A hedge is a strategic investment designed to reduce the risk of adverse price movements in an asset by taking an offsetting position in a related security. Utilizing hedging techniques can protect your portfolio from volatility and unexpected market shifts. Explore the rest of the article to understand practical hedging methods that safeguard your investments effectively.
Table of Comparison
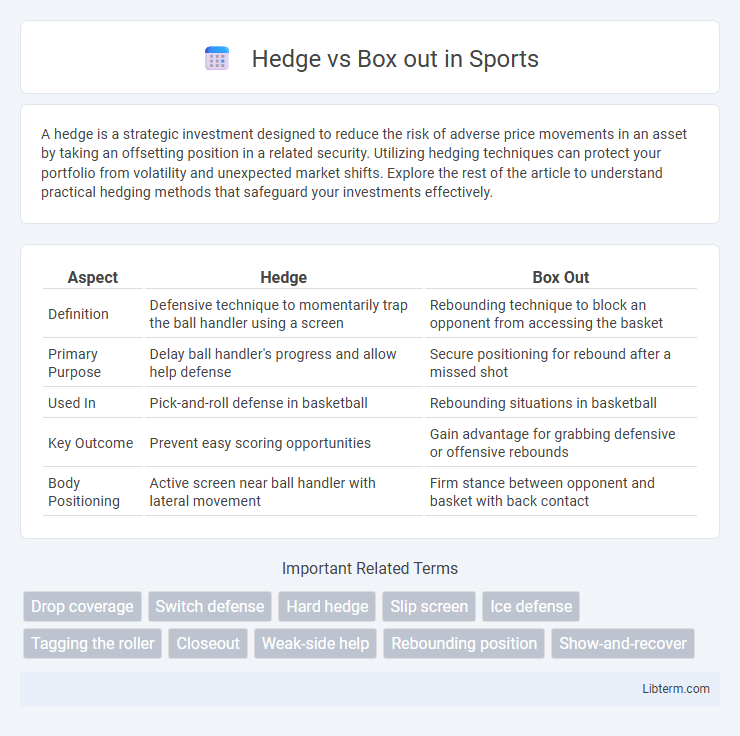
| Aspect | Hedge | Box Out |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Defensive technique to momentarily trap the ball handler using a screen | Rebounding technique to block an opponent from accessing the basket |
| Primary Purpose | Delay ball handler's progress and allow help defense | Secure positioning for rebound after a missed shot |
| Used In | Pick-and-roll defense in basketball | Rebounding situations in basketball |
| Key Outcome | Prevent easy scoring opportunities | Gain advantage for grabbing defensive or offensive rebounds |
| Body Positioning | Active screen near ball handler with lateral movement | Firm stance between opponent and basket with back contact |
Understanding the Basics: What Are Hedge and Box Out?
Hedge and box out are defensive basketball strategies designed to limit offensive player movement and prevent easy scoring opportunities. Hedging involves a defender momentarily stepping out to impede a screen setter and disrupt the ball handler's path while maintaining awareness of their original assignment. Box out focuses on positioning to block opponents from obtaining rebounds by sealing off space between the basket and the opposing player.
Key Differences Between Hedging and Boxing Out
Hedging in sports defense involves a player temporarily guarding an opponent to prevent quick passes or screens, while boxing out focuses on positioning oneself to secure rebounds by blocking opponents from the basket. Hedging requires quick, reactive movement to disrupt offensive plays, whereas boxing out relies on strategic physical positioning and maintaining contact. The key difference lies in hedging's role in interrupting ball movement versus boxing out's emphasis on controlling space for rebound advantage.
The Importance of Hedge in Basketball Defense
Hedging in basketball defense is crucial for disrupting pick-and-roll plays by momentarily halting the ball handler's progress and forcing a difficult decision. This tactic effectively delays offensive actions, allowing the defender's teammate to recover and maintain defensive integrity around the screen. Proper hedging reduces scoring opportunities and enhances team defensive cohesion by controlling ball movement and minimizing open shots.
Mastering the Art of Boxing Out for Rebounds
Mastering the art of boxing out is crucial for securing rebounds by establishing superior positioning between the opponent and the basket. Effective box out technique involves maintaining a low center of gravity, using the body to shield the competitor, and anticipating the ball's trajectory to ensure control of the rebound. Compared to hedging in defensive schemes, boxing out demands consistent physicality and spatial awareness, directly improving rebounding statistics for players and teams.
When to Use Hedge vs Box Out Situations
Use hedge defense when a quick trap is needed to disrupt a ball handler's dribble and force a turnover or bad pass, typically in pick-and-roll scenarios. Box out is crucial in rebounding situations to establish position and prevent opponents from grabbing offensive rebounds, especially after a missed shot. Understanding game context, such as offensive pressure or shot attempts, dictates the strategic choice between hedging and boxing out.
Common Mistakes in Executing Hedge and Box Out
Common mistakes in executing a hedge include over-committing and losing defensive positioning, leaving open driving lanes or mismatches on switches. In box out errors, players often fail to establish a strong, wide base or lose focus on their assigned opponent, leading to easy offensive rebounds. Both errors reduce defensive efficiency and increase opponents' second-chance scoring opportunities.
Skills and Techniques for Effective Hedging
Effective hedging in basketball requires precise communication and quick footwork to momentarily double-team the ball handler without losing defensive positioning. Skilled defenders use angled body positioning and hand activity to disrupt passing lanes while maintaining awareness of their original assignment. Mastering anticipation and timing enables defenders to hedge efficiently, preventing offensive penetration and facilitating seamless rotations.
Drills to Improve Box Out Performance
Effective drills to improve box out performance include partner resistance drills, where one player maintains contact while another attempts to box out, enhancing strength and positioning. Rebounding drills using a basketball thrown off the backboard simulate game-like scenarios and reinforce boxing out immediately after the shot. Incorporating timed reaction drills with multiple players accelerates decision-making and spatial awareness crucial for successful box outs in competitive play.
Advanced Strategies: Combining Hedge and Box Out
Combining hedge and box out techniques enhances defensive effectiveness in basketball by simultaneously disrupting ball handlers while securing optimal rebounding position. Advanced strategies involve defenders executing quick hedges to contain pick-and-roll threats, then seamlessly transitioning to box out opponents for missed shots. This dual approach maximizes possession control and limits second-chance scoring opportunities by integrating spatial awareness and coordinated team defense.
Impact of Hedge and Box Out on Team Success
Hedge and box out techniques significantly influence team success in basketball by enhancing defensive efficiency and securing possession. Effective hedging disrupts opponent ball handlers, reducing scoring opportunities, while box out tactics ensure rebounds, limiting second-chance points for opponents. Teams proficient in both strategies typically exhibit stronger defensive ratings and higher control of game tempo, key factors in winning outcomes.
Hedge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com