Critical consciousness enhances your ability to recognize social injustices and question dominant power structures deeply influencing society. Developing this awareness empowers individuals to challenge inequality and advocate for meaningful change effectively. Explore the rest of the article to understand how cultivating critical consciousness can transform your perspective and actions.
Table of Comparison
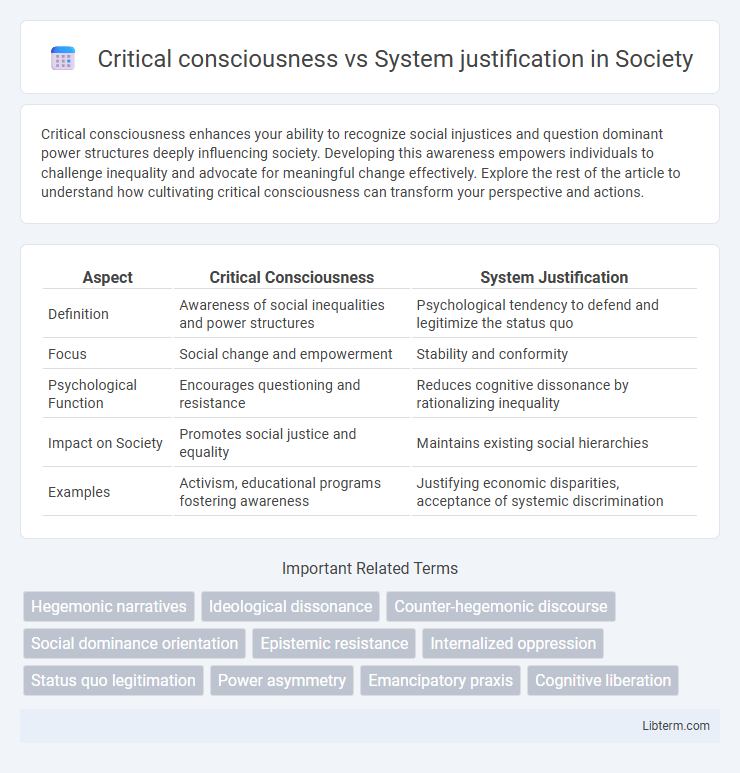
| Aspect | Critical Consciousness | System Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Awareness of social inequalities and power structures | Psychological tendency to defend and legitimize the status quo |
| Focus | Social change and empowerment | Stability and conformity |
| Psychological Function | Encourages questioning and resistance | Reduces cognitive dissonance by rationalizing inequality |
| Impact on Society | Promotes social justice and equality | Maintains existing social hierarchies |
| Examples | Activism, educational programs fostering awareness | Justifying economic disparities, acceptance of systemic discrimination |
Understanding Critical Consciousness: A Brief Overview
Critical consciousness involves recognizing and challenging social inequalities by developing awareness of systemic oppression and power structures, enabling individuals to question dominant ideologies. System justification theory explains how people rationalize and defend existing social, economic, and political arrangements to maintain stability and reduce cognitive dissonance. Understanding critical consciousness requires examining how individuals move beyond system justification to critically analyze and transform unjust societal systems.
Defining System Justification Theory
System Justification Theory explains the psychological process where individuals defend and rationalize existing social, economic, and political systems, even when these systems may be disadvantageous to them. This theory highlights how people maintain status quo beliefs to preserve a sense of order, stability, and legitimacy in social structures. In contrast, critical consciousness involves recognizing and challenging the injustices within these systems to promote social change and equity.
Historical Roots of Critical Consciousness and System Justification
The historical roots of critical consciousness trace back to Paulo Freire's pedagogy of the oppressed, emphasizing awareness of social injustices and empowerment to challenge inequality. System justification theory emerged from social psychology research in the 1990s, focusing on the cognitive processes that cause individuals to defend and rationalize existing social, economic, and political systems even when disadvantaged. These contrasting frameworks highlight the tension between awareness-driven resistance and psychological mechanisms that maintain societal status quos.
Psychological Mechanisms Behind System Justification
System justification theory explains the psychological mechanisms that drive individuals to defend and rationalize existing social, economic, and political arrangements, even when they may be disadvantaged by them. Cognitive dissonance reduction, motivation for epistemic security, and the need for social stability contribute to system justification by fostering acceptance of inequality and status quo legitimacy. This contrasts with critical consciousness, which involves recognizing systemic oppression and actively questioning and resisting unjust systems.
The Role of Education in Fostering Critical Consciousness
Education plays a pivotal role in fostering critical consciousness by encouraging learners to question social inequalities and recognize systemic injustices. Critical pedagogy techniques empower students to analyze power structures and develop agency to challenge oppressive systems. This contrasts sharply with system justification, which education can inadvertently reinforce when curricula promote conformity and acceptance of existing social orders without critical examination.
Social Implications: Empowerment vs Social Stability
Critical consciousness fosters empowerment by encouraging individuals to recognize and challenge social injustices, leading to increased social activism and transformative change. System justification promotes social stability by motivating acceptance and rationalization of existing social arrangements, reducing conflict and maintaining the status quo. The tension between these dynamics influences societal progress, balancing between empowerment-driven reform and stability-preserving conformity.
Case Studies: When Critical Consciousness Challenges the Status Quo
Case studies illustrating critical consciousness reveal how marginalized groups actively recognize and challenge systemic inequalities, disrupting entrenched societal norms. In contrast, system justification explains the psychological mechanisms that lead individuals, even those disadvantaged, to defend and rationalize existing power structures. Examining movements such as the civil rights activism and recent global protests demonstrates critical consciousness confronting system justification, catalyzing social transformation.
The Influence of Media on System Justification and Awareness
Media significantly shapes system justification by framing social hierarchies as natural and inevitable, reinforcing acceptance of existing power structures. Critical consciousness emerges when media exposes inequalities and promotes awareness, encouraging individuals to question and challenge systemic norms. The balance between these influences determines public engagement with social change and resistance movements.
Critical Consciousness in Social Movements and Activism
Critical consciousness empowers individuals within social movements to recognize and challenge systemic inequalities, fostering collective action against oppression. Rooted in Paulo Freire's pedagogy, it emphasizes awareness of social, political, and economic contradictions, enabling activists to disrupt dominant narratives and promote transformative change. This heightened awareness is crucial for mobilizing marginalized communities and sustaining long-term commitment to social justice activism.
Bridging the Gap: Towards Social Change and Collective Well-being
Critical consciousness empowers individuals to recognize and challenge systemic inequalities, fostering active engagement in social transformation. System justification, by contrast, perpetuates existing social hierarchies through acceptance and rationalization of the status quo. Bridging the gap between these constructs involves creating educational frameworks and community dialogues that promote awareness while addressing cognitive biases, ultimately advancing collective well-being and sustainable social change.
Critical consciousness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com