Mestizaje represents the cultural and biological blending of Indigenous, European, and African ancestries, shaping diverse identities across Latin America. This process influences languages, traditions, and social structures, reflecting centuries of interaction and adaptation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how mestizaje continues to impact your cultural heritage and society today.
Table of Comparison
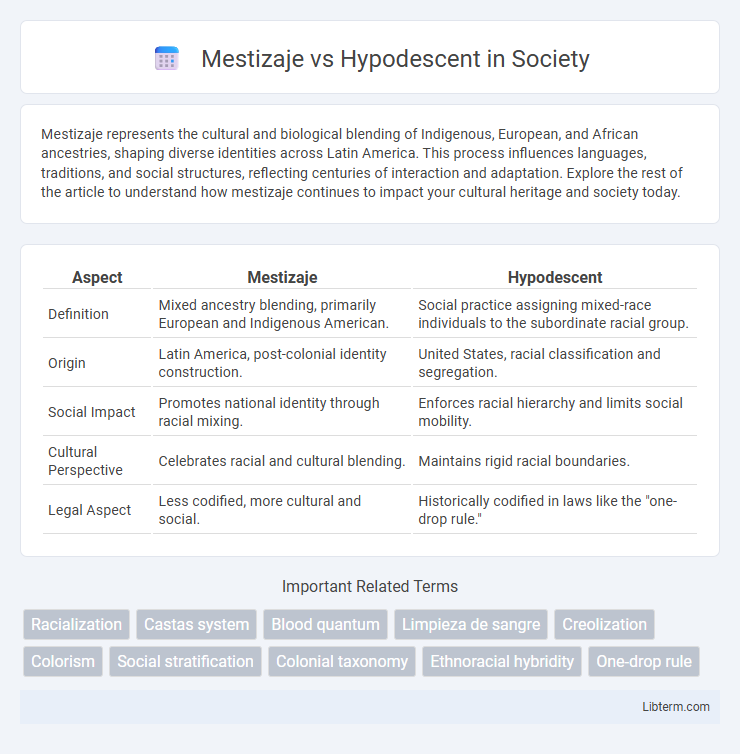
| Aspect | Mestizaje | Hypodescent |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mixed ancestry blending, primarily European and Indigenous American. | Social practice assigning mixed-race individuals to the subordinate racial group. |
| Origin | Latin America, post-colonial identity construction. | United States, racial classification and segregation. |
| Social Impact | Promotes national identity through racial mixing. | Enforces racial hierarchy and limits social mobility. |
| Cultural Perspective | Celebrates racial and cultural blending. | Maintains rigid racial boundaries. |
| Legal Aspect | Less codified, more cultural and social. | Historically codified in laws like the "one-drop rule." |
Introduction to Mestizaje and Hypodescent
Mestizaje refers to the process of racial and cultural mixing primarily in Latin America, emphasizing the blending of Indigenous, European, and African ancestries into a new, hybrid identity. Hypodescent, commonly known as the "one-drop rule," classifies individuals with any trace of African ancestry as solely Black, reinforcing rigid racial boundaries. Understanding these contrasting concepts highlights different approaches to identity formation and racial categorization in multicultural societies.
Historical Origins of Mestizaje
Mestizaje originated in colonial Latin America as a process of racial and cultural mixing between Indigenous peoples and Europeans, primarily Spaniards, during the 16th century. This concept emphasized the blending of races and cultures as a foundation for emerging national identities in countries like Mexico, contrasting with the rigid racial classifications of hypodescent used in Anglo-American contexts. Mestizaje encouraged the idea of a mixed-race society, shaping social and political ideologies centered on integration and cultural synthesis rather than racial exclusion.
The Concept of Hypodescent Explained
The concept of hypodescent assigns a child's racial classification to the socially subordinate group in mixed-race parentage, reinforcing historical systems of racial hierarchy. This principle, often termed the "one-drop rule," was legally codified in the United States to maintain white racial purity by classifying anyone with African ancestry as Black. Hypodescent contrasts with mestizaje, which embraces mixed racial identities, highlighting divergent social and cultural approaches to race categorization.
