Indulgence refers to the act of allowing yourself or others to enjoy a special treat or luxury, often as a way to relax or reward hard work. It plays a crucial role in maintaining mental well-being by balancing discipline with occasional pleasure. Explore the rest of this article to discover how indulgence can positively impact your lifestyle.
Table of Comparison
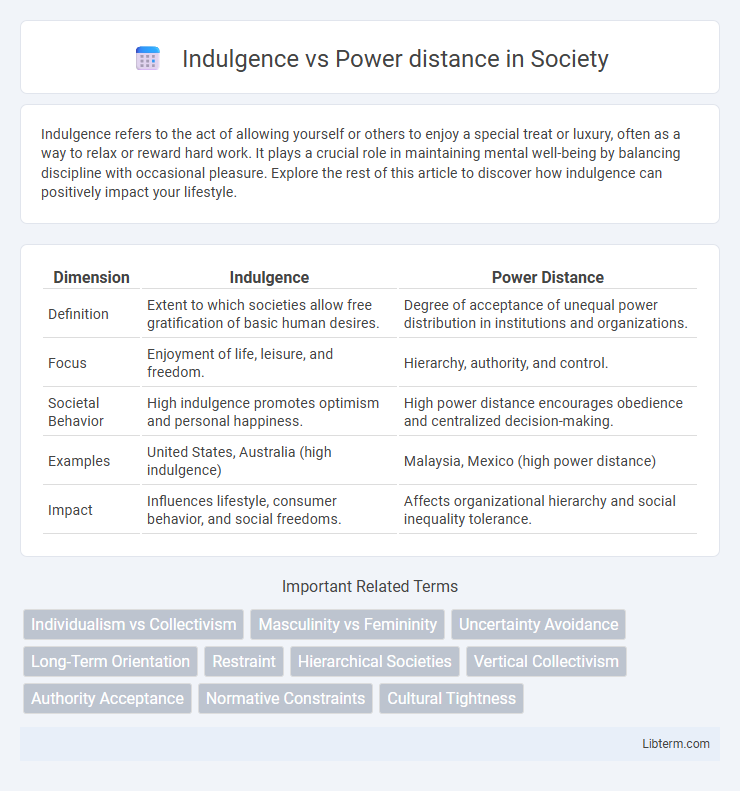
| Dimension | Indulgence | Power Distance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Extent to which societies allow free gratification of basic human desires. | Degree of acceptance of unequal power distribution in institutions and organizations. |
| Focus | Enjoyment of life, leisure, and freedom. | Hierarchy, authority, and control. |
| Societal Behavior | High indulgence promotes optimism and personal happiness. | High power distance encourages obedience and centralized decision-making. |
| Examples | United States, Australia (high indulgence) | Malaysia, Mexico (high power distance) |
| Impact | Influences lifestyle, consumer behavior, and social freedoms. | Affects organizational hierarchy and social inequality tolerance. |
Understanding Indulgence and Power Distance
Indulgence measures a society's allowance for free gratification of human desires related to enjoying life and having fun, while Power Distance assesses the extent to which less powerful members expect and accept unequal power distribution. High indulgence cultures emphasize leisure, freedom, and personal happiness, contrasting with cultures high in power distance that stress hierarchical structures and authority acceptance. Understanding these dimensions helps organizations and individuals navigate cultural expectations in communication, management, and social behaviors effectively.
Core Concepts: Definitions and Origins
Indulgence measures the extent to which societies allow relatively free gratification of basic and natural human desires related to enjoying life and having fun, while Power Distance reflects the degree to which less powerful members accept and expect unequal power distribution within institutions and organizations. These core concepts originate from Geert Hofstede's cultural dimensions theory, developed through extensive cross-cultural research in the 1970s to analyze value differences among nations. Indulgence versus restraint indicates societal attitudes towards happiness and leisure, whereas Power Distance highlights hierarchical structures and authority acceptance in social systems.
Historical Development of the Dimensions
Indulgence and power distance dimensions emerged from Geert Hofstede's cultural framework, reflecting societal attitudes towards gratification and hierarchical authority, respectively. Historical development shows that indulgence correlates with economic prosperity and democratic evolution, promoting personal freedom and leisure, while high power distance originates from traditional societies with centralized governance and rigid social structures. Over time, globalization and modernization have influenced shifts in both dimensions, with many societies experiencing a gradual decrease in power distance and an increase in indulgence, driven by education, technological advancements, and evolving social norms.
Cultural Implications of Indulgence
Indulgence cultures promote gratification of desires and emphasize leisure, pleasure, and freedom of expression, impacting consumer behavior and workplace motivation. Power distance influences how societies accept hierarchical structures and authority, leading to variations in interpersonal communication and organizational dynamics within indulgent societies. Understanding these cultural dimensions helps multinational companies tailor management practices and marketing strategies to resonate with local values and social norms.
The Role of Power Distance in Societies
Power distance measures the extent to which less powerful members in a society accept unequal power distribution, influencing social hierarchy and organizational behavior. High power distance societies tend to emphasize authority and centralized decision-making, while low power distance cultures promote equality and participative management. This cultural dimension significantly shapes communication patterns, workplace dynamics, and governance structures worldwide.
Comparing Indulgence and Power Distance Across Nations
Indulgence measures the extent to which societies allow relatively free gratification of basic human desires, whereas power distance reflects how much less powerful members of a society accept unequal power distribution. Nations with high indulgence scores, such as Mexico and Sweden, often emphasize personal freedom and leisure, contrasting with countries like Malaysia and Russia, which exhibit high power distance and focus on hierarchical order and authority. Comparing these dimensions reveals that societies valuing indulgence tend to have lower power distance, promoting individual autonomy over rigid social structures.
Impact on Workplace Culture and Management
Indulgence societies encourage a relaxed workplace culture where employees feel free to express creativity and seek work-life balance, enhancing motivation and job satisfaction. In contrast, high power distance cultures emphasize hierarchical structures and authoritative management styles, often limiting open communication and employee autonomy. These cultural dimensions significantly influence leadership approaches, decision-making processes, and overall organizational climate, affecting productivity and employee engagement.
Influence on Communication Styles
Indulgence cultures emphasize open, expressive communication styles that prioritize personal gratification and emotional expression, fostering informal and spontaneous interactions. In contrast, high power distance cultures promote formal, hierarchical communication where respect for authority and indirectness prevail to maintain social order. Understanding these dynamics improves cross-cultural communication by aligning message delivery with cultural expectations around authority and personal freedom.
Societal Outcomes: Happiness, Inequality, and Control
Indulgence societies often exhibit higher happiness levels due to a cultural emphasis on leisure, freedom, and personal gratification, which fosters positive societal outcomes. In contrast, high power distance cultures tend to have greater inequality and less autonomy, as hierarchical control limits individual influence and access to opportunities. These differences significantly impact social control mechanisms, with indulgent societies promoting open expression and power distance societies reinforcing structured obedience and authority.
Navigating Balance: Strategies for Global Interactions
Navigating the balance between indulgence and power distance in global interactions requires understanding cultural attitudes toward gratification and hierarchical structures, which influence communication and decision-making. High indulgence cultures prioritize leisure and freedom, while low indulgence societies emphasize restraint, affecting negotiation styles and workplace dynamics. Strategies include adapting leadership approaches to respect varying power distances and aligning motivational techniques with cultural indulgence preferences to foster collaboration and trust.
Indulgence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com