Informal social sanctions are everyday social cues and reactions, such as disapproval, ridicule, or exclusion, that guide individual behavior without formal enforcement. These sanctions play a crucial role in maintaining social order by encouraging conformity to community norms and discouraging deviance. Explore the article to understand how your interactions are shaped by these subtle yet powerful social mechanisms.
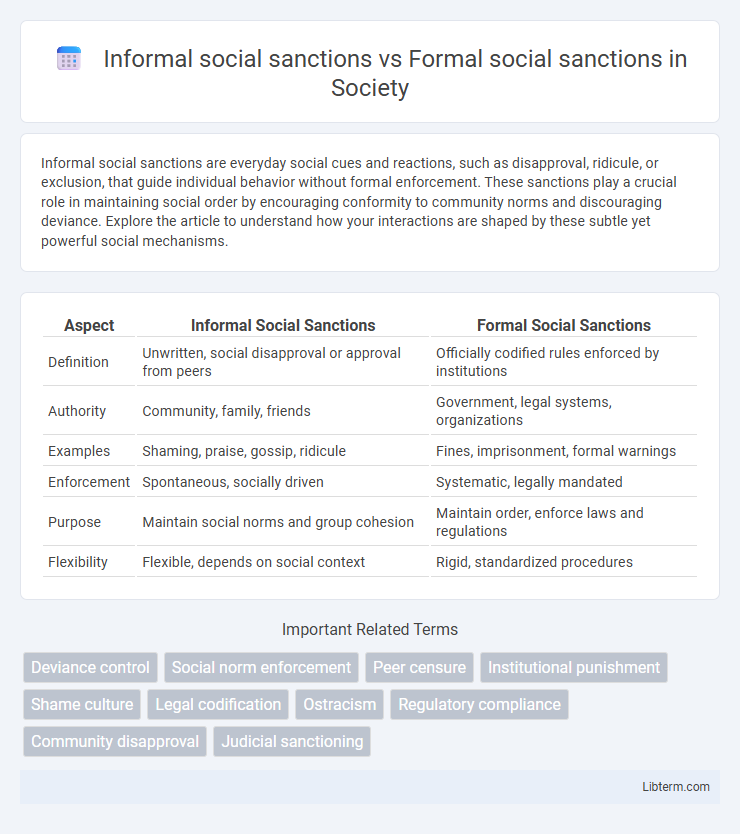
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Informal Social Sanctions | Formal Social Sanctions |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unwritten, social disapproval or approval from peers | Officially codified rules enforced by institutions |
| Authority | Community, family, friends | Government, legal systems, organizations |
| Examples | Shaming, praise, gossip, ridicule | Fines, imprisonment, formal warnings |
| Enforcement | Spontaneous, socially driven | Systematic, legally mandated |
| Purpose | Maintain social norms and group cohesion | Maintain order, enforce laws and regulations |
| Flexibility | Flexible, depends on social context | Rigid, standardized procedures |
Introduction to Social Sanctions
Informal social sanctions are the unwritten, socially enforced reactions such as praise, ridicule, or ostracism that guide individual behavior within communities. Formal social sanctions involve codified rules and laws enforced by official institutions like courts, police, or regulatory agencies. Both types of sanctions play critical roles in maintaining social order by promoting conformity and deterring deviance through different mechanisms of control.
Defining Informal Social Sanctions
Informal social sanctions refer to unwritten rules and social cues, such as gossip, ridicule, or praise, that regulate behavior within a community through social approval or disapproval. Unlike formal social sanctions imposed by institutions like laws or regulations, informal sanctions rely on shared social norms and collective behavior to encourage conformity. These sanctions play a critical role in maintaining social order by subtly enforcing accepted behaviors without legal intervention.
Understanding Formal Social Sanctions
Formal social sanctions are officially imposed by recognized institutions such as governments, courts, and law enforcement agencies to regulate behavior and maintain social order. These sanctions include legal penalties like fines, imprisonment, and community service, which are codified in laws and regulations to ensure consistency and enforceability. Understanding formal social sanctions is crucial for comprehending how societies deter deviance and promote compliance with established norms through authoritative mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Informal and Formal Social Sanctions
Informal social sanctions include unwritten rules and social cues such as praise, ridicule, or ostracism used by peers to regulate behavior, whereas formal social sanctions encompass codified laws and official punishments imposed by institutions like courts or law enforcement agencies. Informal sanctions operate through social norms and community enforcement without legal authority, while formal sanctions are backed by legal systems and carry official consequences such as fines, imprisonment, or formal reprimands. The key difference lies in the source of authority and enforcement mechanisms, with informal sanctions relying on social influence and formal sanctions depending on institutional power.
Examples of Informal Social Sanctions in Everyday Life
Informal social sanctions include behaviors such as gossip, social ostracism, ridicule, and expressions of disapproval like frowning or sighing, which regulate conduct without formal authority. These sanctions operate in everyday life through peer pressure, family expectations, and community norms, influencing individuals to conform to accepted standards. Unlike formal sanctions enforced by laws or institutions, informal sanctions rely on social interactions and shared values to maintain order and cohesion.
Illustrative Cases of Formal Social Sanctions
Formal social sanctions involve official penalties enforced by institutions such as courts or regulatory bodies to maintain order and uphold laws. Illustrative cases include criminal convictions resulting in imprisonment, fines issued by regulatory agencies for corporate misconduct, and school expulsions due to code violations. These sanctions are documented, structured, and recognized legally, distinguishing them from informal sanctions like gossip or social ostracism.
The Role of Culture in Social Sanctions
Culture shapes the application and perception of informal social sanctions by influencing community norms, values, and unwritten rules that govern everyday behavior. In contrast, formal social sanctions are codified within legal and institutional frameworks, reflecting a society's collective agreement on acceptable conduct and punishment, often embedded within its cultural and historical context. The interplay between culture and social sanctions determines how individuals internalize norms and respond to both informal disapproval and formal penalties.
Effectiveness of Informal vs Formal Sanctions
Informal social sanctions, such as peer disapproval and social ostracism, often exert immediate behavioral influence due to their basis in close social relationships and community norms. Formal social sanctions, including legal penalties and institutional punishments, provide structured consequences that reinforce societal rules but may lack the personal impact of informal sanctions. Research indicates that informal sanctions are particularly effective in small-group settings where social bonds and reputations are strong, while formal sanctions are essential for maintaining order in larger, more complex societies.
Social Implications of Sanctions on Behavior
Informal social sanctions, such as praise, ridicule, or ostracism, shape individual behavior through everyday social interactions, reinforcing societal norms without legal enforcement. Formal social sanctions involve codified laws and institutional penalties like fines, imprisonment, or official reprimands, directly influencing behavior by establishing clear consequences. Both types of sanctions play crucial roles in maintaining social order, with informal sanctions fostering internalized norms and formal sanctions deterring violations through external authority.
Conclusion: Balancing Informal and Formal Sanctions in Society
Balancing informal social sanctions, such as peer pressure and social disapproval, with formal social sanctions like legal penalties and institutional punishments is essential for maintaining social order. Informal sanctions foster community cohesion and encourage norm adherence through everyday interactions, while formal sanctions provide clear consequences for violations of laws and regulations. A society that effectively integrates both types of sanctions promotes compliance, deters deviant behavior, and supports a stable social structure.
Informal social sanctions Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com