Direct routes offer the fastest and most efficient way to reach your destination by minimizing travel time and avoiding unnecessary stops. They are ideal for busy travelers seeking convenience and simplicity in their journey. Explore the rest of the article to discover how choosing a direct route can enhance your travel experience.
Table of Comparison
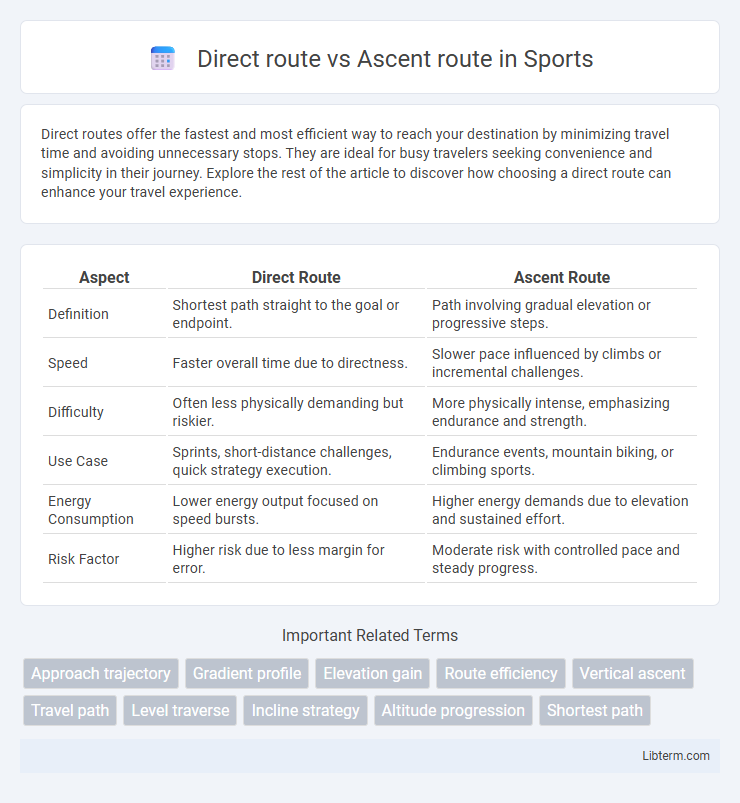
| Aspect | Direct Route | Ascent Route |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shortest path straight to the goal or endpoint. | Path involving gradual elevation or progressive steps. |
| Speed | Faster overall time due to directness. | Slower pace influenced by climbs or incremental challenges. |
| Difficulty | Often less physically demanding but riskier. | More physically intense, emphasizing endurance and strength. |
| Use Case | Sprints, short-distance challenges, quick strategy execution. | Endurance events, mountain biking, or climbing sports. |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy output focused on speed bursts. | Higher energy demands due to elevation and sustained effort. |
| Risk Factor | Higher risk due to less margin for error. | Moderate risk with controlled pace and steady progress. |
Understanding Direct and Ascent Routes
Direct routes prioritize the shortest and most straightforward path to a destination, optimizing travel time and reducing complexity by minimizing detours and stops. Ascent routes involve a gradual elevation gain or increasing difficulty level, often chosen for training, scenic value, or to manage physical exertion over time. Understanding the distinction helps travelers or climbers effectively plan based on goals like speed, endurance, or experience level.
Key Differences Between Direct and Ascent Routes
The Direct route features a shorter, more challenging path that demands advanced technical climbing skills and greater physical endurance. The Ascent route typically follows a longer, less steep trajectory, prioritizing safety and gradual elevation gain with more established camps or rest points. Key differences include route difficulty, distance, altitude acclimatization, and the type of equipment required for successful navigation.
Advantages of the Direct Route
The Direct Route offers a more efficient ascent by significantly reducing the overall climbing distance and time, allowing climbers to reach higher elevations faster. This route typically involves steeper terrain, which demands advanced technical skills but provides a more direct and challenging path to the summit. Climbers opting for the Direct Route benefit from quicker acclimatization and reduced exposure to prolonged adverse weather conditions due to the shortened duration of the climb.
Pros and Cons of the Ascent Route
The Ascent Route offers a more gradual incline, reducing physical strain and making it suitable for climbers with moderate experience or those prioritizing safety. However, it typically requires a longer time to complete compared to the Direct Route, which can be a disadvantage in rapidly changing weather conditions. The extended duration on the Ascent Route may also increase exposure to altitude-related challenges and potential fatigue.
Efficiency and Time Comparison
The Direct route offers improved efficiency by minimizing distance and reducing overall travel time, making it ideal for rapid transit scenarios. The Ascent route, though longer in distance, provides gradual elevation changes that enhance safety and energy conservation, especially for heavy or less powerful vehicles. Time comparison typically favors the Direct route for speed, while the Ascent route is preferred for stability and lower fuel consumption during uphill climbs.
Safety Considerations for Both Routes
The Direct route involves steep inclines and exposed sections, increasing risks of falls and requiring advanced technical skills and proper safety gear. The Ascent route, often longer but less steep, presents fewer technical challenges and more stable terrain, reducing the likelihood of accidents for climbers with moderate experience. Proper assessment of weather conditions, individual skill level, and use of protective equipment are critical safety measures for both routes to prevent injuries.
Suitability for Different Skill Levels
The Direct route offers a more straightforward and less technical path, making it ideal for beginners and moderately experienced climbers seeking a safer and quicker ascent. In contrast, the Ascent route involves more complex terrain and requires advanced climbing skills, suitable for experienced mountaineers comfortable with technical challenges. Choosing between the two routes depends on the climber's skill level, experience, and specific safety considerations.
Terrain and Environmental Factors
The Direct route features steep, exposed sections with loose rock and minimal natural protection, demanding advanced climbing skills and heightened caution. In contrast, the Ascent route offers more stable terrain with gradual slopes and established trails, reducing risk from falling debris and environmental hazards. Weather variability, such as sudden storms or strong winds, impacts both routes but poses greater danger on the Direct route due to limited shelter and challenging terrain.
Popular Destinations: Which Route is Preferred?
The Direct Route remains a preferred choice for adventurers seeking the fastest ascent to the summit, notably favored in popular climbing destinations like Everest and Kilimanjaro due to its efficient path and reduced exposure to prolonged altitude challenges. Meanwhile, the Ascent Route attracts climbers in regions such as the Alps and Andes who prioritize scenic views and acclimatization opportunities, often choosing it for a safer and more gradual climb. Popularity depends heavily on destination-specific factors, including terrain difficulty, weather patterns, and the climber's experience level.
Choosing the Right Route: Factors to Consider
Choosing between the Direct route and the Ascent route depends on factors such as terrain difficulty, climber experience, and weather conditions. The Direct route often offers a shorter but steeper path, requiring technical skills and better physical fitness, while the Ascent route is longer with gradual inclines, suitable for acclimatization and safer progression. Evaluating individual stamina, risk tolerance, and environmental challenges is essential for optimizing safety and success during the climb.
Direct route Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com