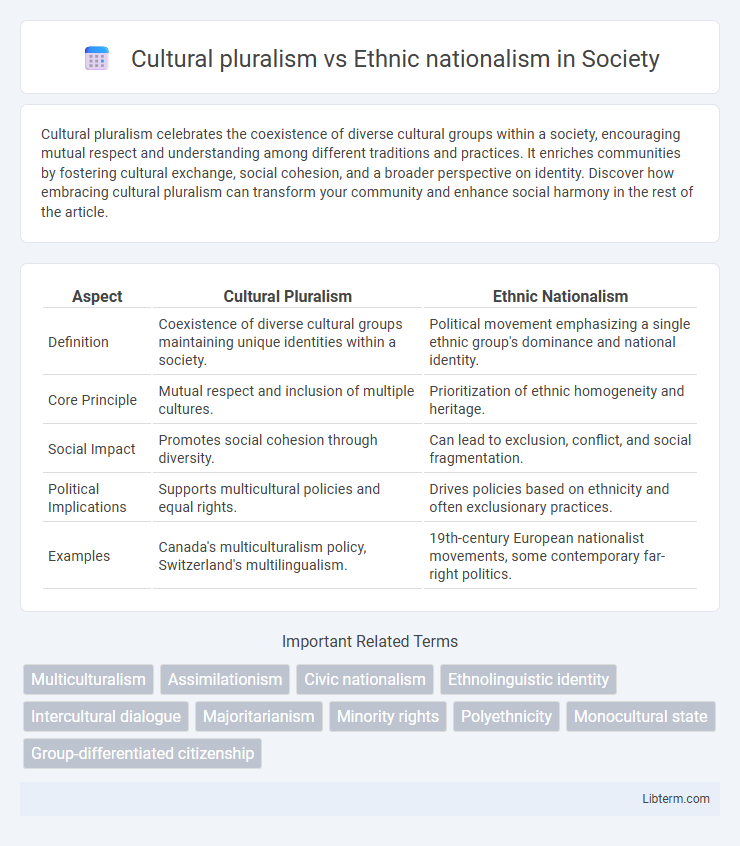
| Aspect | Cultural Pluralism | Ethnic Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Coexistence of diverse cultural groups maintaining unique identities within a society. | Political movement emphasizing a single ethnic group's dominance and national identity. |
| Core Principle | Mutual respect and inclusion of multiple cultures. | Prioritization of ethnic homogeneity and heritage. |
| Social Impact | Promotes social cohesion through diversity. | Can lead to exclusion, conflict, and social fragmentation. |
| Political Implications | Supports multicultural policies and equal rights. | Drives policies based on ethnicity and often exclusionary practices. |
| Examples | Canada's multiculturalism policy, Switzerland's multilingualism. | 19th-century European nationalist movements, some contemporary far-right politics. |
Defining Cultural Pluralism and Ethnic Nationalism
Cultural pluralism refers to a societal framework where multiple distinct cultural groups coexist, maintaining their unique traditions, languages, and identities while participating equally in the broader community. Ethnic nationalism emphasizes the promotion and prioritization of a specific ethnic group's shared heritage, culture, and ancestry as the foundation of national identity and political legitimacy. These concepts differ in their approach to diversity, with cultural pluralism advocating inclusivity across groups and ethnic nationalism focusing on the dominance or preservation of one ethnic identity.
Historical Origins and Evolution
Cultural pluralism emerged in the early 20th century as a response to increasing immigration and the need to acknowledge diverse cultural identities within pluralistic societies, emphasizing coexistence and mutual respect. Ethnic nationalism has roots in 19th-century romantic nationalism, where nation-states were conceived based on shared ethnicity, language, and heritage, often prioritizing ethnic homogeneity. Over time, cultural pluralism evolved to support multicultural policies and inclusive governance, while ethnic nationalism frequently intensified in reaction to globalization and perceived threats to ethnic identity.
