Multiculturalism enriches societies by embracing diverse cultures, traditions, and perspectives, fostering greater social harmony and innovation. It promotes inclusivity and mutual respect while challenging stereotypes and prejudices. Discover how understanding multiculturalism can positively impact Your community and relationships throughout this article.
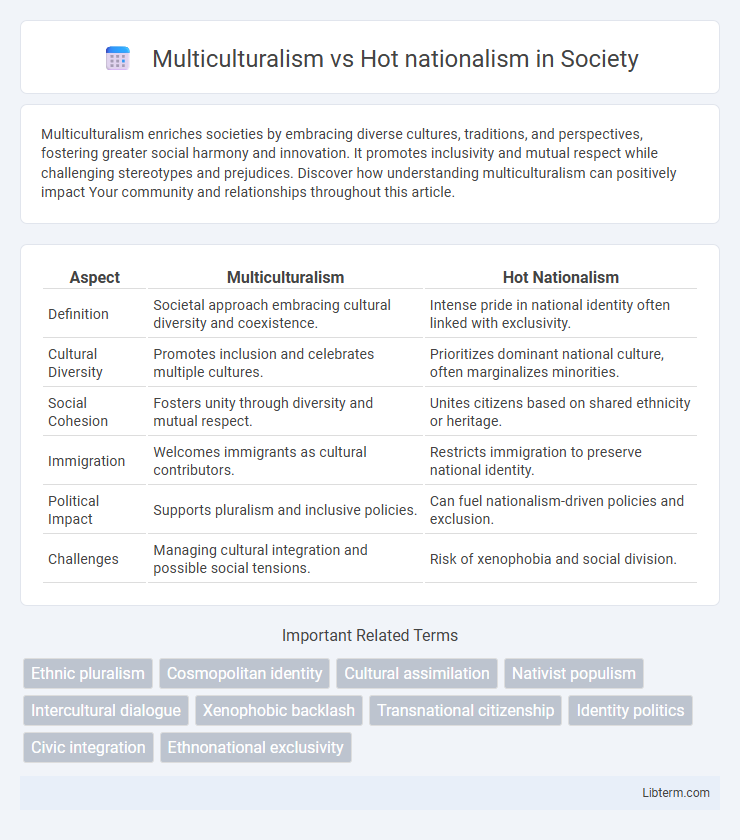
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Multiculturalism | Hot Nationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Societal approach embracing cultural diversity and coexistence. | Intense pride in national identity often linked with exclusivity. |
| Cultural Diversity | Promotes inclusion and celebrates multiple cultures. | Prioritizes dominant national culture, often marginalizes minorities. |
| Social Cohesion | Fosters unity through diversity and mutual respect. | Unites citizens based on shared ethnicity or heritage. |
| Immigration | Welcomes immigrants as cultural contributors. | Restricts immigration to preserve national identity. |
| Political Impact | Supports pluralism and inclusive policies. | Can fuel nationalism-driven policies and exclusion. |
| Challenges | Managing cultural integration and possible social tensions. | Risk of xenophobia and social division. |
Understanding Multiculturalism: Core Principles and Values
Multiculturalism emphasizes the coexistence of diverse cultural identities within a unified society, promoting values such as inclusivity, mutual respect, and equal opportunity. Core principles include cultural pluralism, social integration, and the protection of minority rights, fostering an environment where diverse traditions and languages are preserved and celebrated. This approach contrasts with hot nationalism, which centers on ethnic homogeneity and often prioritizes a singular national identity over cultural diversity.
The Rise of Hot Nationalism: Definition and Dynamics
The rise of hot nationalism is characterized by an intense and emotional form of national pride that emphasizes cultural purity, territorial sovereignty, and often exclusionary policies. This dynamic contrasts with multiculturalism, which promotes cultural diversity, inclusion, and the coexistence of multiple ethnic groups within a single nation-state. Hot nationalism often emerges during periods of political or economic instability, fueled by fears of globalization, immigration, and perceived threats to national identity.
Historical Context: Roots of Multiculturalism and Nationalism
Multiculturalism emerged in the mid-20th century as a response to increased immigration and decolonization, promoting cultural diversity and social inclusion within nations. Hot nationalism, often traced to 19th-century Romanticism and the fallout of imperial decline, emphasizes intense emotional loyalty to a shared national identity and cultural homogeneity. Both ideologies reflect historical reactions to social change, with multiculturalism rooted in pluralistic societies and hot nationalism arising from nationalist movements seeking to assert sovereign unity.
Social Cohesion: Integration vs Exclusion
Multiculturalism promotes social cohesion through integration by encouraging diverse cultural groups to coexist and engage in mutual respect and inclusion within society. Hot nationalism often fosters exclusion by prioritizing a singular national identity, which can marginalize minority communities and create societal divisions. Effective social cohesion depends on policies that balance cultural diversity with shared values, minimizing exclusionary practices that undermine unity.
Policy Approaches: Governance in Diverse Societies
Policy approaches to governance in diverse societies often contrast multiculturalism, which promotes inclusive frameworks recognizing cultural differences and protecting minority rights, with hot nationalism, which emphasizes homogeneity and prioritizes dominant cultural identities. Multicultural policies typically involve power-sharing, anti-discrimination laws, and multicultural education to foster social cohesion and equitable representation. In contrast, hot nationalism policies may enforce stricter immigration controls, cultural assimilation, and nationalist rhetoric to maintain state sovereignty and unity.
Economic Impacts: Diversity’s Role vs Nationalist Protectionism
Multiculturalism boosts economic growth by fostering innovation, expanding global market access, and enhancing workforce adaptability through diverse perspectives. In contrast, hot nationalism prioritizes protectionist policies that can restrict trade, limit foreign investment, and reduce economic dynamism by focusing on domestic industries. Studies show economies embracing diversity often experience higher GDP growth rates and increased competitiveness compared to nationalist-driven economies with restricted market openness.
Identity Politics: Belonging in a Multicultural World
Identity politics in a multicultural world highlights the tension between inclusive belonging and exclusive nationalism, where multiculturalism promotes diverse cultural recognition and social cohesion. Hot nationalism, characterized by intense national pride and often xenophobic sentiments, challenges multicultural frameworks by prioritizing homogenous identity constructs. Navigating these opposing forces requires balancing respect for cultural plurality with the desire for a unified national identity to foster social stability and inclusion.
Security and Conflict: Risks of Polarized Nationalism
Polarized nationalism intensifies security risks by fostering exclusionary ideologies that marginalize minority groups, leading to social unrest and potential violence. Multiculturalism promotes inclusive policies that mitigate conflict by encouraging coexistence and mutual respect among diverse communities. Nationalistic extremism increases the likelihood of intergroup tensions and destabilizes national security through fragmented social cohesion.
Globalization: Challenges to Multicultural and Nationalist Ideals
Globalization intensifies challenges to both multiculturalism and hot nationalism by promoting interconnectedness that blurs cultural boundaries. Multiculturalism faces tensions as global migration fosters cultural blending, creating demands for inclusive policies and social cohesion. In contrast, hot nationalism reacts against these changes by asserting rigid identities and exclusionary practices to protect perceived national sovereignty and cultural purity.
Future Perspectives: Balancing Diversity and National Unity
Future perspectives on multiculturalism emphasize creating inclusive policies that celebrate cultural diversity while fostering social cohesion to avoid fragmentation. Hot nationalism, driven by intense emotional identification with the nation, poses challenges to pluralistic societies but can be moderated through dialogue that promotes shared values and common goals. Sustainable national unity depends on balancing respect for diverse identities with commitments to democratic principles and civic participation.
Multiculturalism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com