Social innovation transforms communities by developing novel solutions that address pressing social challenges, boosting wellbeing and equity. These initiatives foster collaboration across sectors, leveraging creativity and technology to create sustainable impact. Explore the rest of the article to discover how social innovation can empower your community and drive meaningful change.
Table of Comparison
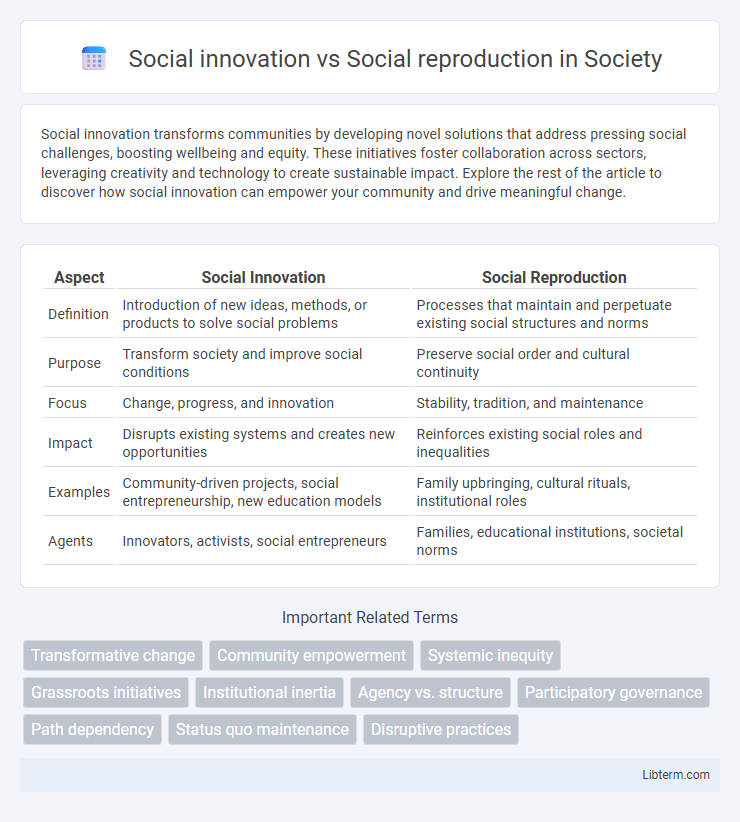
| Aspect | Social Innovation | Social Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Introduction of new ideas, methods, or products to solve social problems | Processes that maintain and perpetuate existing social structures and norms |
| Purpose | Transform society and improve social conditions | Preserve social order and cultural continuity |
| Focus | Change, progress, and innovation | Stability, tradition, and maintenance |
| Impact | Disrupts existing systems and creates new opportunities | Reinforces existing social roles and inequalities |
| Examples | Community-driven projects, social entrepreneurship, new education models | Family upbringing, cultural rituals, institutional roles |
| Agents | Innovators, activists, social entrepreneurs | Families, educational institutions, societal norms |
Defining Social Innovation: Concepts and Characteristics
Social innovation refers to novel solutions that address social needs, improve community well-being, and create systemic change through creative collaboration and inclusive participation. It emphasizes adaptability, sustainability, and scalability in transforming social practices and institutions. Contrarily, social reproduction involves the maintenance and perpetuation of existing social structures, norms, and cultural traditions that sustain daily life and social order.
Understanding Social Reproduction: Core Principles
Social reproduction encompasses the daily and generational processes that sustain and regenerate the labor force, including caregiving, education, and cultural transmission. Core principles highlight the maintenance of social norms, economic stability, and the reproduction of social inequalities through family dynamics, gender roles, and institutional practices. Understanding social reproduction provides crucial insights into how societies perpetuate existing power structures while enabling social innovation to challenge and transform them.
Key Differences Between Social Innovation and Social Reproduction
Social innovation involves creating novel solutions to address social challenges, emphasizing change and improvement in societal structures. Social reproduction refers to the processes that sustain and perpetuate existing social norms, values, and institutions across generations. The key difference lies in social innovation's goal to transform society, while social reproduction maintains and reinforces current social patterns.
Historical Contexts Shaping Both Phenomena
Social innovation and social reproduction each emerge from distinct historical contexts that shape their roles in society. Social innovation often arises during periods of rapid social change, such as industrialization or digital transformation, seeking novel solutions to evolving societal challenges. In contrast, social reproduction is deeply rooted in traditional structures and practices, maintaining and transmitting cultural norms, economic resources, and social roles across generations within stable or slower-changing historical frameworks.
The Role of Institutions in Social Change
Institutions play a crucial role in social innovation by enabling new ideas, practices, and structures that challenge existing norms and drive transformative change. In contrast, social reproduction relies on institutions to maintain and perpetuate established social patterns, roles, and inequalities across generations. Understanding the dynamic interaction between institutional frameworks and social processes is essential for analyzing how social change is either facilitated or constrained.
Case Studies: Examples of Social Innovation
Social innovation case studies highlight transformative projects like microfinance initiatives in Bangladesh, which empower marginalized communities by providing access to credit and fostering entrepreneurship. The Grameen Bank exemplifies how social innovation addresses systemic poverty through sustainable financial inclusion, contrasting with social reproduction that perpetuates existing inequalities. These examples demonstrate scalable solutions that disrupt traditional social structures and enable long-term societal progress.
Mechanisms of Social Reproduction in Society
Mechanisms of social reproduction encompass the processes through which societies maintain and perpetuate their structural norms, values, and inequalities across generations, including education, family roles, and labor division. Social innovation challenges these mechanisms by introducing novel practices and ideas designed to disrupt established social patterns and foster inclusive change. Understanding the dynamics between social innovation and social reproduction reveals how transformative efforts can either reinforce or break cycles of social inequality.
Social Innovation’s Impact on Existing Structures
Social innovation redefines existing societal structures by introducing novel solutions that address persistent social challenges, fostering systemic change and improving community well-being. Unlike social reproduction, which maintains and perpetuates established norms and institutions, social innovation actively disrupts traditional patterns, promoting inclusivity and sustainability. The impact of social innovation manifests in reshaping policy frameworks, economic models, and cultural practices to create more equitable and adaptive social systems.
Challenges and Critiques of Social Innovation vs Social Reproduction
Social innovation faces challenges such as scalability, sustainability, and potential co-optation by market forces, which can dilute its transformative impact. In contrast, social reproduction often struggles with inadequate recognition, undervaluation of care work, and persistent gender and class inequalities embedded in existing social structures. Critics argue that social innovation may overlook systemic issues that social reproduction theory highlights, leading to fragmented solutions rather than addressing root causes of social inequality.
Future Prospects: Integrating Innovation and Reproduction for Sustainable Change
Future prospects in social development emphasize integrating social innovation with social reproduction to ensure sustainable change by combining novel solutions with the preservation of cultural and institutional knowledge. Leveraging technology, community engagement, and adaptive governance enhances social resilience while maintaining continuity of core social functions. This synergy facilitates scalable, long-term impact in areas such as healthcare, education, and environmental sustainability.
Social innovation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com