Core Principles and Beliefs
Cultural pluralism emphasizes the coexistence and mutual respect of diverse cultural groups within a society, promoting inclusivity and shared values without forcing assimilation. Ethnic nationalism centers on the belief that a nation's identity is fundamentally tied to a specific ethnic group, prioritizing ethnic homogeneity and often advocating for political sovereignty based on common ancestry. Core principles of cultural pluralism include multiculturalism, equality, and intercultural dialogue, while ethnic nationalism upholds ethnic unity, heritage preservation, and exclusive national membership.
Impacts on Social Cohesion
Cultural pluralism promotes social cohesion by encouraging mutual respect and integration among diverse ethnic groups, fostering inclusive communities where multiple identities coexist harmoniously. Ethnic nationalism, in contrast, often leads to social fragmentation and exclusion, as it prioritizes a single ethnic identity, which can result in intergroup tensions and conflicts. The contrasting impacts on social cohesion highlight the importance of embracing cultural pluralism to build stable, unified societies.
Political Implications and Governance
Cultural pluralism promotes inclusive governance by recognizing and accommodating diverse cultural identities within a political system, fostering social cohesion and reducing ethnic conflicts. Ethnic nationalism prioritizes the interests of a specific ethnic group, often leading to exclusionary policies, marginalization of minorities, and potential political instability. The tension between these approaches significantly affects policy-making, representation, and the protection of minority rights in multiethnic states.
Case Studies from Around the World
Cultural pluralism promotes peaceful coexistence by valuing diverse ethnic identities within a single nation, as demonstrated by Switzerland's multilingual cantons and Canada's official bilingualism policies. Ethnic nationalism emphasizes a shared heritage and often marginalizes minorities, exemplified by the conflict between the Sinhalese and Tamil populations in Sri Lanka. Case studies reveal that cultural pluralism fosters political stability and social inclusion, whereas ethnic nationalism can lead to ethnic tensions and separatist movements.
Challenges and Criticisms
Cultural pluralism faces challenges such as the risk of social fragmentation and difficulties in achieving cohesive national identity, often criticized for promoting cultural relativism that can undermine shared societal values. Ethnic nationalism encounters criticisms for fostering exclusion, discrimination, and potential conflict by prioritizing one ethnic group's identity and interests over others. Both models struggle to balance group identity preservation with inclusive governance in increasingly diverse societies.
Intercultural Dialogue and Integration
Cultural pluralism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse ethnic groups maintaining distinct cultural identities within a shared society, fostering intercultural dialogue that promotes mutual respect and understanding. Ethnic nationalism prioritizes a unified national identity based on a single ethnic group, often limiting integration by emphasizing cultural homogeneity and restricting multicultural interaction. Intercultural dialogue in cultural pluralism encourages inclusive policies and social cohesion, whereas ethnic nationalism may hinder integration by favoring exclusionary practices.
The Role of Education and Media
Education shapes cultural pluralism by promoting inclusivity and understanding of diverse traditions, fostering social cohesion through curricula that emphasize multicultural values and human rights. Media serves as a powerful tool in either supporting ethnic nationalism by highlighting ethnic identity and exclusivity or advancing cultural pluralism by showcasing diverse narratives and encouraging intercultural dialogue. The balance between educational content and media representation significantly influences public perceptions and the durability of multicultural societies versus ethnically homogenous national identities.
Future Perspectives and Global Trends
Cultural pluralism promotes inclusive societies where diverse ethnic groups coexist, fostering social cohesion and innovation as globalization intensifies interconnectivity. Ethnic nationalism increasingly challenges this model by emphasizing ethnic identity and sovereignty, which may lead to political fragmentation and conflict in multicultural states. Future global trends suggest a dynamic tension between rising ethnic nationalism and efforts to sustain cultural pluralism through international cooperation and policy frameworks supporting diversity.
Cultural pluralism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com