A substitute runner plays a crucial role in maintaining a team's performance during a race by stepping in when the primary runner is unable to continue. Their ability to seamlessly integrate and keep up the pace ensures the team's competitive edge remains strong. Discover how having a skilled substitute runner can impact your race strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
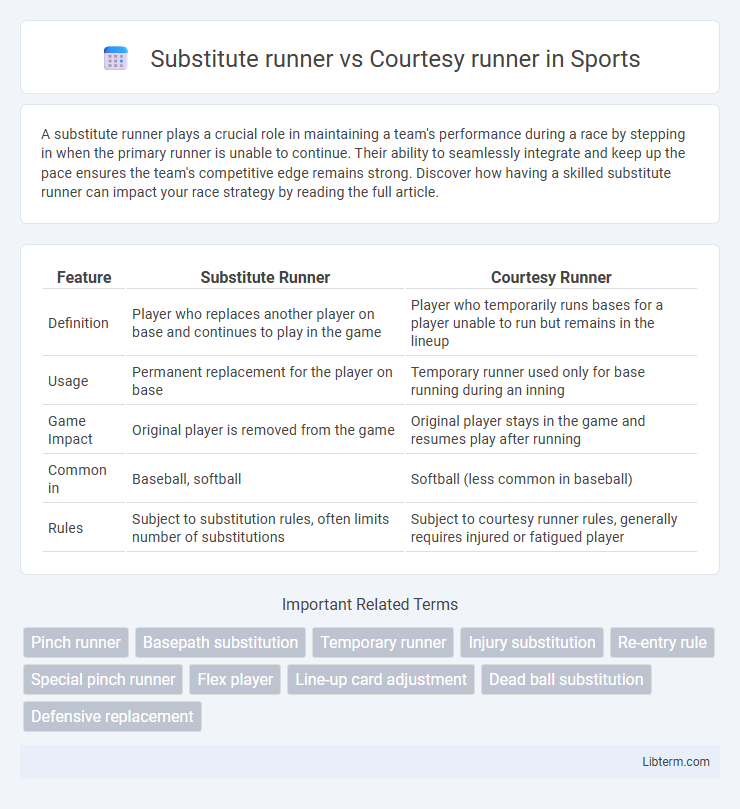
| Feature | Substitute Runner | Courtesy Runner |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Player who replaces another player on base and continues to play in the game | Player who temporarily runs bases for a player unable to run but remains in the lineup |
| Usage | Permanent replacement for the player on base | Temporary runner used only for base running during an inning |
| Game Impact | Original player is removed from the game | Original player stays in the game and resumes play after running |
| Common in | Baseball, softball | Softball (less common in baseball) |
| Rules | Subject to substitution rules, often limits number of substitutions | Subject to courtesy runner rules, generally requires injured or fatigued player |
Introduction to Substitute and Courtesy Runners
A substitute runner is a player who replaces another player on base or in the batting order for strategic or injury reasons, officially becoming part of the game roster. A courtesy runner, by contrast, is a temporary replacement specifically allowed to speed up the game when the original runner is injured or slow, without altering the team's lineup. Both roles are governed by specific league rules to maintain fairness while accommodating player needs and game efficiency.
Key Definitions: Substitute Runner vs Courtesy Runner
A substitute runner replaces a player who is officially removed from the game, taking over all responsibilities and statistics associated with the original player. A courtesy runner temporarily runs for a player on base without affecting the player's official status or statistics, typically used to speed up the game or rest a player. Substitute runners result in a permanent lineup change, while courtesy runners do not alter the game's official player records.
Historical Background of Running Substitutions
Running substitutions have evolved from strict player replacement rules in early baseball history to the adoption of specialized roles like the substitute runner and courtesy runner aimed at maintaining game pace and player stamina. The courtesy runner, introduced in the mid-20th century, allows a player to temporarily bat while a runner advances bases without officially substituting players, whereas the substitute runner replaces a runner permanently in the lineup. These innovations reflect changes in baseball strategy, influenced by evolving rules to enhance game flow and competitive fairness.
League-Specific Rules and Regulations
Substitute runners and courtesy runners differ notably across leagues, with Major League Baseball (MLB) allowing substitute runners who permanently replace a player, while courtesy runners, often used in amateur and youth leagues, temporarily run for a player without exiting the game. In softball and college baseball, courtesy runners are common for pitchers or catchers to expedite the game, adhering to specific league regulations on eligibility and frequency. Understanding each league's nuanced rules, such as the National Federation of State High School Associations (NFHS) limiting courtesy runners to one per inning, ensures compliance and strategic use during gameplay.
Eligibility Criteria for Substitute and Courtesy Runners
Substitute runners are typically eligible when a player is injured or unable to continue, requiring official approval before entering the game, while courtesy runners are allowed for specific situations such as replacing a catcher or injured baserunner without formal substitution. Eligibility for substitute runners often requires the player to have been officially listed on the lineup or roster prior to the game, ensuring compliance with league rules. Courtesy runners must meet criteria like not having previously run for the same player during the game, maintaining fair play and strategic integrity.
Common Scenarios for Using Each Runner Type
Substitute runners are typically used when a player is permanently replaced in the lineup due to injury or strategic changes, ensuring the team maintains optimal defense or offense throughout the game. Courtesy runners are employed to save time and preserve the pitcher's stamina by allowing a player to temporarily replace the runner on base, often seen in late innings with pitchers or slower runners. Common scenarios include a substitute runner entering after a player is injured or ejected, while courtesy runners usually appear during critical moments to speed up the game or protect key players.
Strategic Advantages and Disadvantages
A substitute runner replaces a player permanently, allowing the team to optimize lineup flexibility but risks losing a key batter or defensive player later. Courtesy runners provide temporary base-running relief without permanent lineup changes, preserving player availability but requiring the original player to re-enter, which can disrupt game rhythm. Teams must balance these choices strategically based on game situation, player stamina, and long-term lineup impact for optimal performance.
Impact on Game Flow and Outcomes
A substitute runner replaces a player who is injured or unable to continue, potentially causing delay due to official substitutions and lineup adjustments, impacting the game flow noticeably. A courtesy runner temporarily enters to run bases for the current batter without altering the batting order, maintaining pace and minimizing game interruptions. The strategic use of courtesy runners can enhance offensive efficiency and scoring opportunities, while substitute runners often influence defensive dynamics and game strategy.
Notable Examples in Competitive Play
Notable examples in competitive play highlight the distinct use of substitute runners and courtesy runners in baseball. In Major League Baseball, courtesy runners like MLB legend Lou Gehrig frequently came in to maintain game pace without replacing the original player, emphasizing strategic advantages during critical moments. Conversely, substitute runners, such as those used by the New York Yankees in playoff games, replace the original player entirely, often to leverage a faster runner's speed, showcasing tactical depth in high-stakes competition.
Summary: Choosing the Right Runner Option
Choosing between a substitute runner and a courtesy runner depends on game context and roster rules; a substitute runner permanently replaces the original player, affecting lineup strategy, while a courtesy runner temporarily runs for a player to save time or avoid injury without lineup changes. Managers must evaluate team depth, player fatigue, and game situation to decide which option optimizes performance and maintains roster flexibility. Understanding league-specific regulations on runner substitutions ensures compliance and strategic advantage during gameplay.
Substitute runner Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com