Humanism emphasizes the inherent dignity and value of human beings, focusing on reason, ethics, and justice rather than supernatural beliefs. It promotes critical thinking, individual freedom, and the pursuit of knowledge to improve human welfare and society. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your understanding of how humanism shapes modern thought and culture.
Table of Comparison
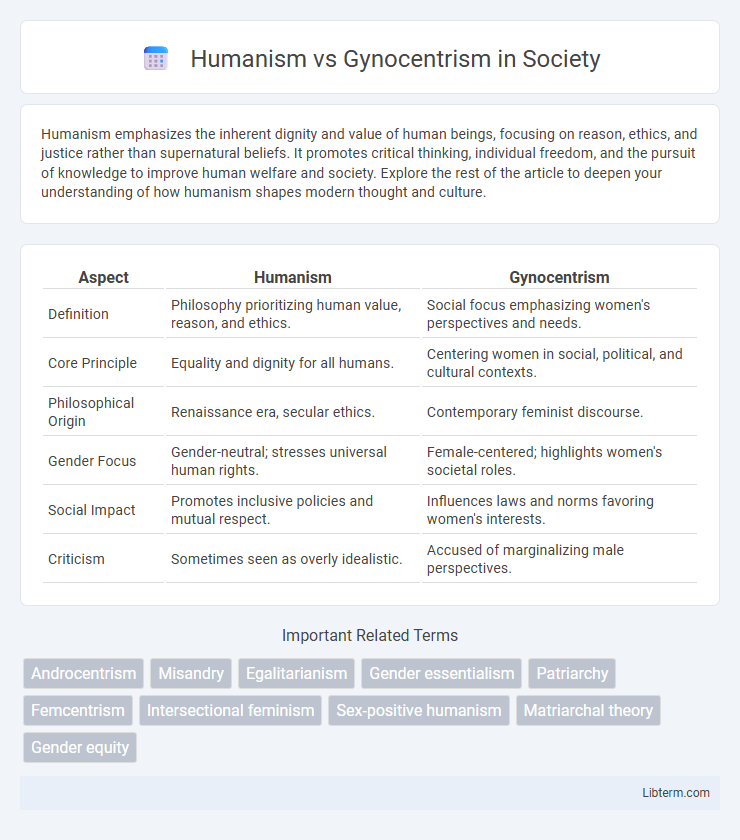
| Aspect | Humanism | Gynocentrism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Philosophy prioritizing human value, reason, and ethics. | Social focus emphasizing women's perspectives and needs. |
| Core Principle | Equality and dignity for all humans. | Centering women in social, political, and cultural contexts. |
| Philosophical Origin | Renaissance era, secular ethics. | Contemporary feminist discourse. |
| Gender Focus | Gender-neutral; stresses universal human rights. | Female-centered; highlights women's societal roles. |
| Social Impact | Promotes inclusive policies and mutual respect. | Influences laws and norms favoring women's interests. |
| Criticism | Sometimes seen as overly idealistic. | Accused of marginalizing male perspectives. |
Introduction to Humanism and Gynocentrism
Humanism emphasizes the value and agency of human beings, promoting reason, ethics, and justice as fundamental principles for societal progress. Gynocentrism prioritizes the experiences, needs, and perspectives of women, often influencing social and cultural norms to center female interests. Understanding the contrast between Humanism and Gynocentrism is vital for analyzing gender dynamics and philosophical approaches to equality and human rights.
Historical Origins of Humanism
Humanism emerged during the Renaissance as an intellectual movement emphasizing the value of human beings, individual dignity, and reason, rooted in the revival of classical Greek and Roman texts. It focused on human potential and achievements rather than divine or supernatural matters, shaping modern education, philosophy, and arts. Gynocentrism, contrastingly, centers societal structures around women's perspectives and roles, lacking a similarly defined historical origin compared to the well-documented development of humanism.
Roots and Evolution of Gynocentrism
Gynocentrism, rooted in ancient matriarchal traditions and reinforced by evolutionary biology emphasizing female reproductive strategy, shifted societal focus towards women's needs and perspectives. Over time, cultural, religious, and social norms evolved, entrenching gynocentric frameworks within many civilizations, often privileging female roles in family and community life. This evolution contrasts with humanism, which emphasizes universal human rights and equality, challenging gynocentric biases by advocating for a balanced consideration of all genders.
Key Principles of Humanism
Humanism emphasizes individual dignity, rationality, and ethical responsibility, advocating for human rights and secularism based on reason and empathy. It promotes universal values such as equality, freedom of thought, and the pursuit of knowledge without reliance on supernatural beliefs. Unlike gynocentrism, which centers on prioritizing women's perspectives, humanism seeks a balanced approach highlighting shared human experience and mutual respect across all genders.
Core Tenets of Gynocentrism
Gynocentrism centers on prioritizing women's experiences, needs, and perspectives as fundamental to societal values and decision-making processes. It emphasizes the importance of female-centered ethics, female welfare, and the protection of maternal and reproductive roles. This core tenet often challenges traditional humanist frameworks by shifting focus from universal human equality to gender-specific considerations.
Humanism vs Gynocentrism: Philosophical Differences
Humanism emphasizes the inherent dignity and worth of all human beings, promoting equality and individual rights based on rationality and shared humanity. Gynocentrism centers social and cultural values around women's needs and perspectives, often prioritizing female experiences in ethical and social considerations. Philosophically, humanism advocates universalism and egalitarianism, while gynocentrism highlights gender-specific prioritization, resulting in divergent approaches to justice, ethics, and societal organization.
Societal Impacts of Humanism
Humanism promotes individual dignity and critical thinking, fostering inclusive societies that value human rights and equality. It discourages biases rooted in gender or identity, encouraging policies that prioritize universal welfare over group-specific interests. As a result, humanism supports social cohesion and progressive reforms by advocating reason and empathy in public discourse.
Social Consequences of Gynocentrism
Gynocentrism, prioritizing women's needs and perspectives often at the expense of gender equality, can lead to social imbalances, including systemic biases against men in family law, education, and employment. This social framework may contribute to increased gender polarization, perpetuating stereotypes and reducing cooperative dialogue between genders. The marginalization of men's issues under gynocentric policies risks fostering resentment and social fragmentation, undermining the humanistic pursuit of equal dignity and rights for all individuals.
Modern Debates: Balancing Humanism and Gynocentrism
Modern debates on balancing Humanism and Gynocentrism emphasize the need to harmonize universal human rights with the recognition of gender-specific experiences and challenges. Advocates argue for an inclusive framework that respects individual dignity while addressing systemic biases faced by women. Data from social justice initiatives reveal that integrating both perspectives fosters equitable policies and promotes social cohesion.
Conclusion: Toward Inclusive Social Progress
Humanism advocates for equal rights and inherent dignity of all individuals regardless of gender, promoting a balanced and just society. Gynocentrism centers on female experiences and interests, often influencing social structures and cultural norms in ways that prioritize women. Toward inclusive social progress, integrating humanist principles with an awareness of gynocentric influences encourages equitable policies that recognize diverse perspectives and foster mutual respect across genders.
Humanism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com