Social compliance ensures businesses adhere to ethical labor standards, workplace safety, and human rights regulations. It aims to create fair and transparent working environments while minimizing risks associated with unethical practices. Explore the rest of the article to learn how social compliance can benefit your organization and build long-term trust.
Table of Comparison
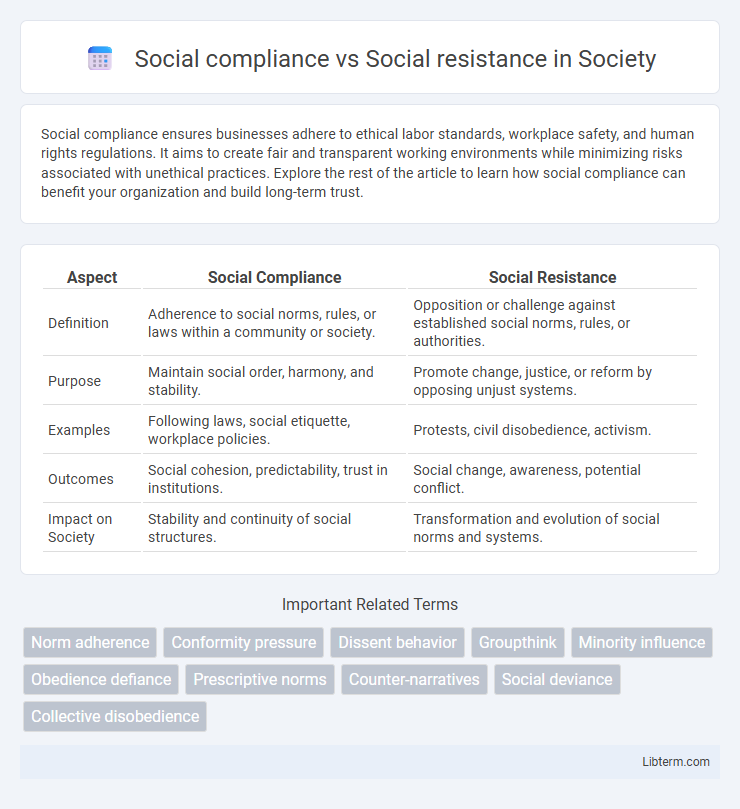
| Aspect | Social Compliance | Social Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to social norms, rules, or laws within a community or society. | Opposition or challenge against established social norms, rules, or authorities. |
| Purpose | Maintain social order, harmony, and stability. | Promote change, justice, or reform by opposing unjust systems. |
| Examples | Following laws, social etiquette, workplace policies. | Protests, civil disobedience, activism. |
| Outcomes | Social cohesion, predictability, trust in institutions. | Social change, awareness, potential conflict. |
| Impact on Society | Stability and continuity of social structures. | Transformation and evolution of social norms and systems. |
Understanding Social Compliance: Definition and Importance
Social compliance refers to the adherence to social norms, rules, and laws established within a community or society, ensuring harmonious interactions and order. It plays a crucial role in maintaining social cohesion, preventing conflicts, and fostering trust between individuals and institutions. Understanding social compliance is essential for developing effective policies and organizational practices that promote ethical behavior and collective well-being.
What Drives Social Resistance? Key Factors Explored
Social resistance is driven by factors such as perceived injustice, lack of representation, and threats to cultural identity, which motivate collective action against prevailing social norms. Economic disparity and political exclusion further amplify resistance by fostering feelings of marginalization and disempowerment among affected groups. Additionally, awareness raised through social media platforms intensifies mobilization, enabling rapid dissemination of dissenting perspectives and coordination of protests.
The Psychology Behind Following Social Norms
The psychology behind following social norms reveals that social compliance often stems from the human need for acceptance and belonging, influenced by conformity and obedience to authority. In contrast, social resistance arises when individuals prioritize personal values or critical thinking over group expectations, driven by cognitive dissonance or perceived injustice. Understanding these psychological mechanisms clarifies how social behavior is regulated through internal motivations and external pressures.
Mechanisms of Social Resistance: From Protest to Nonconformity
Mechanisms of social resistance encompass a spectrum from organized protests to everyday nonconformity, challenging dominant social norms and policies. Protest actions, such as demonstrations and strikes, serve as visible, collective efforts to oppose systemic injustices, while nonconformity includes subtle acts like civil disobedience and lifestyle choices that reject mainstream cultural expectations. These forms of resistance disrupt social compliance by creating spaces for alternative narratives and fostering social change through persistent, though varied, dissent.
Social Compliance vs Social Resistance: Core Differences
Social compliance involves individuals or groups adhering to established social norms, rules, or laws, often driven by a desire for acceptance or fear of sanctions. Social resistance occurs when people actively oppose or challenge these norms or authorities to promote change or express dissent. The core difference lies in compliance supporting existing structures, while resistance seeks to disrupt or transform them.
Impacts of Compliance on Societal Stability
Social compliance fosters societal stability by promoting adherence to laws, norms, and ethical standards, which reduces conflict and enhances collective trust. High levels of compliance empower institutions to function effectively, facilitating social order and economic development. Conversely, excessive enforcement without addressing underlying grievances may risk social unrest, highlighting the importance of balancing compliance with inclusive governance.
Social Resistance as a Catalyst for Change
Social resistance acts as a powerful catalyst for change by challenging existing social norms and institutional injustices that social compliance often perpetuates. It mobilizes marginalized communities and activists to confront systemic issues such as inequality, discrimination, and environmental degradation, thereby driving transformative social movements. By disrupting complacency and prompting public discourse, social resistance fosters policy reforms and cultural shifts that advance social justice and human rights.
Real-World Examples: Compliance and Resistance in Action
Social compliance manifests in real-world scenarios such as widespread mask-wearing during the COVID-19 pandemic, where individuals adhere to public health guidelines to protect community health. In contrast, social resistance surfaces in movements like the 2020 Black Lives Matter protests, highlighting collective opposition to systemic racism and calling for societal reform. These examples illustrate the dynamic interplay between conformity to social norms and active dissent driving social change.
Influences of Culture on Compliance and Resistance
Cultural norms and values significantly shape social compliance by reinforcing behaviors aligned with collective expectations and societal roles, promoting harmony and order. In contrast, cultural frameworks that prioritize individualism or question authority often fuel social resistance, encouraging challenge and change against established norms. The dynamic interplay between tradition, power structures, and cultural identity determines whether populations are more inclined toward conformity or resistance in social contexts.
Finding the Balance: Encouraging Positive Social Engagement
Finding the balance between social compliance and social resistance requires fostering environments where individuals feel empowered to express dissent while respecting communal norms. Encouraging positive social engagement involves promoting open dialogue, critical thinking, and active participation in decision-making processes to build trust and collaboration. Effective strategies integrate accountability mechanisms with opportunities for constructive feedback, ensuring social cohesion without suppressing individuality or necessary change.
Social compliance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com