Colonial Legacies in Racial Classification
Mestizaje and hypodescent represent contrasting colonial legacies in racial classification, where mestizaje emphasizes mixed-race identity as a form of cultural blending primarily in Latin America, while hypodescent enforces a rigid "one-drop rule," classifying individuals according to the subordinate racial group, mainly in the United States. Colonial powers institutionalized these systems to control social hierarchies and maintain racial boundaries, with mestizaje promoting assimilation and racial mixing under Spanish colonial rule, and hypodescent codifying racial purity and segregation under Anglo-American influence. These divergent legacies continue to shape racial identity, social stratification, and policies in postcolonial societies.
Social Implications of Mestizaje
Mestizaje, promoting the blending of Indigenous, European, and African ancestries, tends to emphasize cultural integration and national unity, often overshadowing distinct racial identities. This ideology can obscure systemic inequalities by framing mixed heritage as a harmonious social ideal, leading to the erasure of Afro-descendant and Indigenous struggles. In contrast to hypodescent, which rigidly assigns mixed-race individuals to subordinate racial categories, mestizaje influences social dynamics by encouraging a fluid identity that may complicate race-based activism and policy implementation.
Hypodescent in the United States Context
Hypodescent in the United States context refers to the social and legal practice of classifying individuals with mixed racial heritage into the subordinate racial group, often the minority or non-white category. This racial categorization system historically enforced segregation and discrimination by automatically assigning the status of "one-drop rule" to anyone with any African ancestry. Hypodescent contrasts with mestizaje, which emphasizes racial and cultural blending, by perpetuating rigid racial boundaries and maintaining white supremacy through legal and social mechanisms.
Mestizaje and National Identity Formation
Mestizaje, the process of racial and cultural mixing primarily between Indigenous peoples and Europeans, plays a central role in shaping national identity in many Latin American countries by promoting a unified, mixed heritage as a foundational element of society. This concept contrasts with hypodescent, which enforces racial hierarchy by categorizing individuals with any minority ancestry into subordinate groups, often marginalizing mixed identities. Emphasizing mestizaje fosters inclusion and cultural hybridity, influencing national narratives and policies aimed at social integration and the celebration of diverse ancestries within a cohesive national identity.
Legal Frameworks Shaping Racial Boundaries
Legal frameworks historically establish and enforce mestizaje and hypodescent by codifying racial boundaries that define social identity and inheritance rights. Mestizaje laws promote racial mixing and cultural blending, often recognizing mixed-race individuals within national identities, whereas hypodescent operates under strict legal rules assigning mixed-race individuals the status of the subordinate group, reinforcing racial hierarchies. These differing legal constructs influence citizenship, property rights, and social mobility, shaping the lived experiences of racially categorized populations across Latin America and the United States.
Contemporary Debates: Mestizaje vs Hypodescent
Contemporary debates on mestizaje and hypodescent center on their differing approaches to racial identity and social classification in Latin America and the United States. Mestizaje emphasizes cultural and racial mixing as a unifying national identity while often downplaying systemic racism, whereas hypodescent enforces racial boundaries by automatically classifying mixed-race individuals into the socially subordinate group, typically Black or Indigenous. Critics argue mestizaje can perpetuate colorblind ideologies that obscure inequalities, whereas hypodescent highlights persistent racial hierarchies and discrimination.
Toward Inclusive Understandings of Identity
Mestizaje emphasizes the blending and coexistence of diverse racial and cultural identities, promoting a fluid and inclusive understanding of identity that celebrates hybridity. Hypodescent, contrastingly, enforces rigid racial categorization by assigning individuals to the socially subordinate group, often marginalizing mixed heritage populations. Moving toward inclusive understandings of identity requires dismantling hypodescent's binary logic and embracing mestizaje's recognition of complexity and multiplicity in identity formation.
Mestizaje Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com