Mainstream society shapes cultural norms, values, and behaviors that influence daily life and social interactions. Understanding its impact helps you navigate social expectations and challenges effectively. Explore the rest of the article to gain deeper insights into how mainstream society affects identity and community.
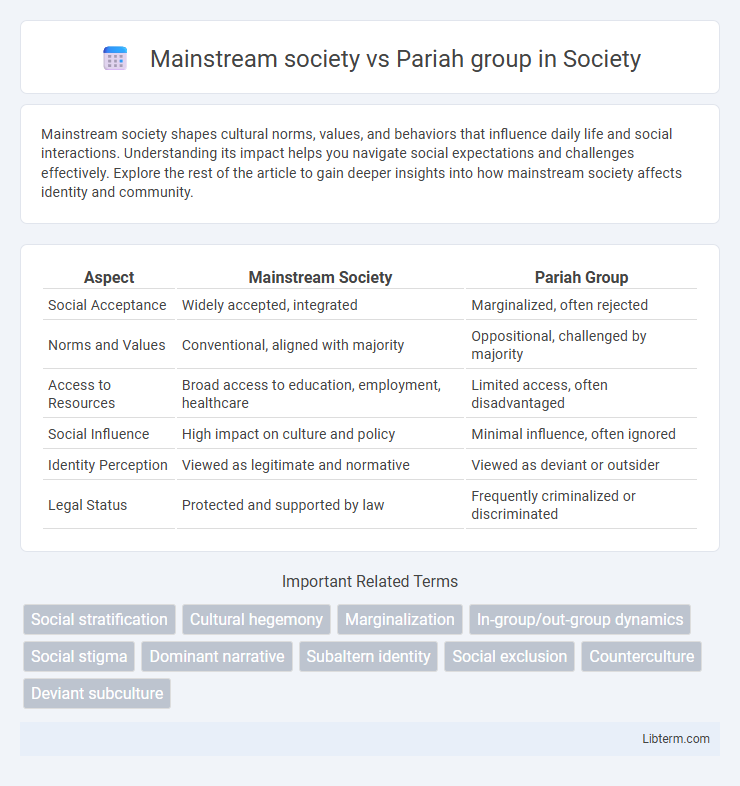
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mainstream Society | Pariah Group |
|---|---|---|
| Social Acceptance | Widely accepted, integrated | Marginalized, often rejected |
| Norms and Values | Conventional, aligned with majority | Oppositional, challenged by majority |
| Access to Resources | Broad access to education, employment, healthcare | Limited access, often disadvantaged |
| Social Influence | High impact on culture and policy | Minimal influence, often ignored |
| Identity Perception | Viewed as legitimate and normative | Viewed as deviant or outsider |
| Legal Status | Protected and supported by law | Frequently criminalized or discriminated |
Defining Mainstream Society: Characteristics and Values
Mainstream society is characterized by widely accepted cultural norms, social values, and institutions that promote stability, conformity, and collective identity. Its values often emphasize lawfulness, economic productivity, education, and social cohesion, reflecting dominant ideologies and practices. These shared beliefs and behaviors create a framework for social integration and influence individuals' roles within the community.
Who Are the Pariah Groups? An Overview
Pariah groups consist of social collectives that are socially ostracized, stigmatized, or marginalized by mainstream society due to their beliefs, behaviors, or identities that deviate from dominant cultural norms. These groups often face exclusion, discrimination, and reduced access to societal resources, reinforcing their outsider status. Understanding the dynamics and characteristics of pariah groups is crucial for examining social cohesion, conflict, and processes of inclusion or exclusion within a society.
Historical Roots of Social Exclusion
Mainstream society has historically constructed social norms and cultural standards that define acceptable behaviors, often marginalizing groups that deviate from these norms as pariah groups. This process of social exclusion is deeply rooted in historical power dynamics, where dominant groups enforce boundaries to maintain economic, political, and cultural control. The stigmatization of pariah groups frequently reflects systemic inequalities embedded in colonialism, caste systems, and class hierarchies established over centuries.
Mechanisms of Othering: Language, Policy, and Practice
Mechanisms of othering between mainstream society and pariah groups manifest through language that stigmatizes and dehumanizes, reinforcing social exclusion. Policies often institutionalize discrimination, marginalizing these groups by restricting access to resources, rights, and representation. Everyday practices perpetuate exclusion by normalizing stereotypes and discriminatory behaviors that maintain social hierarchies and prevent integration.
Power Dynamics: Inclusion vs Exclusion
Mainstream society wields power through inclusion, controlling narratives and resources that define social norms and marginalized group identities. Pariah groups experience systemic exclusion, limiting their access to economic opportunities, political participation, and cultural representation. This power dynamic reinforces hierarchical structures where mainstream acceptance dictates social legitimacy and pariah status perpetuates marginalization.
Cultural Identity and the Struggle for Recognition
Mainstream society often enforces dominant cultural norms that marginalize pariah groups, undermining their cultural identity and limiting opportunities for social recognition. Pariah groups actively resist assimilation by preserving unique traditions, languages, and values, asserting their identity against societal exclusion. The ongoing struggle for recognition centers on achieving equal rights, representation, and respect within social, political, and cultural institutions.
The Impact of Stigma on Pariah Communities
Stigma profoundly affects pariah groups by fostering social exclusion, limiting access to resources, and reinforcing negative stereotypes within mainstream society. This marginalization results in reduced economic opportunities, diminished mental health, and barriers to social integration for members of these communities. Persistent stigma perpetuates systemic inequality, making it difficult for pariah groups to achieve parity or social acceptance.
Resistance, Resilience, and Advocacy
Mainstream society often enforces norms that pariah groups resist through acts of defiance and maintaining cultural identity. Pariah groups exhibit resilience by preserving their traditions and fostering strong internal support networks despite social exclusion. Advocacy efforts by these groups aim to challenge stigmatization and seek equal rights, influencing broader societal change over time.
Mainstream Reactions: Integration, Assimilation, or Marginalization?
Mainstream society often responds to pariah groups through integration, assimilation, or marginalization, each representing different levels of acceptance and exclusion. Integration involves incorporating pariah group members into societal norms while preserving some distinct cultural traits, whereas assimilation expects full absorption and abandonment of original identities. Marginalization excludes these groups from mainstream social, economic, and political participation, reinforcing their outsider status and limiting upward mobility.
Toward an Inclusive Society: Bridging the Divide
Mainstream society often marginalizes pariah groups through systemic exclusion and social stigmatization, perpetuating inequality and limiting access to resources. Bridging the divide requires implementing inclusive policies that promote equal participation, representation, and cultural acceptance for marginalized communities. Fostering dialogue and empathy between mainstream populations and pariah groups cultivates social cohesion and dismantles barriers to integration.
Mainstream society Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com