Odd man rush is a fast-paced hockey play where a player exploits a numerical advantage against fewer defenders, often leading to scoring opportunities. It requires quick decision-making, precise passing, and effective positioning to capitalize on the advantage. Explore how mastering the odd man rush can elevate your game and create more chances to score.
Table of Comparison
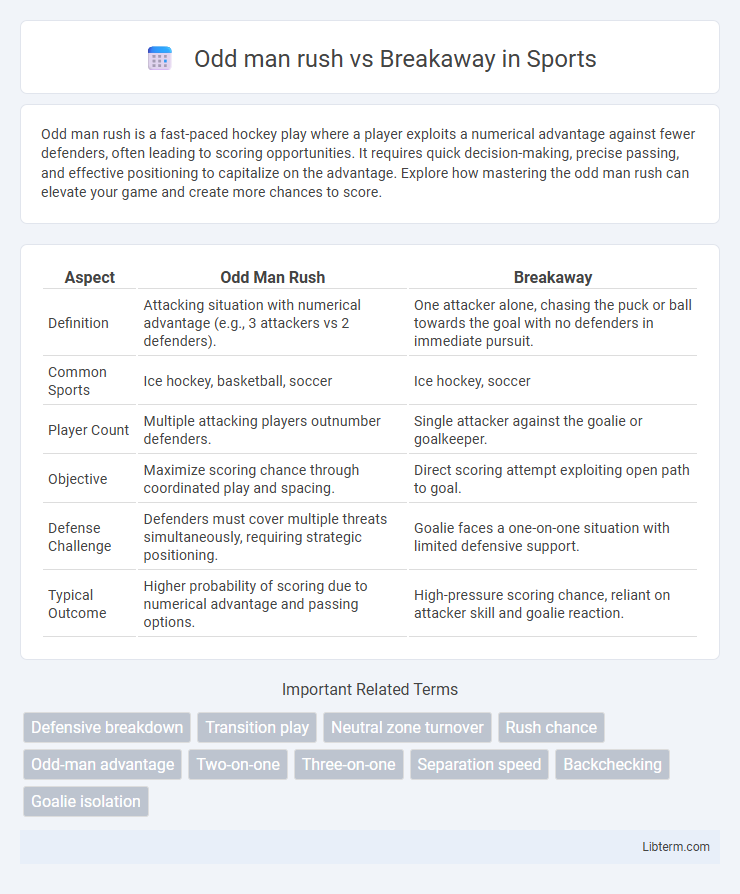
| Aspect | Odd Man Rush | Breakaway |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Attacking situation with numerical advantage (e.g., 3 attackers vs 2 defenders). | One attacker alone, chasing the puck or ball towards the goal with no defenders in immediate pursuit. |
| Common Sports | Ice hockey, basketball, soccer | Ice hockey, soccer |
| Player Count | Multiple attacking players outnumber defenders. | Single attacker against the goalie or goalkeeper. |
| Objective | Maximize scoring chance through coordinated play and spacing. | Direct scoring attempt exploiting open path to goal. |
| Defense Challenge | Defenders must cover multiple threats simultaneously, requiring strategic positioning. | Goalie faces a one-on-one situation with limited defensive support. |
| Typical Outcome | Higher probability of scoring due to numerical advantage and passing options. | High-pressure scoring chance, reliant on attacker skill and goalie reaction. |
Understanding Odd Man Rush and Breakaway
Odd Man Rush occurs when a team is outnumbered defensively, typically 3 attackers against 2 defenders, creating a high-pressure situation that demands quick decision-making and positioning. A Breakaway happens when a single player gains clear control of the puck ahead of all defenders, offering a prime opportunity to score with a one-on-one chance against the goalie. Both scenarios emphasize speed, tactical awareness, and precise execution to capitalize on scoring chances in hockey.
