Hypodescent is the social and legal practice of classifying a person of mixed race into the subordinate racial group, often affecting identity and social status. This concept has historically shaped racial dynamics and inequalities by enforcing rigid racial boundaries. Explore the rest of the article to understand how hypodescent influences contemporary society and your own perceptions.
Table of Comparison
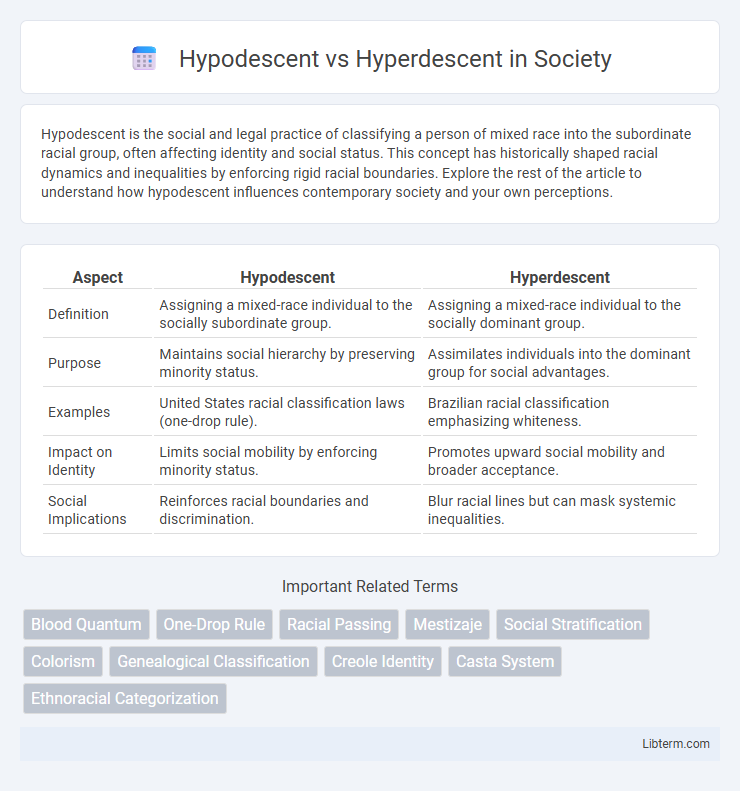
| Aspect | Hypodescent | Hyperdescent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assigning a mixed-race individual to the socially subordinate group. | Assigning a mixed-race individual to the socially dominant group. |
| Purpose | Maintains social hierarchy by preserving minority status. | Assimilates individuals into the dominant group for social advantages. |
| Examples | United States racial classification laws (one-drop rule). | Brazilian racial classification emphasizing whiteness. |
| Impact on Identity | Limits social mobility by enforcing minority status. | Promotes upward social mobility and broader acceptance. |
| Social Implications | Reinforces racial boundaries and discrimination. | Blur racial lines but can mask systemic inequalities. |
Introduction to Hypodescent and Hyperdescent
Hypodescent is the social classification practice assigning mixed-race individuals to the subordinate or minority group, often used historically in racial caste systems such as the U.S. one-drop rule. Hyperdescent, less common, classifies mixed-race individuals as belonging to the dominant or majority group, emphasizing upward racial assimilation. Understanding these concepts reveals how societies construct racial identities and maintain social hierarchies through classification rules.
Historical Context of Descent Classifications
Hypodescent and hyperdescent classifications originated in colonial and post-colonial societies to navigate racial and social hierarchies, with hypodescent assigning mixed-race individuals to the subordinate group and hyperdescent attributing them to the dominant group. These classifications were legally codified in laws such as the United States' "one-drop rule" during the Jim Crow era and contrasted with certain Latin American countries' fluid caste systems favoring hyperdescent. The historic application of these descent rules reflects broader power dynamics, racial ideologies, and efforts to control social identity and resource access throughout history.
Defining Hypodescent: The “One-Drop” Rule
Hypodescent, commonly known as the "One-Drop" Rule, is a social and legal principle that classifies individuals with any African ancestry as Black, regardless of the proportion of their heritage. This rule emerged in the United States during the 19th and 20th centuries as a means of enforcing racial segregation and maintaining white supremacy. In contrast, hyperdescent assigns mixed-race individuals to the more socially prestigious or dominant racial group, which is less common in American racial classification.
Understanding Hyperdescent: Claiming Higher-Status Heritage
Hyperdescent involves individuals claiming ancestry from a higher-status or socially dominant ethnic group, often to elevate their social identity or gain social advantages. This practice contrasts with hypodescent, where mixed-race individuals are assigned to the lower-status group. Understanding hyperdescent sheds light on social dynamics where heritage claims reflect power structures and identity negotiations within multicultural societies.
Cultural and Social Implications
Hypodescent assigns an individual to the subordinate racial group, often reinforcing systemic inequalities and limiting social mobility within marginalized communities. Hyperdescent, by contrast, aligns a person with the dominant or higher-status group, which can facilitate access to cultural capital and socioeconomic advantages. These classifications deeply influence identity formation, societal acceptance, and the distribution of resources within multicultural societies.
Hypodescent vs Hyperdescent in Different Societies
Hypodescent classifies individuals into the socially subordinate group in mixed-race unions, commonly observed in the United States, where children of mixed black and white ancestry are typically identified as black. Hyperdescent, found in societies like Brazil and some parts of Latin America, assigns mixed-race individuals to the socially dominant or higher-status group, often emphasizing European or higher-status ancestry. These contrasting systems reflect distinct social hierarchies and racial dynamics, influencing identity, legal status, and social mobility across different cultures.
Legal Perspectives and Policy Impacts
Hypodescent laws historically assigned mixed-race individuals to the subordinate racial group, reinforcing racial hierarchies and segregation in legal systems, particularly in the United States. Hyperdescent policies, though less common, recognized lineage from the dominant group, influencing inheritance rights and social status in some colonial and indigenous legal frameworks. Legal perspectives on hypodescent and hyperdescent directly impact civil rights legislation, social welfare policies, and identity recognition, shaping access to resources and minority protections.
Modern Examples and Case Studies
Hypodescent typically assigns mixed-race individuals to the subordinate or minority group, evident in U.S. Census classifications where multiracial people are often categorized by their non-white ancestry, as demonstrated in studies of African American and Latino identities. Hyperdescent, less common, involves affiliating individuals with the dominant or majority group, seen in certain Latin American countries like Brazil, where mixed-race individuals may be identified as white to reflect social stratification and privilege. Modern case studies highlight how these classifications affect social policy and identity politics, influencing educational opportunities and legal rights in multicultural societies.
Controversies Surrounding Descent Classifications
Hypodescent assigns individuals of mixed ancestry to the socially subordinate group, while hyperdescent attributes them to the socially dominant group, sparking significant controversy over identity and social stratification. Critics argue that hypodescent perpetuates systemic inequalities by reinforcing rigid racial boundaries, while supporters maintain it reflects historical power dynamics. Disputes intensify in multicultural societies where descent classifications influence legal rights, social status, and resource allocation, highlighting the complexities of race, identity, and societal hierarchy.
Conclusion: Rethinking Identity and Classification
Hypodescent and hyperdescent represent contrasting approaches to racial classification, with hypodescent assigning mixed-race individuals to the subordinate group, and hyperdescent affiliating them with the dominant group. Rethinking identity and classification requires acknowledging the fluidity and social construction of race rather than rigid binary categories. Emphasizing individual self-identification and dismantling institutionalized classification systems foster more inclusive and accurate understandings of racial identity.
Hypodescent Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com