A three-pointer is a basketball shot made from beyond the three-point line, earning the team three points instead of the usual two. Mastering the three-pointer can significantly increase your scoring potential and shift the momentum of the game. Discover how to improve your three-point shooting skills and the strategies behind its impact in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
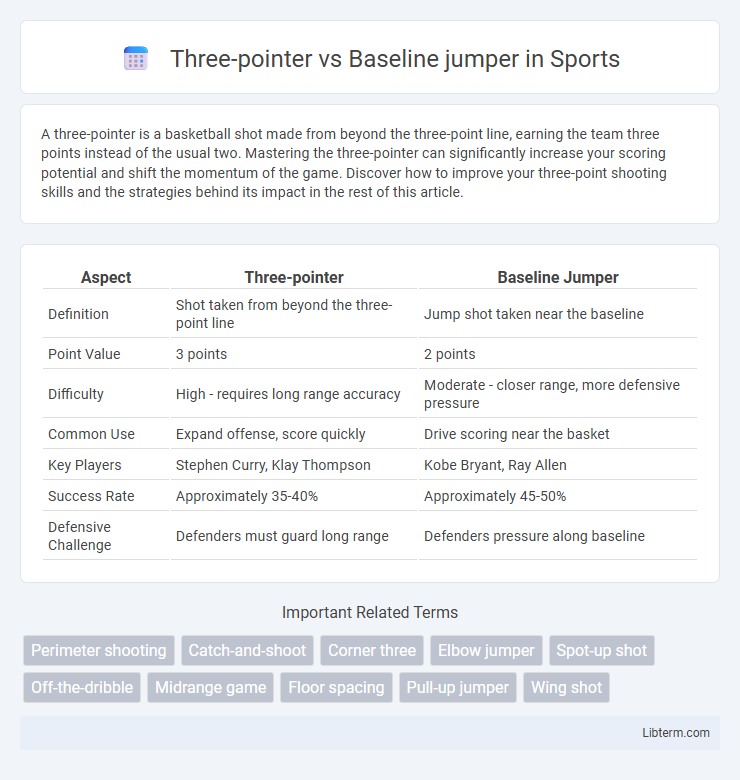
| Aspect | Three-pointer | Baseline Jumper |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shot taken from beyond the three-point line | Jump shot taken near the baseline |
| Point Value | 3 points | 2 points |
| Difficulty | High - requires long range accuracy | Moderate - closer range, more defensive pressure |
| Common Use | Expand offense, score quickly | Drive scoring near the basket |
| Key Players | Stephen Curry, Klay Thompson | Kobe Bryant, Ray Allen |
| Success Rate | Approximately 35-40% | Approximately 45-50% |
| Defensive Challenge | Defenders must guard long range | Defenders pressure along baseline |
Introduction to Basketball Shot Types
Three-pointers and baseline jumpers represent key shooting techniques in basketball that influence scoring strategies. A three-pointer is executed beyond the three-point arc, awarding three points for a successful shot, while a baseline jumper is taken near the court's edge, often used to exploit defensive gaps and create mid-range scoring opportunities. Both shot types require precise footwork, wrist control, and situational awareness to maximize scoring efficiency and adapt to defensive pressure.
Anatomy of the Three-Pointer
The three-pointer requires greater range and shooting mechanics, engaging the lower body and core for stability, along with precise wrist and finger control for accuracy from beyond the arc. Its longer distance amplifies the need for explosive leg power and balance to maintain a consistent shooting form compared to the baseline jumper. The baseline jumper emphasizes quick footwork, body control near the basket, and rapid release over raw power, focusing more on mid-range shooting anatomy rather than extended range muscle activation.
Understanding the Baseline Jumper
The baseline jumper is a crucial shot in basketball, executed near the court's edge to exploit defensive gaps and create scoring opportunities. Distinct from the three-pointer, which is taken beyond the three-point line and scores higher points, the baseline jumper offers a higher percentage shot due to its closer proximity to the basket. Mastering the baseline jumper improves offensive versatility, allowing players to challenge defenders and maintain scoring efficiency in tight spaces.
Shot Selection: When and Why
Three-pointers are ideal when spacing and floor balance are key, offering higher point value but requiring longer-range accuracy and more time to shoot. Baseline jumpers are effective in mid-range scenarios, especially when defenders collapse on the paint, allowing for quick release and increased scoring efficiency from close-range angles. Choosing between these shots depends on defensive pressure, player positioning, and game pace to maximize scoring opportunities.
Scoring Impact: Points and Possessions
Three-pointers yield higher scoring impact by awarding three points per successful shot compared to two points from baseline jumpers, enhancing a team's point total more rapidly. Additionally, three-pointers can increase possessions' expected value due to their greater point efficiency despite often lower shooting percentages. Teams leveraging effective three-point shooting improve offensive efficiency metrics and can shift defensive spacing, indirectly contributing to higher scoring outcomes.
Skill Set Required for Each Shot
Mastering a three-pointer requires exceptional long-range shooting accuracy, strong hand-eye coordination, and the ability to generate consistent shooting mechanics under defensive pressure. A baseline jumper demands precise footwork, quick release, and sharp body control to navigate tight spaces near the basket while maintaining balance. Both shots necessitate advanced spatial awareness and mental focus, but the three-pointer emphasizes range and rhythm, while the baseline jumper highlights agility and mid-range precision.
Defensive Challenges and Strategies
Defensive challenges against a three-pointer include closing out quickly to contest long-range shots while maintaining balance to prevent drives, necessitating perimeter defenders with high agility and lateral quickness. In contrast, defending a baseline jumper requires protecting the paint and forcing shooters away from the baseline, often engaging help defense and strong closeouts to disrupt shooter rhythm. Strategies for both include anticipating shooter tendencies and effectively switching defensive assignments to deny open looks, with an emphasis on communication and positioning to minimize scoring opportunities.
Statistical Comparisons: Efficiency and Usage
Three-pointers have a higher points-per-shot value, with an average success rate around 35-38%, generating approximately 1.05 points per attempt, compared to baseline jumpers, which typically convert at about 40-45% but yield only 2 points, resulting in roughly 0.80 points per attempt. Usage rates in professional leagues show three-pointers constituting up to 35-40% of total field goal attempts, reflecting strategic emphasis on spacing and floor stretching, while baseline jumper attempts remain less frequent, around 5-10%. Efficiency metrics combined with frequency reveal three-pointers as a more valuable offensive weapon, driving modern offensive schemes prioritizing effective shot selection.
Iconic Moments Featuring Each Shot
Steph Curry's game-winning three-pointer in the 2016 NBA playoffs epitomizes the high-stakes excitement and long-range precision synonymous with three-pointers. Conversely, Kobe Bryant's baseline jumper during the 2010 Finals showcased the shot's elegance and effectiveness in tight, defensive scenarios. Both shots highlight strategic brilliance, with three-pointers stretching defenses and baseline jumpers exploiting close-range angles.
Conclusion: Evolving Trends in Modern Basketball
Three-pointers increasingly dominate modern basketball analytics due to higher expected points per shot and spacing benefits, while baseline jumpers offer strategic value in tight defense and mid-range versatility. The evolution of player skill sets blends deep shooting with mid-range proficiency, reflecting adaptive offensive strategies. Emphasizing efficient shot selection, teams prioritize three-point attempts but maintain baseline jumpers to diversify scoring options and exploit defensive weaknesses.
Three-pointer Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com