Predator and prey dynamics are fundamental to ecosystem balance, influencing population control and biodiversity. The strategies predators use to capture prey and the adaptations prey develop for survival drive evolutionary changes. Explore the rest of this article to understand how these interactions shape the natural world around you.
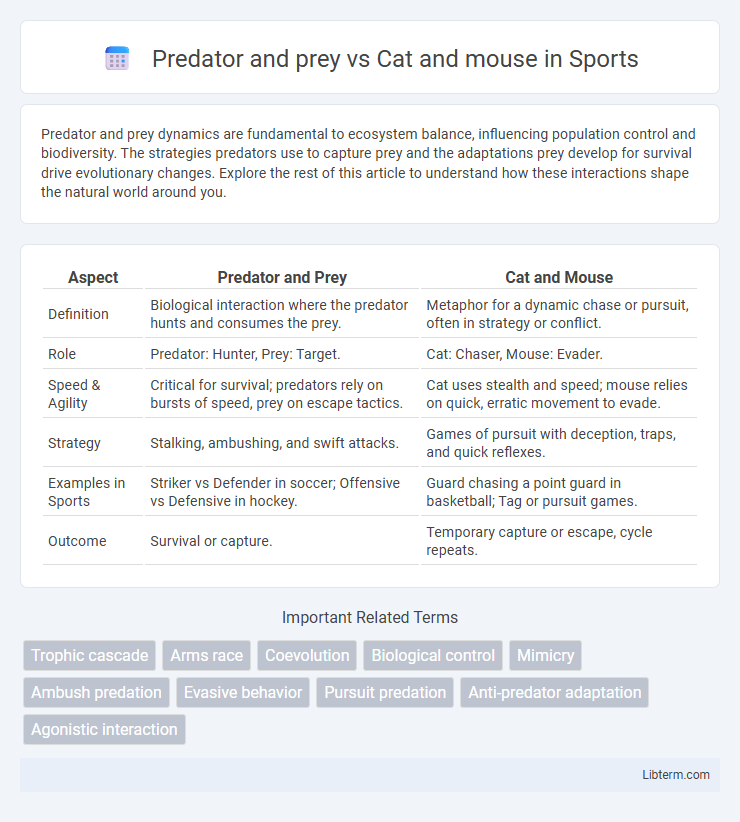
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Predator and Prey | Cat and Mouse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Biological interaction where the predator hunts and consumes the prey. | Metaphor for a dynamic chase or pursuit, often in strategy or conflict. |
| Role | Predator: Hunter, Prey: Target. | Cat: Chaser, Mouse: Evader. |
| Speed & Agility | Critical for survival; predators rely on bursts of speed, prey on escape tactics. | Cat uses stealth and speed; mouse relies on quick, erratic movement to evade. |
| Strategy | Stalking, ambushing, and swift attacks. | Games of pursuit with deception, traps, and quick reflexes. |
| Examples in Sports | Striker vs Defender in soccer; Offensive vs Defensive in hockey. | Guard chasing a point guard in basketball; Tag or pursuit games. |
| Outcome | Survival or capture. | Temporary capture or escape, cycle repeats. |
Understanding Predator-Prey Dynamics
Predator-prey dynamics reveal complex ecological interactions where predators regulate prey populations, maintaining ecosystem balance through natural selection and resource competition. In contrast, the cat and mouse analogy simplifies these interactions to a constant chase, overlooking factors like prey adaptation and environmental influence. Studying predator-prey relationships deepens understanding of species survival strategies, population cycles, and biodiversity conservation.
The Classic Cat-and-Mouse Analogy
The classic cat-and-mouse analogy illustrates the dynamic interaction between predator and prey, emphasizing the strategic and often cyclical nature of their relationship. This analogy captures the tactical pursuit and evasion seen in ecological systems, where cats (predators) employ cunning and stealth to capture mice (prey), which in turn develop adaptive behaviors to avoid predation. Understanding this analogy provides valuable insights into evolutionary arms races and survival strategies within natural ecosystems.
