Uniformity ensures consistency and reliability across processes, products, or environments, enhancing quality control and predictability. Achieving uniformity reduces variability, which can minimize errors and increase efficiency. Explore the full article to learn how uniformity can benefit your operations and improve overall performance.
Table of Comparison
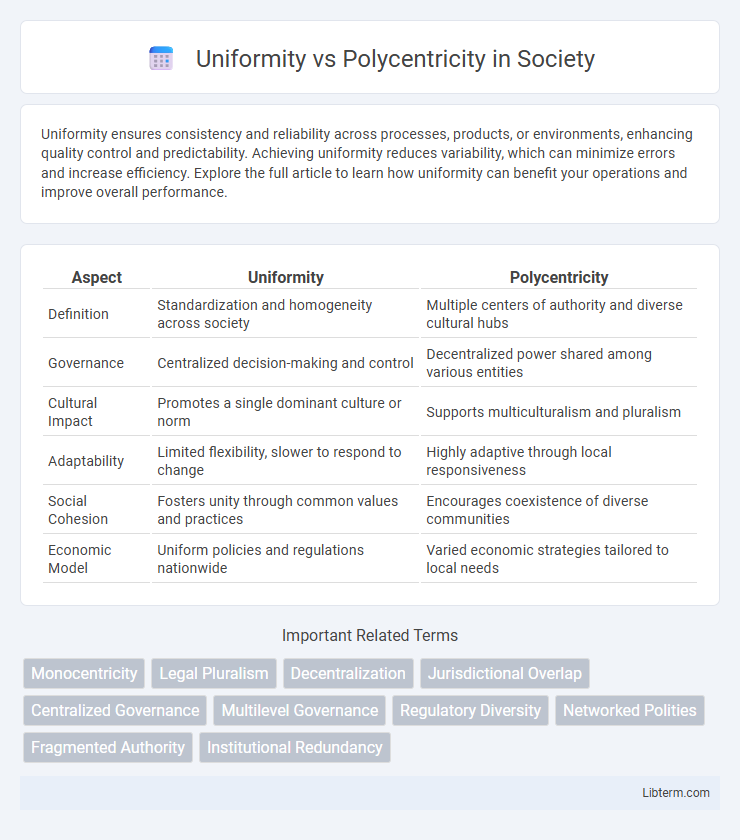
| Aspect | Uniformity | Polycentricity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardization and homogeneity across society | Multiple centers of authority and diverse cultural hubs |
| Governance | Centralized decision-making and control | Decentralized power shared among various entities |
| Cultural Impact | Promotes a single dominant culture or norm | Supports multiculturalism and pluralism |
| Adaptability | Limited flexibility, slower to respond to change | Highly adaptive through local responsiveness |
| Social Cohesion | Fosters unity through common values and practices | Encourages coexistence of diverse communities |
| Economic Model | Uniform policies and regulations nationwide | Varied economic strategies tailored to local needs |
Understanding Uniformity and Polycentricity
Uniformity emphasizes consistent policies and regulations applied universally across all jurisdictions, ensuring standardized governance and predictable legal frameworks. Polycentricity, in contrast, promotes multiple centers of decision-making authority where diverse local governments or organizations independently develop tailored policies reflecting regional preferences and conditions. Understanding these concepts is essential for analyzing governance models in federal systems, urban planning, and multinational organizations where the balance between centralized control and decentralized autonomy impacts effectiveness and responsiveness.
Historical Context of Legal Systems
The historical context of legal systems reveals a tension between uniformity and polycentricity, with uniform legal codes emerging from centralized states aiming to standardize laws across diverse regions, such as the Napoleonic Code in France. In contrast, polycentric legal traditions, exemplified by medieval Europe's overlapping jurisdictions or indigenous legal pluralism, allowed multiple legal authorities and systems to coexist within the same territory. This divergence reflects how state formation, cultural diversity, and colonial history influenced the evolution and coexistence of centralized and pluralistic legal governance structures.
Key Principles of Uniformity
Uniformity emphasizes consistent policies, rules, and procedures across all organizational units to ensure predictability and efficiency. This approach minimizes regional variations and promotes centralized control, facilitating standardized decision-making and streamlined operations. Key principles include centralized authority, standardized processes, and uniform application of practices to maintain coherence and reduce complexity.
Key Principles of Polycentricity
Polycentricity emphasizes multiple centers of decision-making authority, allowing diverse governance units to operate independently yet cohesively within a system. Key principles include decentralization, local autonomy, and overlapping jurisdictions that foster collaboration and adaptability across various scales. This approach enhances responsiveness to specific local needs while maintaining coordination through shared rules and mutual trust.
Advantages of Uniform Legal Frameworks
Uniform legal frameworks enhance predictability and reduce compliance costs by establishing consistent rules across jurisdictions, which benefits multinational corporations and investors. Such standardization fosters a stable business environment, facilitating cross-border trade and investment by minimizing legal uncertainties and disputes. Uniformity also simplifies regulatory enforcement and promotes fairness by ensuring equal treatment regardless of location.
Benefits of Polycentric Governance
Polycentric governance enhances local decision-making by allowing tailored policies that address specific community needs, improving responsiveness and adaptability. It promotes innovation through diverse problem-solving approaches across multiple centers of authority, fostering experimentation and learning. This governance model also encourages stakeholder participation and collaboration, leading to increased legitimacy, accountability, and resource sharing among overlapping jurisdictions.
Challenges of Uniformity in Practice
Uniformity in organizational structures often encounters challenges such as reduced flexibility and limited responsiveness to local market needs, which can hinder innovation and adaptability. Centralized decision-making under uniformity may create bottlenecks, slowing down processes and ignoring cultural nuances vital for regional success. These constraints frequently result in decreased employee engagement and difficulties in addressing diverse stakeholder expectations effectively.
Risks and Drawbacks of Polycentricity
Polycentricity in governance or organizational structures often leads to challenges such as fragmented decision-making and inconsistent policy implementation, increasing the risk of inefficiency. Diverse centers of authority can cause coordination difficulties and conflicting priorities, which may undermine strategic alignment and resource allocation. Moreover, polycentric systems can result in accountability issues, as overlapping jurisdictions blur responsibility and hinder effective oversight.
Comparative Case Studies: Uniform vs Polycentric Models
Comparative case studies of urban governance reveal distinct outcomes between uniform and polycentric models, with uniform systems often providing streamlined policy implementation but limited local adaptability. Polycentric models demonstrate enhanced responsiveness and innovation through decentralized authority, as seen in metropolitan regions like California and Denmark. Data indicates that polycentric governance supports greater stakeholder engagement and more effective management of complex, multi-jurisdictional issues compared to uniform centralized approaches.
Future Trends in Governance and Legal Systems
Future trends in governance and legal systems increasingly emphasize the tension between uniformity and polycentricity, with a growing shift toward polycentric approaches that enable localized decision-making and adaptive regulatory frameworks. Digital transformation and global interconnectedness promote decentralized governance models, fostering collaboration across multiple legal jurisdictions while maintaining core principles of rule of law and compliance. Emerging technologies such as blockchain and AI support transparency and efficiency in hybrid systems that balance standardized regulations with diverse regional governance needs.
Uniformity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com