Social policy addresses the organization and regulation of welfare systems aimed at improving societal well-being through healthcare, education, housing, and employment support. Effective social policy promotes equity and access, reducing poverty and social exclusion to foster a more inclusive community. Explore this article to understand how social policy impacts your daily life and society as a whole.
Table of Comparison
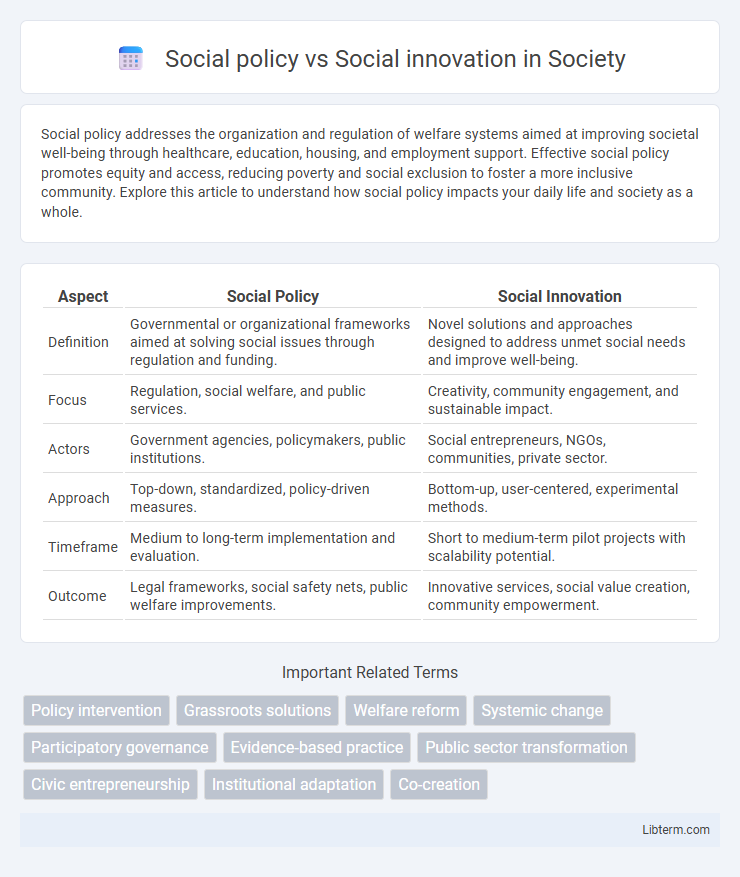
| Aspect | Social Policy | Social Innovation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Governmental or organizational frameworks aimed at solving social issues through regulation and funding. | Novel solutions and approaches designed to address unmet social needs and improve well-being. |
| Focus | Regulation, social welfare, and public services. | Creativity, community engagement, and sustainable impact. |
| Actors | Government agencies, policymakers, public institutions. | Social entrepreneurs, NGOs, communities, private sector. |
| Approach | Top-down, standardized, policy-driven measures. | Bottom-up, user-centered, experimental methods. |
| Timeframe | Medium to long-term implementation and evaluation. | Short to medium-term pilot projects with scalability potential. |
| Outcome | Legal frameworks, social safety nets, public welfare improvements. | Innovative services, social value creation, community empowerment. |
Understanding Social Policy: Definition and Scope
Social policy encompasses government actions and legislation designed to promote social welfare and address issues such as healthcare, education, housing, and poverty alleviation across various populations. It establishes frameworks and regulations that guide resource allocation and ensure equitable access to essential services within society. Understanding its scope highlights how social policy aims to maintain social cohesion and improve quality of life through systemic interventions and public programs.
What is Social Innovation? Key Concepts
Social innovation refers to the development and implementation of novel solutions that effectively address complex social challenges, improving societal well-being and equity. Key concepts include collaboration across sectors, user-centered design, scalability, and sustainability, emphasizing systemic change rather than temporary fixes. Unlike traditional social policies, social innovation leverages creativity, technology, and social entrepreneurship to empower communities and transform social systems.