Key Differences: Predator vs. Prey and Cat vs. Mouse
Predator and prey dynamics involve a biological relationship where predators hunt and consume prey for survival, emphasizing energy transfer within ecosystems. In contrast, the cat and mouse metaphor represents a strategic chase or competition, often used to describe psychological or tactical interactions rather than actual predation. Key differences lie in the natural ecological roles and survival dependencies between predator and prey versus the symbolic, often playful or strategic connotations of cat and mouse interactions.
Evolutionary Adaptations in Predators and Prey
Predator and prey dynamics drive evolutionary adaptations, resulting in predator traits such as stealth, speed, and acute senses, while prey develop camouflage, agility, and defensive behaviors. In the cat and mouse relationship, cats evolve sharp claws, night vision, and keen hearing, whereas mice enhance their quick reflexes, burrowing instincts, and alertness to avoid capture. These co-evolutionary pressures create an ongoing arms race, shaping survival strategies and influencing species' evolutionary paths.
Behavioral Tactics: Hunt, Chase, and Escape
Predator and prey dynamics involve strategic hunting behaviors where predators use stealth, speed, and ambush tactics to capture elusive prey employing camouflage and evasive maneuvers. In contrast, cat and mouse interactions emphasize a game of cunning pursuit and evasion, with the cat leveraging patience and sudden bursts of speed while the mouse relies on quick reflexes and knowledge of escape routes. Both scenarios showcase evolved behavioral adaptations focused on survival through optimized chase and escape mechanisms.
Predator and Prey in the Animal Kingdom
Predator and prey relationships in the animal kingdom involve complex interactions where predators hunt and consume prey for survival, driving evolutionary adaptations on both sides. This dynamic shapes behaviors, physical traits, and ecosystems, enhancing biodiversity and maintaining ecological balance. Unlike the cat and mouse metaphor often used to describe strategic games or conflicts, predator and prey interactions are fundamental biological processes critical for natural selection.
Cat-and-Mouse Games: Beyond Domestic Felines
Cat-and-mouse games extend beyond domestic felines, describing strategic interactions where one party pursues and the other evades, mirroring predator and prey dynamics in nature. These games encapsulate adaptive behaviors, tactical decision-making, and continuous learning, often studied in fields like game theory, cybersecurity, and evolutionary biology. The metaphor highlights complex, ongoing conflicts where survival depends on anticipating and outmaneuvering the opponent in competitive environments.
Ecological Impacts of Predator-Prey Relationships
Predator-prey relationships regulate population dynamics, maintaining ecosystem balance by controlling species abundance and preventing overpopulation. The interactions result in natural selection pressures that drive evolutionary adaptations, enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. In contrast to simplistic cat-and-mouse analogies, true predator-prey systems entail complex ecological roles influencing nutrient cycling, habitat structure, and energy flow within communities.
Cultural and Literary Uses of the Cat-and-Mouse Metaphor
The cat-and-mouse metaphor, widely used in literature and culture, symbolizes a dynamic of pursuit and evasion that reflects cunning, strategy, and power struggles between opposing forces. Unlike the straightforward predator-prey relationship rooted in biological survival, this metaphor emphasizes psychological warfare and tactical maneuvering, frequently depicted in espionage, crime fiction, and political narratives. Iconic examples include Sherlock Holmes's cat-and-mouse chases with Moriarty, highlighting intellectual rivalry and suspense through metaphorical tension.
Real-World Applications: Learning from Nature’s Chase
Predator and prey dynamics in ecosystems provide critical insights for developing strategies in cybersecurity, where systems mimic natural defense mechanisms to detect and respond to threats. The cat and mouse analogy extends to technological innovation, illustrating the constant adaptation between hackers and software developers to outsmart each other. Understanding these natural interactions enhances real-world applications in fields such as robotics, AI, and environmental management by fostering adaptive and anticipatory responses.
Predator and prey Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com