Localism prioritizes empowering communities by promoting local decision-making, supporting small businesses, and preserving cultural identity. It fosters economic resilience and strengthens social bonds by encouraging local production and consumption, reducing reliance on distant markets. Discover how embracing localism can transform Your community's development by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
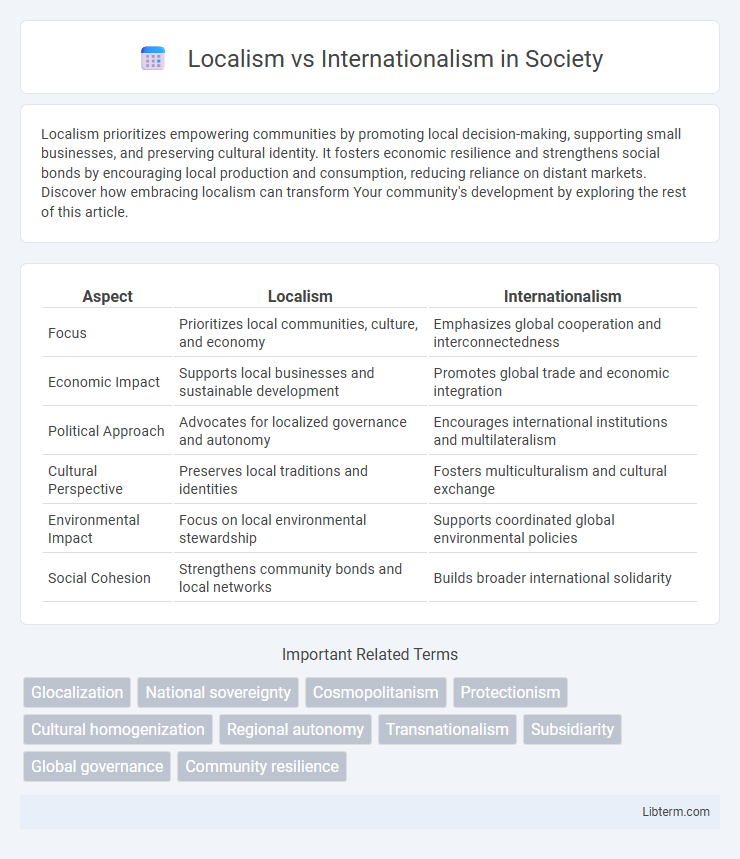
| Aspect | Localism | Internationalism |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Prioritizes local communities, culture, and economy | Emphasizes global cooperation and interconnectedness |
| Economic Impact | Supports local businesses and sustainable development | Promotes global trade and economic integration |
| Political Approach | Advocates for localized governance and autonomy | Encourages international institutions and multilateralism |
| Cultural Perspective | Preserves local traditions and identities | Fosters multiculturalism and cultural exchange |
| Environmental Impact | Focus on local environmental stewardship | Supports coordinated global environmental policies |
| Social Cohesion | Strengthens community bonds and local networks | Builds broader international solidarity |
Understanding Localism: Definition and Key Principles
Localism emphasizes prioritizing local communities, economies, and cultures in decision-making processes, ensuring resources and opportunities benefit nearby populations. Key principles include community empowerment, decentralization of power, support for local businesses, and preservation of regional identities and traditions. This approach fosters sustainable development by aligning economic activities with local needs and environmental stewardship.
Internationalism Explained: Concept and Evolution
Internationalism promotes global cooperation and interconnectedness, emphasizing the importance of cross-border collaboration in addressing worldwide challenges such as climate change, trade, and human rights. The concept evolved significantly during the 20th century, driven by the formation of institutions like the League of Nations and the United Nations, which aimed to foster peace and collective security. Modern internationalism advocates for multilateralism, economic integration, and cultural exchange to create a more unified global community.
Historical Roots of Localism and Internationalism
Localism emerged from historical movements emphasizing community autonomy, cultural preservation, and resistance to centralized power, notably during the rise of nation-states and colonial resistance in the 18th and 19th centuries. Internationalism originated from Enlightenment ideals and post-World War cooperation efforts, promoting global solidarity, peace, and interconnected governance structures like the League of Nations and later the United Nations. These historical roots shaped ongoing debates about sovereignty, globalization, and the balance between local identities and global responsibilities.
Economic Impacts: Local vs. Global Approaches
Localism promotes economic resilience by supporting small businesses and keeping capital within communities, leading to job creation and sustainable development. Internationalism facilitates global trade, allowing access to diverse markets, cost efficiencies, and innovation through cross-border collaboration. Balancing local economic empowerment with global integration maximizes growth opportunities and mitigates risks associated with economic dependence or isolation.
Cultural Preservation in a Connected World
Localism emphasizes safeguarding unique cultural identities and traditions by promoting community-driven practices and resisting homogenizing global influences. Internationalism encourages cross-cultural exchange and cooperation, fostering mutual understanding while risking dilution of distinct cultural heritage. Balancing cultural preservation requires integrating local customs within global networks to sustain diversity amid increasing digital connectivity.
Political Dynamics: Governance on Different Scales
Localism emphasizes decentralized governance, empowering communities to make decisions tailored to regional needs, which often enhances political accountability and citizen participation. In contrast, internationalism advocates for collaborative governance structures that address global challenges through supranational institutions and treaties, fostering cooperation across borders. The political dynamics between these scales involve balancing local autonomy with international cooperation to achieve effective policymaking and sustainable development.
Environmental Considerations: Local Solutions vs. Global Strategies
Localism emphasizes tailored environmental solutions that address specific ecological challenges within communities, leveraging regional knowledge and resources to enhance sustainability. Internationalism advocates for coordinated global strategies to combat widespread issues like climate change, promoting unified policies and resource sharing for greater impact. Balancing localized actions with global cooperation ensures that both unique environmental contexts and overarching planetary health are effectively managed.
Social Cohesion and Identity in Localist vs. Internationalist Contexts
Localism fosters social cohesion through shared cultural heritage and strengthened community identity, reinforcing localized values and traditions. In contrast, internationalism promotes inclusive social bonds across diverse cultures, encouraging global identity that transcends national boundaries. Balancing local pride with international cooperation enhances social cohesion by integrating distinct identities into a broader, harmonious framework.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Philosophies
Localism faces challenges such as economic inefficiencies, limited resource access, and potential isolation from global innovation, while critics argue it can foster parochialism and reduce cultural exchange. Internationalism encounters issues including uneven power dynamics, exploitation of developing nations, and dilution of local identities, with detractors highlighting its complexity and potential to prioritize global elites over grassroots concerns. Both philosophies struggle to balance autonomy and cooperation, often sparking debates on sovereignty, equity, and sustainable development.
Future Trends: Balancing Localism and Internationalism
Future trends indicate a growing emphasis on balancing localism and internationalism through hybrid governance models that integrate local autonomy with global cooperation. Technological advancements in communication and data sharing facilitate cross-border collaboration while preserving cultural identities and local economic priorities. Policies promoting sustainable development increasingly advocate for localized solutions aligned with international frameworks to address global challenges such as climate change and economic inequality.
Localism Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com