Historical Evolution of Social Policy
Social policy has evolved historically through systematic government interventions aimed at addressing welfare, poverty, and public health since the Industrial Revolution, shaping the foundation of modern welfare states. Social innovation, emerging prominently in the late 20th century, focuses on novel solutions and cross-sector collaboration to tackle complex social challenges beyond traditional policy frameworks. The historical evolution of social policy highlights the transition from state-centric welfare models to more dynamic, inclusive strategies incorporating social innovation principles.
Drivers and Motivations Behind Social Innovation
Social innovation is driven by the need to address unmet social challenges through creative and collaborative approaches that often go beyond traditional social policy frameworks. Motivations behind social innovation include empowering communities, enhancing social equity, and fostering sustainable development by leveraging technology, participatory methods, and cross-sector partnerships. Unlike social policy, which is typically top-down and government-led, social innovation originates from grassroots initiatives aimed at systemic change and improved social outcomes.
Major Differences between Social Policy and Social Innovation
Social policy primarily refers to government programs and regulations designed to address societal issues such as poverty, healthcare, and education through formal frameworks and public funding. Social innovation involves the development and implementation of new ideas, services, or models aimed at solving social problems more effectively or sustainably, often originating from non-governmental organizations, social entrepreneurs, or community initiatives. The major differences lie in their approach: social policy relies on top-down regulation and institutional support, whereas social innovation emphasizes bottom-up creativity and adaptability in addressing social challenges.
The Role of Government in Social Policy vs Social Innovation
Governments primarily create and enforce social policies aimed at addressing societal issues through legislation, regulation, and public services. In contrast, social innovation involves novel solutions developed by diverse actors, including governments, nonprofits, and private sectors, to improve social outcomes beyond traditional policies. The government's role in social innovation is often to facilitate, fund, and scale initiatives that demonstrate effective social impact but may not yet be codified into formal policy frameworks.
Impact Measurement: Social Policy vs Social Innovation
Social policy impact measurement primarily relies on established metrics, such as poverty reduction rates, employment statistics, and public health indicators, which provide quantifiable data reflecting societal changes over time. In contrast, social innovation impact measurement emphasizes qualitative assessments, including user feedback, behavioral changes, and scalability potential, focusing on transformative solutions that address unmet social needs. Both approaches benefit from mixed-method evaluations combining quantitative and qualitative data to effectively capture short-term outcomes and long-term societal effects.
Collaboration Between Public and Private Sectors
Collaboration between public and private sectors in social policy often involves regulatory frameworks and funding mechanisms to address societal challenges through established institutional approaches. In contrast, social innovation emphasizes co-creation and dynamic partnerships that leverage private sector agility and public sector resources to develop novel solutions to social issues. Effective collaboration integrates policy-driven objectives with innovative practices to enhance impact and sustainability in addressing community needs.
Challenges and Opportunities in Social Policy and Innovation
Social policy faces challenges such as addressing systemic inequality, securing sustainable funding, and adapting to rapidly changing societal needs, while social innovation struggles with scaling impact, measuring effectiveness, and navigating regulatory constraints. Opportunities in social policy include leveraging data-driven approaches for targeted interventions and fostering inclusive policymaking frameworks, whereas social innovation benefits from collaborative networks, technology integration, and flexible pilot programs that drive community-centric solutions. Both fields intersect in their potential to create adaptive, resilient systems that respond to complex social issues through evidence-based strategies and participatory engagement.
Future Trends: The Intersection of Social Policy and Social Innovation
Future trends reveal increasing convergence between social policy and social innovation, driven by data analytics and participatory governance models to address complex social challenges. Emphasis on sustainability, digital inclusion, and adaptive regulation fosters collaborative frameworks where governments, nonprofits, and tech-driven startups co-create scalable, impact-focused solutions. Emerging technologies like AI and blockchain are reshaping policy implementation, enabling real-time monitoring and citizen engagement for more responsive and equitable social interventions.
Social policy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com