Bureaucratic enforcement ensures that laws and regulations are implemented uniformly through structured government agencies, maintaining order and compliance. It involves detailed procedures and oversight to prevent arbitrary decisions and promote accountability within public administration. Discover how bureaucratic enforcement impacts your daily life and influences policy execution by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
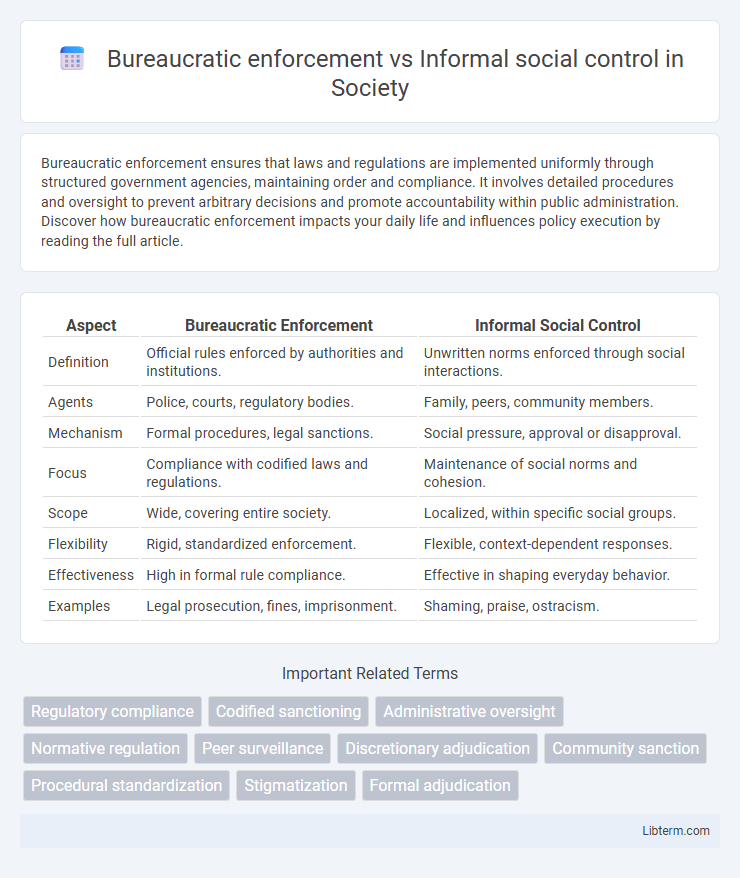
| Aspect | Bureaucratic Enforcement | Informal Social Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Official rules enforced by authorities and institutions. | Unwritten norms enforced through social interactions. |
| Agents | Police, courts, regulatory bodies. | Family, peers, community members. |
| Mechanism | Formal procedures, legal sanctions. | Social pressure, approval or disapproval. |
| Focus | Compliance with codified laws and regulations. | Maintenance of social norms and cohesion. |
| Scope | Wide, covering entire society. | Localized, within specific social groups. |
| Flexibility | Rigid, standardized enforcement. | Flexible, context-dependent responses. |
| Effectiveness | High in formal rule compliance. | Effective in shaping everyday behavior. |
| Examples | Legal prosecution, fines, imprisonment. | Shaming, praise, ostracism. |
Understanding Bureaucratic Enforcement
Bureaucratic enforcement relies on formal rules, regulations, and systematically applied penalties to maintain order and ensure compliance within organizations or governments. It operates through hierarchical structures, documented procedures, and official authorities responsible for monitoring and sanctioning behavior. This method contrasts with informal social control, which depends on unwritten norms, social pressures, and community-based influences rather than legal or administrative frameworks.
Defining Informal Social Control
Informal social control refers to the unwritten rules and social norms enforced through everyday interactions within families, peer groups, and communities, rather than through formal institutions like law enforcement or courts. It relies on social approval, gossip, and peer pressure to regulate behavior and maintain social order. This type of control often operates more flexibly and subtly than bureaucratic enforcement, adapting to cultural and contextual nuances.
Historical Evolution of Social Regulation
Bureaucratic enforcement emerged prominently during the Industrial Revolution, establishing formal institutions like police and courts to regulate complex societies through codified laws. Informal social control, rooted in pre-modern communities, relied on customs, traditions, and social norms to maintain order without formal legal systems. The historical evolution of social regulation shows a gradual shift from informal mechanisms toward bureaucratic structures as societies grew more complex and urbanized.
Key Differences Between Formal and Informal Mechanisms
Bureaucratic enforcement relies on formal institutions like police, courts, and regulatory agencies to impose rules through official procedures, ensuring accountability and standardized sanctions. Informal social control operates through community norms, peer pressure, and socialization processes, promoting conformity without explicit legal authority or codified punishments. The key difference lies in the source of authority: formal mechanisms depend on legal codification and organizational structures, whereas informal mechanisms derive power from social relationships and shared cultural values.
Effectiveness in Maintaining Social Order
Bureaucratic enforcement relies on formal rules, regulations, and institutions to maintain social order, providing consistency and clear consequences for violations, which enhances predictability and accountability. Informal social control operates through social norms, peer pressure, and community influence, fostering cooperation and conformity without the need for official intervention. Effectiveness in maintaining social order depends on the context; bureaucratic enforcement excels in complex, large-scale societies requiring standardized regulation, while informal social control is more effective in close-knit communities where social bonds and shared values are stronger.
Case Studies: Bureaucratic vs Informal Approaches
Case studies comparing bureaucratic enforcement and informal social control reveal distinct impacts on community compliance and cohesion. Bureaucratic approaches rely heavily on codified rules, formal sanctions, and institutional authority, often leading to uniform but rigid enforcement outcomes, as seen in urban policing models. Informal social control, exemplified by neighborhood watch groups and family-based sanctioning in rural communities, leverages social norms and peer pressure, fostering adaptability and stronger local trust networks.
The Role of Cultural Norms in Social Control
Cultural norms play a crucial role in informal social control by shaping individuals' behavior through shared values, beliefs, and expectations within a community. These unwritten rules promote conformity and cooperation, reducing reliance on bureaucratic enforcement mechanisms such as laws and regulations enforced by formal institutions. Informal social control operates through social sanctions, peer pressure, and community approval, effectively maintaining order where cultural norms strongly influence social conduct.
Challenges and Limitations of Bureaucratic Enforcement
Bureaucratic enforcement often faces challenges such as rigidity in procedures, limited flexibility in addressing unique social contexts, and resource constraints that impede timely responses. The formalized nature of bureaucratic systems can create barriers to effective communication and community engagement, reducing their adaptability to evolving societal norms. These limitations emphasize the need to complement bureaucratic enforcement with informal social control mechanisms that leverage local relationships and social norms.
Community Engagement and Informal Influence
Bureaucratic enforcement relies on formal rules and official authorities to maintain order, often limiting direct community involvement. Informal social control thrives through community engagement and informal influence, where social norms and peer pressure guide behavior within neighborhoods. Strong community networks enhance informal social control by fostering mutual trust and collective efficacy, reducing the need for bureaucratic intervention.
Balancing Formal Authority and Social Norms
Balancing formal authority in bureaucratic enforcement with informal social control requires integrating legal regulations with community values to enhance compliance and legitimacy. Bureaucratic enforcement relies on codified rules and institutional power, while informal social control leverages social norms and peer influence to shape behavior. Effective governance combines these mechanisms to ensure order through both official sanctions and the reinforcement of shared cultural expectations.
Bureaucratic enforcement Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com