Key Differences Between Odd Man Rush and Breakaway
Odd Man Rush and Breakaway are pivotal hockey scenarios distinguished by player positioning and tactical dynamics. Odd Man Rush involves a numerical advantage in forward players over defenders, typically creating a 2-on-1 or 3-on-2 situation that emphasizes quick puck movement and passing options. Breakaway occurs when a single attacker has clear possession and a one-on-one opportunity against the goalie, focusing on individual skill and shot accuracy to score.
Origins and Evolution in Hockey
Odd man rush and breakaway are critical offensive strategies in hockey, both originating from early developments in game tactics during the 20th century. The odd man rush evolved as teams recognized the advantage of numerical superiority in transition plays, with historical roots linking it to fluid puck movement and quick line changes. Breakaway emerged from individual skill showcases, where a single player exploiting defensive gaps drives alone towards the goalie, illustrating the sport's progression towards fast-paced and dynamic offensive maneuvers.
Tactical Advantages: Odd Man Rush
An odd man rush creates numerical superiority, allowing the attacking team to exploit gaps in opponent defense with increased puck control and passing options. This tactical advantage forces defenders to make quick decisions, often leading to breakdowns and open shooting lanes for higher quality scoring chances. The ability to outnumber defenders also enhances potential for unpredictable plays and decreases the likelihood of turnovers compared to a standard breakaway.
Tactical Advantages: Breakaway
Breakaway provides a tactical advantage by allowing the attacking player to exploit open ice with speed, forcing the defender and goalie into one-on-one scenarios that increase scoring chances. The attacker can choose between shooting early, deking to create space, or passing to a trailing teammate, making defensive predictions challenging. This dynamic approach leverages speed and decision-making to break defensive formations and capitalize on scoring opportunities.
Common Scenarios for Odd Man Rush
Odd man rushes often occur when a team quickly transitions from defense to offense, creating a numerical advantage against the opposing defense, typically 2-on-1 or 3-on-2 situations. Common scenarios include shorthanded penalties where defenders are pulled for extra attackers, turnovers during neutral zone play, or quick rebounds leading to fast breaks. These situations require precise passing, timing, and positioning to exploit defensive gaps before defenders can recover.
Common Scenarios for Breakaway
Common scenarios for a breakaway in hockey often occur when a player swiftly distances themselves from defenders, creating a clear path toward the goalie with no opposing players obstructing their shot. This situation frequently arises from a defensive turnover or a swift counterattack following a successful faceoff win. Unlike an odd man rush, which involves multiple attackers outnumbering defenders, breakaways are characterized by a single attacker against the goalie, emphasizing speed, precision, and one-on-one skill.
Defensive Strategies Against Each Play
Defensive strategies against an odd-man rush prioritize maintaining proper gap control and ensuring defenders do not overcommit, focusing on blocking passing lanes and supporting the goaltender by cutting down shooting angles. In contrast, defending a breakaway requires defenders to stay disciplined by forcing the attacking player wide, limiting the shooting options and timing their poke checks carefully to avoid penalties. Both plays demand heightened situational awareness and quick decision-making to neutralize scoring threats effectively.
Impact on Game Momentum
Odd man rushes create high-pressure situations that force defenses into quick decision-making, often resulting in scoring opportunities that significantly shift game momentum. Breakaways, characterized by a single attacker facing the goalie, heighten anticipation and can energize a team instantly when converted, swinging momentum decisively. Both situations are critical in dictating the pace and psychological edge during crucial moments in hockey games.
Famous Odd Man Rushes and Breakaways in History
Famous odd man rushes and breakaways have defined some of the most iconic moments in hockey history, such as Wayne Gretzky's breakout rush against the Edmonton Oilers in 1984 and Bobby Orr's legendary breakaway goal in the 1970 Stanley Cup Finals. These plays highlight the raw speed, skill, and strategic positioning that create scoring opportunities involving fewer defenders than attackers. Classic examples continue to inspire players, emphasizing the importance of quick decision-making and teamwork during man-advantage situations on the ice.
Odd man rush Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com