The albatross is one of the largest flying birds known for its impressive wingspan and remarkable ability to glide effortlessly over ocean waves. These seabirds are expertly adapted for life at sea, spending months aloft while covering thousands of miles with minimal wing flapping. Discover more fascinating details about the albatross and its unique lifestyle in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
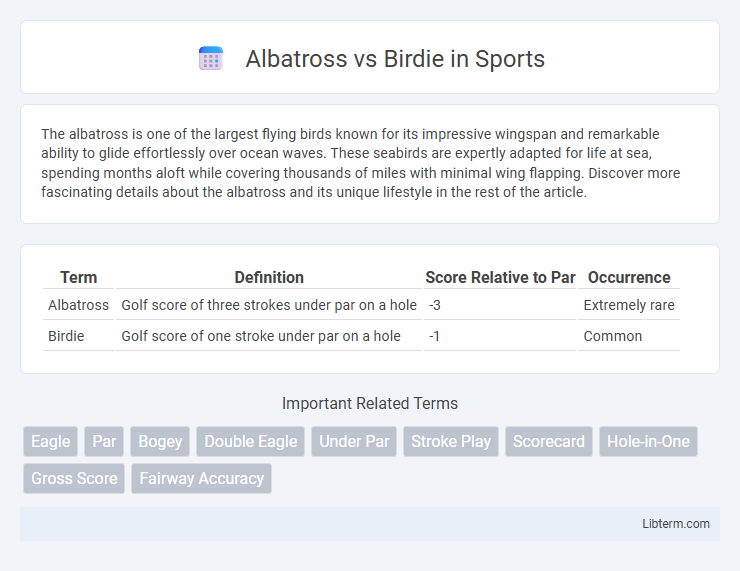
| Term | Definition | Score Relative to Par | Occurrence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albatross | Golf score of three strokes under par on a hole | -3 | Extremely rare |
| Birdie | Golf score of one stroke under par on a hole | -1 | Common |
Introduction: Albatross vs Birdie in Golf
Albatross and birdie are key scoring terms in golf that reflect exceptional shot performance relative to par. An albatross, also known as a double eagle, occurs when a player completes a hole three strokes under par, typically on par-5 holes, making it an extremely rare feat. Birdie represents completing a hole one stroke under par, a more common achievement indicating skilled play.
Defining Albatross and Birdie
An Albatross in golf is a rare score achieved by completing a hole three strokes under par, typically making a 2 on a par-5 hole. A Birdie refers to scoring one stroke under par on a single hole, such as a 3 on a par-4. Both terms signify exceptional performance, with Albatross being significantly less common and more celebrated than Birdie.
Scoring Differences Explained
An albatross in golf occurs when a player scores three strokes under par on a single hole, such as completing a par-5 hole in two shots, while a birdie is one stroke under par, like finishing a par-4 hole in three strokes. The significant scoring difference lies in the albatross being a much rarer and more challenging achievement, representing a double eagle, whereas a birdie is common and reflects a solid, above-par performance. Understanding this gap helps golfers appreciate the impact of these scores on overall game strategy and tournament standings.
Rarity and Occurrence on the Course
An albatross, scoring three under par on a single hole, is significantly rarer than a birdie, which is one under par. In golf, albatrosses occur infrequently, often during par-5 holes, with odds estimated at around 1 in a million rounds, while birdies are common and expected from skilled players. This rarity makes an albatross one of the most celebrated and challenging feats compared to the more routinely achieved birdie.
Historical Moments: Famous Albatrosses and Birdies
The history of golf is marked by iconic moments featuring albatrosses and birdies that have shaped the sport's legacy, such as Gene Sarazen's legendary double eagle at the 1935 Masters, which remains one of the most celebrated albatrosses in tournament history. Birdies, while more common, have been crucial in major victories, exemplified by Tiger Woods' clutch birdies during multiple Masters tournaments, underlining their significance in scoring and momentum shifts. These historic instances highlight the evolving mastery and strategic importance of achieving sub-par holes, solidifying albatrosses and birdies as pivotal milestones in golfing achievements.
Strategy: Achieving an Albatross vs Birdie
Achieving an albatross requires exceptional precision and distance control, as it means completing a hole three strokes under par, often by holing the ball in two shots on a par-5 or one on a par-4. Strategic shot placement prioritizes reaching the green in fewer strokes while avoiding hazards, demanding powerful drives and accurate approach shots. In contrast, a birdie focuses on scoring one stroke under par by combining consistent, risk-managed tee shots with precise putting, emphasizing steady play rather than aggressive distance.
Impact on Player Scorecards
An albatross on a golf scorecard signifies a rare three under par on a single hole, dramatically improving a player's total score and often significantly boosting their position in a tournament. In contrast, a birdie, one under par, provides a more common but still valuable score improvement that steadily benefits the player's round. Both achievements enhance performance metrics, with albatrosses creating standout moments that heavily influence leaderboard rankings.
Psychological Effects on Golfers
An albatross in golf, scoring three under par on a single hole, can significantly boost a golfer's confidence and mental momentum, fostering increased focus and motivation. Achieving a birdie, one stroke under par, often provides a moderate yet positive psychological lift, reinforcing a player's belief in their skill without overwhelming pressure. The rarity and difficulty of an albatross can induce heightened excitement and reduce performance anxiety, sometimes enhancing overall game consistency and mental resilience.
Course Design and Opportunities
Albatross and Birdie golf courses differ significantly in design complexity, with Albatross courses featuring longer fairways, strategically placed hazards, and varied elevation changes to challenge advanced players. Birdie courses emphasize accessibility and shorter hole lengths, providing ample scoring opportunities for beginners and intermediate golfers. Course architects tailor Albatross layouts to promote precision and power shots, while Birdie designs focus on shot variety and player enjoyment.
Conclusion: The Significance of Albatross and Birdie
Albatross and birdie are crucial golf scoring terms, with an albatross representing three strokes under par and a birdie representing one stroke under par, both highlighting exceptional player performance. Achieving an albatross is significantly rarer and demonstrates extraordinary skill or luck, often altering tournament outcomes. Understanding these terms enhances appreciation of golf scoring nuances and player achievements.
Albatross Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com